Updated April 26, 2023
Introduction to Linux Network
Now, most of you people using Linux may already know a few works around for maintaining your network. For people using Windows 2008 or 2012 Servers, configuring a Linux Network environment will be a big deal. But, we people, the ones who have been Linux administrators for quite a long, know that Configuring a Linux network is far easier than Windows and is just a piece of cake as compared to Windows, provided that you know almost all the required syntaxes.
But along the road, things changed, and it became hard. I was later introduced to Linux, and it went completely bonkers for me. But as I learned, I realized the differences, and that’s what I am here to tell you about. Also, we will be taking a look at configuring the Linux Network environment, as that is a must for aspiring L5 Administrators, Security Engineers, and Hackers.
Windows vs Linux Network
Before I start, let me tell you that this blog is just to highlight the strengths and weaknesses, or more preferably, cons, in the case of Linux Network and the Windows Server. Microsoft Windows Server has a graphics-based User interface which makes you think it is actually very easy to set up different things. But is it? Besides, along with easy configuring, there is a more crucial part here which is Security. Microsoft Windows is a purely commercial Operating System which means there will be updates for Security patches, and there are dedicated people assigned to do the job.
Besides, hacking into Windows, even for vulnerability assessment, is a breach of agreement from Windows itself and is considered a major offense. This is to keep Windows as closed source as possible and make them free from security issues. Microsoft Windows is also the most used operating system in the world, be it either for personal or commercial use. Linux, on the other hand, is widely popular, but it is not used that much. One glance at Linux and people can say it is a sophisticated Operating System that has its software assembled from all over the world. But doesn’t that mean it has security issues? Yes and No, both. We will get to that part later on. Nowadays, most configuring Linux network distributions come with Graphical User Interface pre-built. But Linux developers will always prefer using a command-line interface for configuring a Linux network rather than a graphical one because they know the disadvantages and lags in it. So, let’s take a deeper look into both and see who comes out at the top.
Windows Server
First things first, Let me break your uneducated guess and tell you that configuring a Windows network is way too different and difficult from configuring a Linux network. In Windows, you have two ways to set up a specific network. The first way is to use the option of setting up the network with the help of the ‘Network Setup Wizard’. This is the easiest method and is perfect for inexperienced beginners as one has to just read, select and execute and the Windows does most of the job of setting up the environment. However, the second part is the toughest. One has to do everything manually here. The user has to go through all the machines and check all the individual Linux network protocols to see whether they are identical or not and has to make sure there is no mistake. This is for experienced users only since this takes up a lot of time and is a tedious job.
It is still, however, in the beginner stage, but it looks promising. The virtual desktops, multi-user smoothness, super-fast boot time, along with lots of other features make it look promising. But still, Windows being the most popular user choice, the number of viruses and Trojans being in continuous development are uncountable. This is the worst Windows can get since security is not something Windows is very good at. But that does not make Windows Networking Systems an inferior operating system. Windows can still be secured with the help of firewalls, Anti-viruses, but that too at the cost of speed, efficiency, and expenditure. However, it is still very good for businesses that are small or still in development.
Linux Network Environment
Linux, on the other hand, has one of the oldest operating system environments here. It is not the best user-friendly software here, but at least better than the Mac OS. Besides, Security is never an issue in Linux since it is open-source software, and more preferably, there is no specific person to hate or curse when something goes bad. Linux network Windows, on the other hand, Bill Gates has a lot of haters, and not the mention it is consistently under the attack of worms, malware, and Trojans. Most people tend to believe that Linux does not have viruses. This is so not true. Linux has its own type of virus, and these can get extremely hard to remove once they affect the network system.
But, unlike Windows, there is no autorun facility over here. Everything in Linux works with the help of a Script, and it is up to the administrator whether to execute it or not, and that too manually. And since Linux is open source, there are a lot of developers out there who keep on testing the new kernels and bugs. The community and support are much larger than that of Microsoft here, because of which it is much faster for updates on security issues and fixing bugs.
Now that we know the Linux Network environment is far superior to Windows in terms of Server handling and Administration, let’s take a look at Configuring a Linux network.
Configuring Linux Network Environment
Configuring a Linux Network environment for home and for the office are two different things. If you already have some experience in Linux, then you may know that most of the things are done via terminal here, which is similar to that of the command prompt of Windows but is far more advanced and superior. Most Linux administrators prefer to write scripts for any network settings. So, once a script is written, next time onwards, the Administrator just needs to change the permissions of the script using ‘chmod u+x’ and then execute the shell script in any Linux Network. Most people prefer Red Hat or a Debian System for administration. The best tool for configuring a Linux network is a software known as ‘netenv’, meaning ‘network environment’. One can install this tool by typing the following:-
| $ sudo apt-get install netenv |
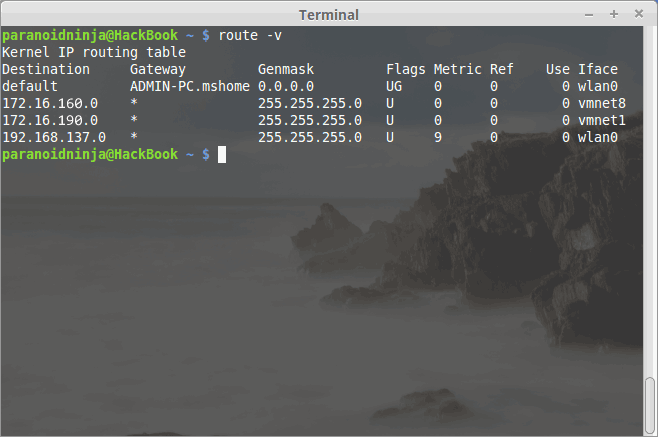
Here, one may not require sudo depending upon whether you are the SuperUser or just a User. The official website for netenv is http://www.netenv.com/. One may also need to use nmap to check whether the Linux network is consistent. Nmap also helps to scan how many systems are connected to the network, which ports are open, what services are being run, what is the operating system, and other stuff. Before I run a Nmap scan, I need to set up a gateway for my other individual systems, and I can do that with the help of the following command:
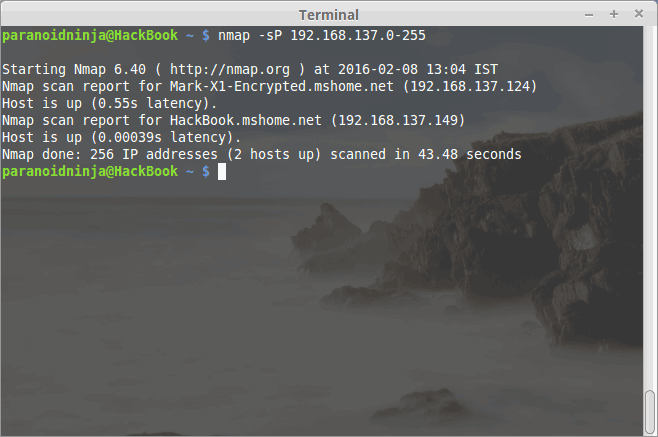
As you can see, my gateway is 192.168.137.0. Once you get the gateway, you can get a list of connected systems by using Nmap. Following is an image of Nmap scan for a list of systems connected to my home Linux Network:
As you can see, I have two devices connected above, one is my Cell Phone, and the other is My Linux Laptop itself. One can also get a good view of the types of systems connected. Similarly, you can also get information about the open ports, services, and connected systems with the help of the following command:
| $sudo nmap -A -O 192.168.x.x |
With the help of other software such as Ettercap, or Wireshark one can also view the packets being sent between multiple computers. And with the help of Aircrack-ng, one can even try to limit the packets or shut down the network environment itself. But that is for a long note. Linux Distributions, by default, have methods to increase or decrease the packet and data distribution.
Configuring Linux Network Environment
Besides the above things, the following are a few other important stuff to know while Configuring a Linux Network environment.
1. Telnet
The Telnet is software used for accessing a computer remotely. Telnet is one of the most used software, and it is also very popular, but it is terminal or, more preferably, console-based. It is based on UNIX. However, the major downside of this application is that this is highly insecure. Anyone can view and trace the Linux network information being sent. This info can also be sniffed via lots of software such as Ettercap or Wireshark. There is, however, an encrypted version that is used instead of the basic telnet known as SSH (Secure Shell), which requires a PGP key to authenticate to the remote host. Similar software is also available for Windows, which is known as Putty. Both of these software are interoperable. SSH can be installed via the following command:
| $ sudo apt-get install OpenSSH-server |
Similar to Telnet, there is also another software which is known as rlogin, which is also widely used.
2. X- Window
X- Window System is a basic standard window system for Graphical UNIX workstations. X-Window consists of two parts: the X- server and the X- Client. The Server here is the workstation from which the Administrator is accessing the client-side workstation. This is very useful because it uses the least possible resource from the CPU. These systems are also known as X- terminals.
3. VNC
VNC or more commonly known as Virtual Network Connection, is a Graphical User Interface that does the same work as that of telnet or X-window but on a Virtual Machine basis. The Administrator uses an IP address and a password for authentication. It is somewhat similar to that of an mstsc of Windows, where one can get a GUI of the remote host, but VNC is much less resource-consuming than the Windows ones. Linux Administrators, most of the time, prefer a Shell login such as SSH since it does most of the job via terminal and is the least resource-consuming of all of them.
There is actually much more to it than just these applications. Things like Tunnelling, Virtual Private Networks, Mobile IP, and configuring static and dynamic IPs using a network manager and np-config. Once you get a basic hang of configuring a Linux network, all of these things come by naturally. One of the best ways to practice configuring a Linux network is by using a Virtual Box or a VMware since both of them satisfy the necessary needs.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Configuring Linux Network” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.