Updated July 28, 2023
Difference Between Cloud Computing vs Virtualization
Cloud Computing is a model for enabling convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Virtualization is Software that creates “separated” multiple hardware and software images on the same machine. This makes installing multiple OS, software, and applications possible on the same physical machine. Cloud is good for public use. Other side, IT companies use Virtualization for cost-efficient data center setup.
Cloud Computing
Cloud computing delivers on-demand resources, including servers, storage, databases, software, and other services, over the Internet. The concept involves utilizing a network of remote servers hosted on the internet, commonly called the cloud, to offer computing services and resources. Cloud computing allows users to access and utilize various resources and applications anywhere and anytime without relying on local servers or personal devices. You can achieve this using a web browser or a dedicated client application. Cloud service providers manage and maintain the cloud infrastructure, ensuring availability, scalability, and security.
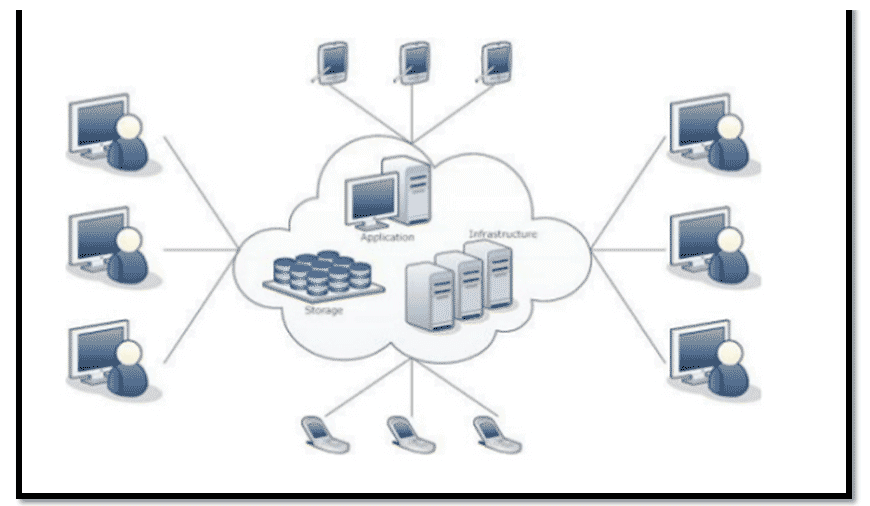
In the above image, various applications, storage, and Infrastructure servers are running over the cloud and accessible for all types of devices, such as Mobile phones, Computers, etc. The cloud can be accessed through the internet, depending upon permissions. The cloud is useful for external user access. Amazon Web Services, Google Cloud, and Dropbox are examples of cloud techniques.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
- It is accessible to all users (with proper credentials) without any restrictions.
- Using the cloud for applications is cost-efficient.
- Least the possibility of access failure due to non-dependency on a single machine.
- Cloud provides you independence from machine access. URL will give you access to your infrastructure all the time.
- Real-time user access. Multiple users can access the same application and can work on it (Example – Google Doc)
- Cloud is reliable for Backup and recovery since data storage is not server-specific.
- Cloud computing is the best platform to showcase your applications/software worldwide. Users can access your application & work on it using a single link.
- The flexibility to access it from anywhere makes it popular among users and service-providing industries.
Virtualization
Virtualization is producing a virtual version rather than a physical). A resource can refer to various things like an operating system, server, storage device, or network. It involves abstracting the underlying physical infrastructure and dividing it into multiple virtual environments, each with its resources and capabilities.
Using virtualization, the software can reduce the cost of hardware, and it increases the utilization, accessibility, and efficiency of the infrastructure. Virtualization works on top of the physical server’s hardware and divides its hardware into multiple segments (Virtually only) where virtual machines are installed.
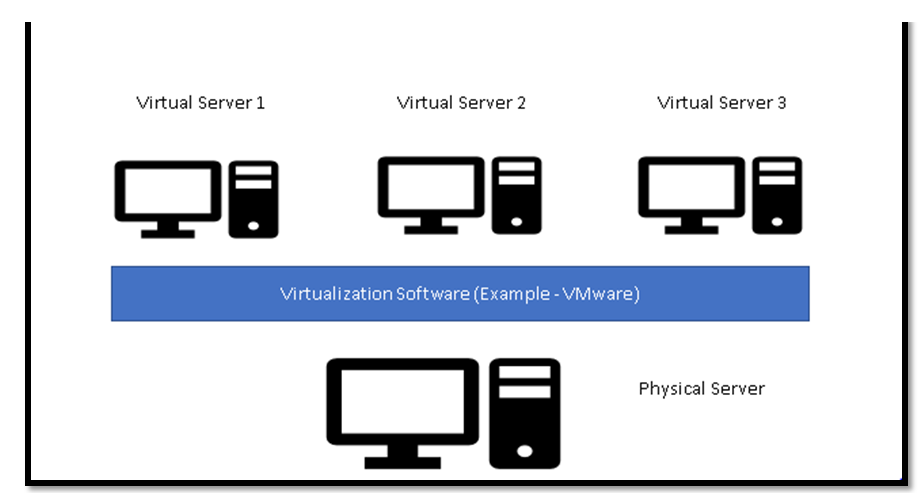
The above image divides Single Physical Machine into multiple virtual machines using Virtualization Software.
Benefits of Virtualization
- Server virtualization is the top reason behind its success.
- IT industries setting up thousands of servers’ machines using a virtualization technique.
- Multiple applications can be installed on a single physical machine despite OS dependency.
- The setup cost is very low. Virtualization can be done on a Personal Computer.
- The desktop virtualization feature provides flexibility to virtualize the whole system with a single click.
- Virtual infrastructure works well with low-speed network access.
- Virtualization has reduced the cost of Hardware in the IT industry because a single server can serve as multiple machines.
- Virtualization is Plug & a play service; Thousands of machines can be created and made available for use without taking much time. Virtualization software can virtualize the physical servers without taking much time.
Head to Head Comparison Between Cloud Computing and Virtualization (Infographics)
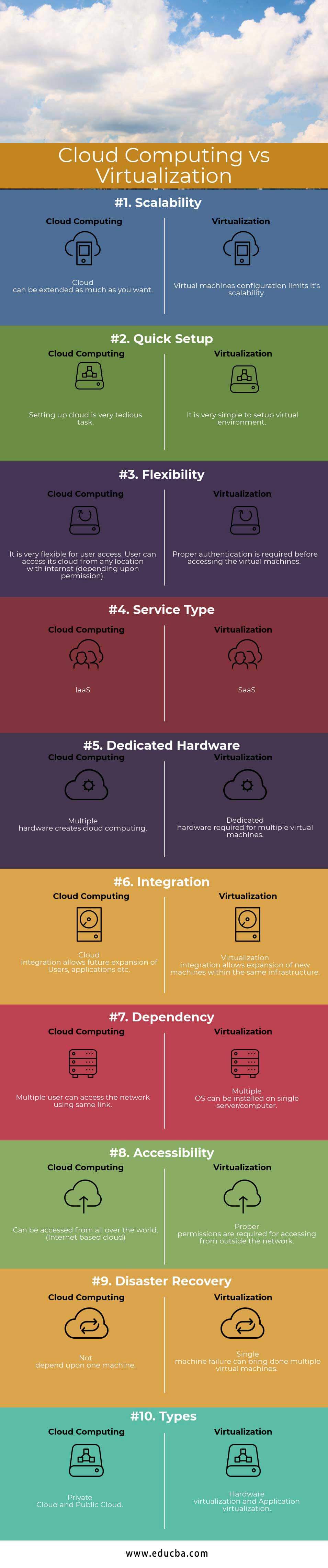
Below is the Top 10 Comparison Between Cloud Computing and Virtualization:
Key Differences Between Cloud Computing and Virtualization
Below is the difference between Cloud Computing and Virtualization:
- Virtualization is software that virtualizes your hardware into multiple machines, while Cloud computing combines multiple hardware devices.
- In Virtualization, a user gets dedicated hardware, while in Cloud computing, multiple hardware devices provide one login environment.
- Cloud computing is best to access from outside the office network, while Virtualization is meant to access from the office only.
- Virtualization doesn’t depend upon the cloud computing environment, while without virtualization, cloud computing can’t exist.
- Cloud computing works on IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service), while virtualization is based upon SaaS (Software as a Service).
- Shared computing resources like software and Hardware provide a cloud computing environment, while Virtualization exists after Machine/Hardware manipulation.
- Cloud Computing provides you flexibility such as pay-as-you-go, self-service, etc., while access to a virtualized environment won’t allow you to access such features.
- Cloud computing is good for selling your service/software to external users, while Virtualization is best for setting up Data centers within the company network/infrastructure.
- Storage capacity is limitless in the Cloud network, while in a Virtualization, it depends upon Physical server capacity.
- Single machine failure won’t impact the cloud infrastructure, while in virtualization, single node failure can impact 100s of virtual machines (If Physical Hardware/Machine is not configured in High Availability)
Cloud Computing and Virtualization Comparison Table
Below is the comparison table between Cloud Computing and Virtualization.
| Key Points | Cloud Computing | Virtualization |
|
Scalability
|
The cloud can be extended as much as you want. | Virtual machine configuration limits its scalability. |
|
Quick Setup
|
Setting up the cloud is a very tedious task. | It is very simple to set up a virtual environment. |
|
Flexibility
|
It is very flexible for user access. A user can access its cloud from any location with the internet (depending upon permission). | Proper authentication is required before accessing the virtual machines. |
|
Service Type
|
IaaS |
SaaS |
|
Dedicated Hardware
|
Multiple hardware creates cloud computing. | Dedicated hardware required for multiple virtual machines |
|
Integration
|
Cloud integration allows future expansion of Users, applications, etc. | Virtualization integration allows the expansion of new machines within the same infrastructure. |
|
Dependency
|
Multiple users can access the network using the same link. | Multiple OS can be installed on a single server/computer. |
|
Accessibility
|
It can be accessed from all over the world. (Internet-based cloud) | Proper permissions are required for accessing from outside the network. |
|
Disaster Recovery
|
Not depend upon one machine. | Single-machine failure can bring multiple virtual machines. |
|
Types |
Private Cloud and Public Cloud | Hardware virtualization and Application virtualization. |
Conclusion
Cloud infrastructure cannot be established without the help of virtualization. It is the foundation of cloud networks. In IT infrastructure, cloud computing, and virtualization are used to build a cloud infrastructure. Virtualization separates the hardware from the physical machine to create multiple virtual machines on the same server. Google Docs is the best example of cloud computing.
Recommended Articles
This has been a guide to Cloud Computing vs Virtualization. We have discussed Cloud Computing vs Virtualization head-to-head comparison, key differences, infographics, and a comparison table here. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –