Updated June 16, 2023
Introduction to C++ fstream
In C++, the concept of the fstream is used for the reading and writing on the file system. In very simple and technical words, it can do dual work, which means it has ofstream and ifstream. So if the file is not there on which we are going to write some contents, then the fstream can write the contents on the file, and at the same time, it also allows us to open the file and display the contents. We should use this if we know that we will create, read and write content on the file.
Syntax:
Below is a simple syntax for the fstream in C++. In the example below, we are first getting or creating a file; we can give any name to the file we are creating here. Second, we are writing some content to the file. In the same way, we can read the file content with the help of the getline function in a while loop.
ofstream creatMyFile(AnyFileName);
creatMyFile << Any text as contents;How fstream work in C++?
We already have a package like ifstream and ofstream, but they can either read and write the file, but what do we do in case we want to perform read and write the file? So for that case, we have the fstream c++ package.
We can create a file if the file does not exist.
- First, we can create a file instance with code like “ofstream of”; here, of will be used as the instance.
- Next, we can pass any file name we want to create, like “open(any filename);”.
- Finally, we can write the contents on the file like cout << “any contents and text data” << endl;
- If needed, we can also read the file’s contents with the help of the getline functions to read data line by line.
Examples of C++ fstream
Given below, we have three significant examples of the fstream of C++. In the examples, we show how we create an empty file, write some contents on the file, and then again read the same file by printing all the contents.
Example #1
Code:
//Importing the package iostream
#include <iostream>
//Importing the package fstream
#include <fstream>
//Importing the string package for string related works
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main () {
string ln;
//Creating a file with name test.txt ,if not exists
ifstream testFile ("test.txt");
//Checking the file opening condition
if (testFile.is_open())
{
//Running a while loop and fetch all the contents line by line
while ( getline (testFile,ln) )
{
//Printing the output of the file contents
cout << ln << '\n';
}
//Here we are closing the opened file
testFile.close();
}
else cout << "File is not there on the given path";
return 0;
}Output:
Example #2
Code:
//Importing the package iostream
#include <iostream>
//Importing the package fstream
#include <fstream>
//Importing the package string for string related work
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main () {
// This code will create a file with name test.txt
ofstream creatMyFile("test.txt");
// Here we are writing contents to the file
creatMyFile << "Hello, C++ is a powerful language";
// Once done with the writing closing the file
creatMyFile.close();
// Here we have created a text file to read the contents and show as the output on the screen
string myText;
// Here we are going to read the file
ifstream readMyFile("test.txt");
// Here we are running the loop and using the function getline and reading each lines of the file.
while (getline (readMyFile, myText)) {
// Output the contents from the file
cout << myText;
}
// Here we are closing the opened file
readMyFile.close();
}Output:
Example #3
Code:
//Importing the package fstream
#include <fstream>
//Importing the package iostream
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main () {
char subject[200];
// Here we are opening the file in the write mode for operations
ofstream of;
//Open the file and create the file if not exists
of.open("test.txt");
//Writing the the data to the file which we have created
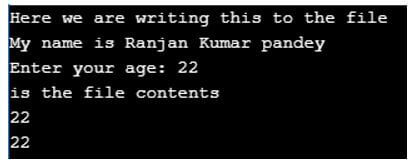
cout << "Here we are writing this to the file" << endl;
cout << "My name is Ranjan Kumar pandey";
cin.getline(subject, 200);
// write inputted data into the file.
of << subject << endl;
cout << "Enter your age: ";
cin >> subject;
cin.ignore();
// Here we are again writing some input data to file
of << subject << endl;
// close the opened file.
of.close();
// Here we are opening the file in read purpose
ifstream inf;
inf.open("test.txt");
cout << "is the file contents" << endl;
inf >> subject;
// Writing some data to it
cout << subject << endl;
// Here we are again going to read the file data and also we are displaying the data
inf >> subject;
cout << subject << endl;
// Here we are performing closing of the file which we have opened
inf.close();
return 0;
}Output:
Advantages of C++ fstream
Given below are the advantages mentioned :
It can perform dual work like it can create a file and simultaneously allows you to write the file’s contents.
- One of the most important things about it is it allows us to use the concept of internalization and localization.
- It gives us a complete object-oriented approach, because of which we can reuse the features many times.
- Because it has a feature where if the file does not exist, it will create the file for us instead of throwing an error.
Conclusion
This tutorial showed the basic concept of the stream and its syntax. We also focused on the working and some of the essential advantages of using the concept of the fstream. We noticed some of important examples also.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “C++ fstream” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.