Updated June 15, 2023
Definition of C++ Read File
C++ is a widely used programming language that offers numerous features to facilitate various tasks. File operations in C++ are as straightforward as console operations using cin and cout. Working with files is a standard method for storing data indefinitely. In C++, the stream library, such as iostream, conducts file operations, enabling read and write capabilities. The stream is only the destination to input or output the data from one location to another. Several datatypes of this library perform specific tasks of file operations. ‘stream’ is one of the data types explicitly used for reading files in C++.
How to Read Files in C++?
Let’s understand the datatypes of ‘ifstream’ mentioned below:
| Data Type Name | Data Type Description |
| ofstream | This data type is used to open the file or write something in the file. It represents the output file stream. |
| ifstream | This data type is used to read the data from the file. It represents the input file stream. |
| fstream | This data type represents a normal file stream and can perform the tasks of both input and output file streams. It can be used to open, create, read, and write in the file. |
Given below is the step-by-step procedure for the file content in C++ :
1. Opening the Already Created File
In order to read the information from the file, we need first to open it. The opening of the file is done using ofstream or fstream object of the file. Files in C++ can be opened in different modes depending on the purpose of writing or reading. Hence, we need to specify the mode of file opening along with the file name.
There are basically 3 default modes that are used while opening a file in C++:
- ofstreamios: : out
- fstreamios: : in | ios: : out
- ofstreamios: :out
Syntax:
void open(filename, ios: : openmodemode_name);2. Read the Information from The File
We can simply read the information from the file using the operator ( >> ) with the file’s name. We need to use the fstream or ifstream object in C++ to read the file. Reading of the file line by line can be done by simply using the while loop along with the function of ifstream ‘getline()’.
3. Close the File
As we all know about C++ memory management, as the program terminates, it frees all the allocated memory and the used resources. However, it is generally considered good practice to close the file after the desired operations are performed.
Syntax:
void close();Examples of C++ Read File
Let’s look at a few examples.
Example #1
Code:
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
using namespace std;
intmain(){
char data[100];
// creating the file variable of the fstream data type for writing
fstreamwfile;
// opening the file in both read and write mode
wfile.open ("demo.txt", ios::out| ios::in );
// Asking the user to enter the content
cout<< "Please write the content in the file." <<endl;
// Taking the data using getline() function
cin.getline(data, 100);
// Writing the above content in the file named 'demp.txt'
wfile<< data <<endl;
// closing the file after writing
wfile.close();
//creating new file variable of data type 'ifstream' for reading
ifstreamrfile;
// opening the file for reading the content
rfile.open ("demo.txt", ios::in| ios::out );
// Reading the content from the file
rfile>> data;
cout<< data <<endl;
//closing the file after reading is done
rfile.close();
return 0;
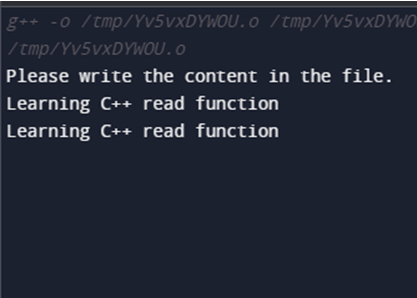
}Output:
Explanation: In the above example, we have created two file variables of ‘fstream’ and ‘ifstream’ data types for writing and reading the file, respectively. In order to read or write the file, we need first to open the file using the open() function and define its mode. After opening, the writing of the content in the file is done through the ( << ) operator, and the file is closed after writing using the close() function. Now the file is opened again to read its content (using >> operator) and display it on the console (using cout function).
Example #2
When the file user is reading is not found.
Code:
#include<iostream>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
intmain()
{
char ch;
//creating the object of the data type 'istream'
ifstreamnew_file;
//opening the above file
new_file.open("demo1.txt",ios::in);
//checking whether the file is available or not
if(!new_file)
{
cout<<"Sorry the file you are looking for is not available"<<endl;
return -1;
}
// reading the whole file till the end
while (!new_file.eof())
{
new_file>>noskipws>>ch;
// printing the content on the console
cout<<ch;
}
//closing the file after reading
new_file.close();
return 0;
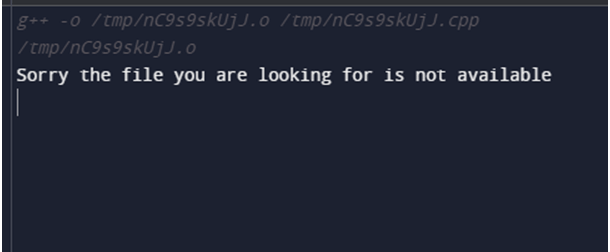
}Output:
Explanation: The code snippet creates an object of the ‘ifstream’ data type to read the file named ‘demo1.txt’. The file is opened using the ‘open()’ function in read mode, indicated by the ‘ios::in’ flag. ‘if’ and ‘else’ statements are used to check if the file is present. If the file is not found, a suitable message is displayed on the console. Otherwise, it will read the whole file using the ‘>>’ operator, and the content is printed on the console. In order to release all the resources and free the memory, the close() function is used.
Conclusion
The above description provides a clear explanation of how file reading is performed in C++ and highlights the different data types of file streams used for specific operations. As working with files is very common in the practical world, it is very important to understand each and every file operation deeply before using them.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “C++ Read Files” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.