Introduction to C++ Data Types
The following article provides an outline for C++ Data Types. In this article, we will look at different data types such as integer, float, double, char, or built-in data types like union, enum, struct, and data types like functions, pointers, arrays. Data types should be defined before the execution as it informs the compiler of the type of data specific variables holds. Integer data type can hold only integer values, it cannot hold the float values or string values.
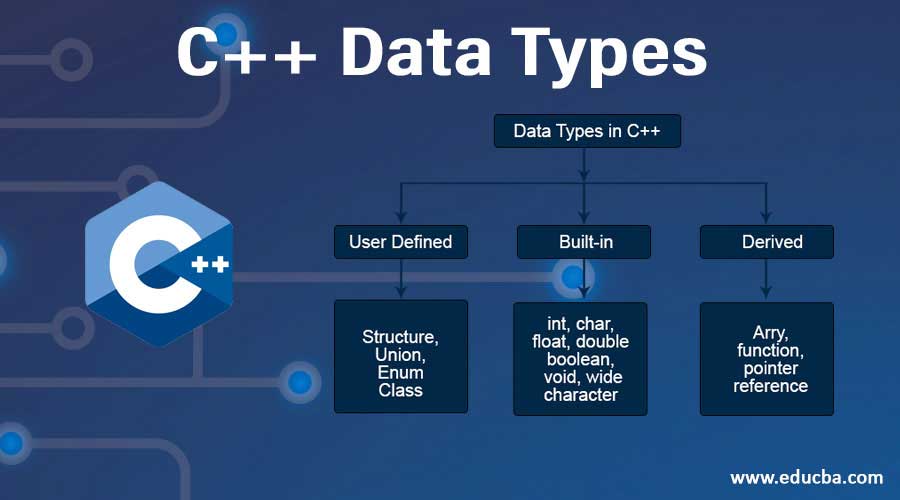
A data type is to let know the variable, what type of element it is and definitely going to determine the memory allocation of that variable. We are aware that each data type has a different memory allocation. There are three different C++ data types namely; Primitive, Derived, and User Defined.
Top 3 Data Types in C++
Here are three different data types in C++ which are given below:
1. Primitive Data Types
These are pre-defined in c++, also called the built-in data types. We can directly use them to declare the variables.
a. Integer: Usually defined by “int”. We can know the size of memory allocated and how the variable is declared as below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a;
cout<< " Size of int is: " << sizeof(a);
}Output:
![]()
b. Character: Usually defined by “char”. We can know the size of memory allocated and how the variable is declared as below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char a;
a='R';
cout<< " Size of char is: " << sizeof(a)<<endl;
cout<< " Value of a is: " << a;
}Output:
![]()
c. Floating Point: Usually defined by “float”. We can know the size of memory allocated and how the variable is declared as below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float a;
a=5.85;
cout<< " Size of float is: " << sizeof(a)<<endl;
cout<< " Value of a is: " << a;
}Output :
![]()
d. Boolean: Usually defined by “bool”. We can know the size of memory allocated and how the variable is declared as below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
bool a;
cout<< " Size of bool is: " << sizeof(a)<<endl;
cout<< " Value of a is: " << a;
}Output :
![]()
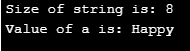
e. String: Usually defined by “String”. We can know the size of memory allocated and how the variable is declared as below.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string a;
a="Happy";
cout<< " Size of string is: " << sizeof(a)<<endl;
cout<< " Value of a is: " << a;
}Output:
Here, we also have the concept of signed, unsigned, short and long. So, what are these? These are called the Data type modifiers. These, in fact, decide the actual length of any particular data type.
Signed values give us the numbers of both below and above zero, which is both positive and negative. Whereas the unsigned values contain data that is only positive. And coming to short and long, through the names itself we can clearly interpret that long data modifier has the capacity to store large amounts of values. And in fact, short is the data type must and will hold a minimum of those numbers of values.
2. Derived Data Types
These are the data types that are derived from the primitive data types; which in turn justifies its name.
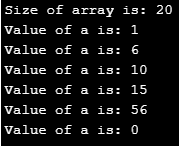
a. Array: Here, we define a series. Let’s see how we can do that here.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[5]={1,6,10,15,56};
cout<< " Size of array is: " << sizeof(a)<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<6;i++)
{
cout<< " Value of a is: " << a[i] <<endl;
}
}Output:
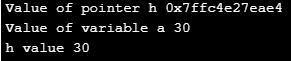
b. Pointer: This enables the call by reference functionality and these pointers play a huge role in declaring or manipulating data in dynamic data structures. For example in creating Stacks, Queues, Linked lists we primarily use these pointers.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
float a = 30;
float *h;
h= &a;
cout << " Value of pointer h "<< h << endl;
cout << " Value of variable a "<< a << endl;
cout << " h value "<< *h ;
}Output:
3. User-Defined Data Types
As the name already suggests, these are the data types which the user can define. Let us see few examples of these.
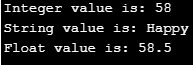
a. Structures: Storing the combination of either similar or different data types under continuous memory locations. As we already saw, in arrays we can store only items with similar data types. But structures can store different data types.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
struct First
{
int a = 58;
string r = "Happy";
float y = 58.5;
} ;
int main()
{
struct First f;
cout<< " Integer value is: "<< f.a <<endl;
cout<< " String value is: "<< f.r << endl;
cout<< " Float value is: "<< f.y;
}Output:
b. Class: It is defined in object-oriented programming. This has functions, variables and is accessed by creating objects.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class First
{
public:
string name;
void show()
{
cout << "Name is: " << name;
}
};
int main()
{
First f;
f.name = "My Name";
f.show();
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
c. Type Def: This data type is for just giving a new or a different name to the data types.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
typedef unsigned char THISONE;
typedef unsigned int OTHERONE;
THISONE b1;
OTHERONE b2;
b1 = 'R';
b2 = 10;
cout << " Check this out: " << b1<<endl;
cout << " Check other out: " << b2;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
And, there are many more. Even Stacks, Queues, Linked lists, and Trees also come under different Data Structures.
d. Enumeration: Defined by the word “enum”. These are generally used when we already know a set of values for a particular variable and choose a single value from them.
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
enum color {Yellow, Red, Green, Blue}col;
int main()
{
col = Green;
cout<<" The color chosen is in the place: "<<col;
return 0;
}Output:
![]()
Conclusion
We have majorly covered many of them. We use these different data types and definitely, these are the basis of any programming language. Without declaring variables with specific data types, we cannot know the exact memory allocations and what set of instructions that a program has to do. Practice and try using different data types with data modifiers and check out how they are behaving too.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to C++ Data Types. Here we discuss the top 3 C++ datatypes such as primitive, derived, and user-defined along with examples and code implementation. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –


