Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Configuring DHCP Server
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol or DHCP is a network management protocol. DHCP is used to assign an Internet protocol (IP) address to any device or any node on a network. A DHCP client uses the DHCP protocol. An IP address can be defined as a unique numeric identifier that is assigned to each computer. Manually we can assign the computers with the IP addresses, but there can be a lot amount of problems that can arise because of this, like the risk of duplicating the IP addresses and so many, and it is a time-consuming process also. To overcome these problems, DHCP is a service that takes care by automatically assigning IP addresses to DHCP clients. In this article, we will learn the process of how to configure a DHCP server.
Configure DHCP Server
- Download the software from the official website.
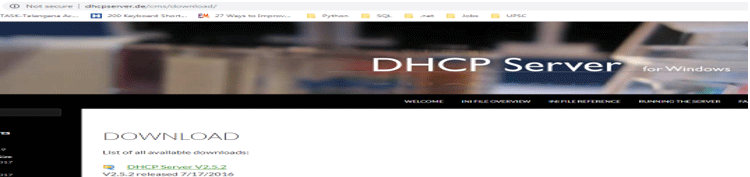
- After downloading the software from the official website, click on the dhcpwiz.exe program.
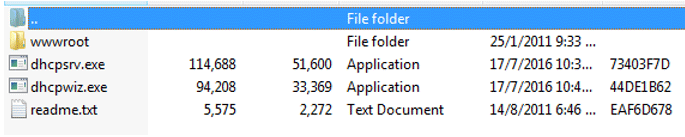
- Click on the run.
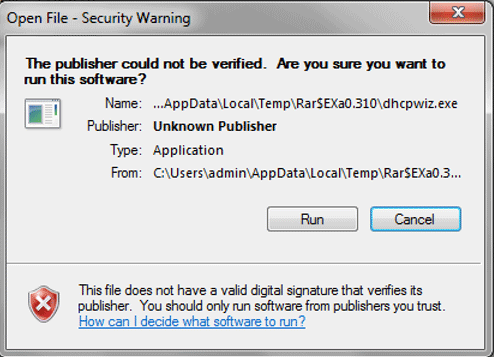
- After clicking on the run, welcome to the DHCP configuration wizard will open. Click on next to proceed.
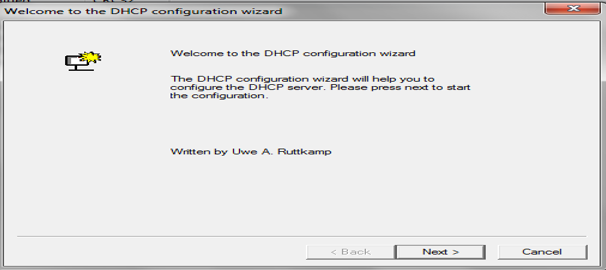
- Select the network interface card.
- It is not recommended to run the DHCP server on a network card that already has DHCP enabled.
- After selecting the network interface card, click on next to proceed further.
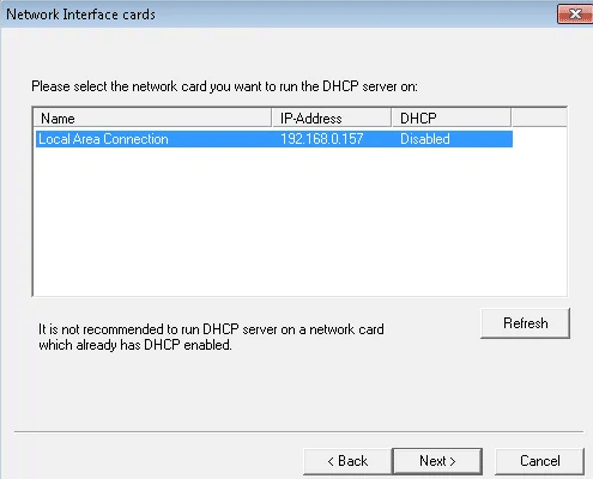
- It consists of two types of protocols. Select the supported protocols.
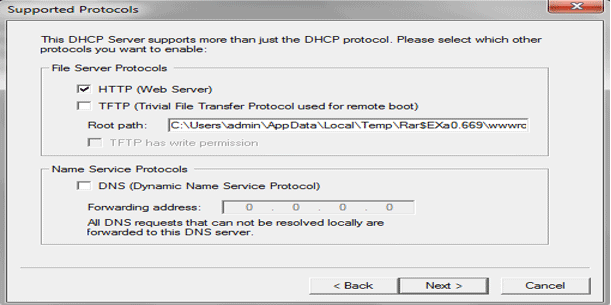
- After selecting the protocols, click on next.
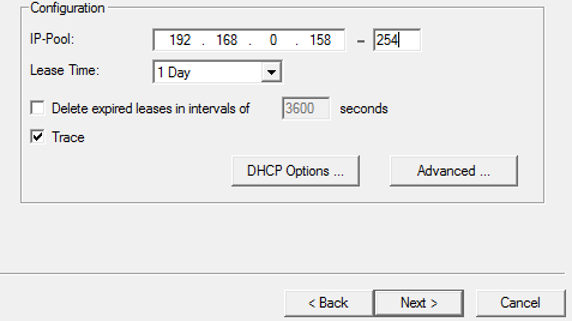
- Configure DHCP for the interface.
- Configure IP-Pool, lease duration, trace and so on and then click on Next.
- Writing the INI file.
- The final result of the DHCP configuration wizard is an INI file. This file will contain all the configuration options.
- The INI file is successfully written (we can see it in the below image).
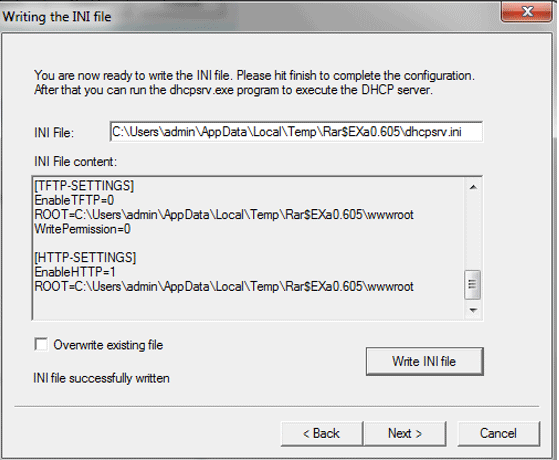
- Click on next.
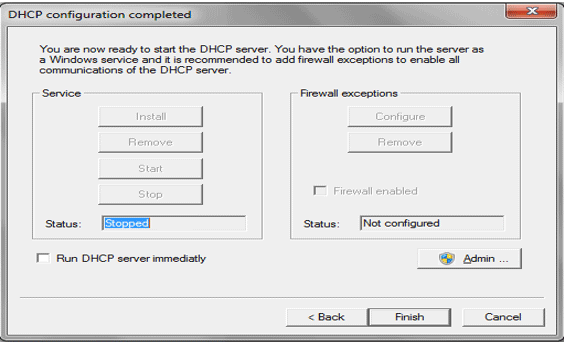
- Click on Admin and then Ok.
- Click on Install, start and then click on configure.
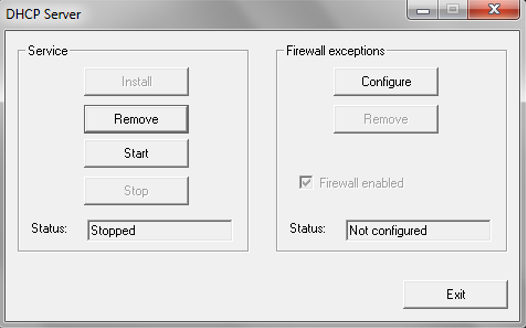
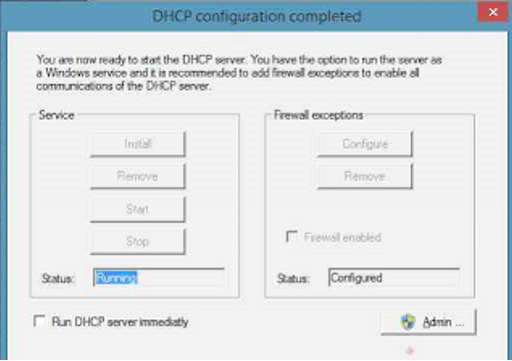
- Tick the checkbox Run DHCP server immediately and click ok, and then click on next.
- Now the configuration of the DHCP server is completed.
Working of DHCP
Working of DHCP are:
- DHCP works on a client-server model.
- DHCP is an extension of the Bootstrap Protocol (BOOTP).
- The difference between the BOOTP and DHCP is DHCP can acquire all IP (Internet Protocol) related configuration information.
- DHCP supports three mechanisms for IP address allocation. They are automatic allocation, dynamic allocation, and manual allocation.
- DHCP runs at the Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) application layer, and both client and server use broadcast messages to communicate with each other.
- The main important characteristics of the DHCP are centralized IP address administration, backward compatible with BOOTP, supports multiple servers, provides a dynamic assignment, allows static assignment and doesn’t interact with domain name service (DNS).
DHCP DISCOVER
- The client connected to a local subnet requests the DHCP information.
- The client sends out a DHCPDISCOVER message requesting an IP address.
- The message is sent out as a broadcast.
- This first datagram is known as a DHCPDISCOVER message, which is a request to any DHCP Server that receives the datagram for configuration information.
- The purpose of a DHCPDISCOVER message is to discover a DHCP server.
- The DHCPDISCOVER message contains an identifier unique to the client.
- The message might also contain other requests, such as requested options (for example, subnet mask to identify the subnet space, domain name, or static route).
- DHCPDISCOVER message is delivered to every connected computer in the Broadcast Domain.
DHCP OFFER
- DHCPDISCOVER message was delivered to every connected computer in the Broadcast Domain.
- If there are multiple servers on the network, the client device receives multiple DHCPOFFER messages. It is up to the client device to select a particular message.
- The DHCP server offers information to the client.
- Any DHCP server that receives the DHCPDISCOVER message might send a DHCPOFFER message in response.
- In case if the DHCP client device received multiple DHCPOFFER, the DHCP client accepts the first DHCPOFFER message that arrives.
- After the DHCP Server receives discover the message, it suggests the IP addressing offering to the client host. It also contains other configuration information that is defined in the DHCP setup like a proposed IP address for the client, subnet mask to identify the subnet space, IP of the default gateway for a subnet, IP of DNS server for name translations.
DHCP REQUEST
- The client accepts the DHCP server offer.
- The client responds via a broadcast message called a DHCPREQUEST.
- The client compares the offers with the settings that it requested and then selects the server that it wants to use.
- It sends a DHCPREQUEST message to accept the offer, indicating which server is selected.
DHCP Pack
- The DHCPREQUEST, which the client sends after receiving it to the server, sends a response message by DHCP Server.
- DHCP server acknowledges the client and leases the IP address.
- The message is the DHCPACK message is an acknowledgement by sending this message; it indicates that it the end of the process which started from DHCPDISCOVER.
- But if the selected server does not meet the requirements of the DHCPREQUEST, it sends a DHCPNAK (Negative Acknowledgement).
- If the client does not either receive a DHCPACK or DHCPNAK before the timeout, it resends DHCPREQUEST.
- The client now can use the IP address, subnet mask, and configuration parameters.
- The client can use the setting until the lease expires or renew the lease by sending a DHCP REQUEST message to the client.
- If the server does not respond, he can use the lease until it expires.
- When the lease has expired, the client must start over with the DHCPDISCOVER process.
- There are three types of address leases. They are a manual lease, automatic lease and dynamic lease.
- The client can end the lease by sending a DHCPRELEASE message to the server to end the lease.
Conclusion – Configuring DHCP Server
The main advantage of using the DHCP is reusing a previously allocated address, and it even saves time by automatically allocating the IP addresses to the clients.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Configuring DHCP Server. Here we discuss how to configure the DHCP server along with the working of DHCP. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


