Updated March 22, 2023
What is a Hive Data Types?
Before understanding the Hive Data Types first, we will study the hive. Hive is a data warehousing technique of Hadoop. Hadoop is the data storage and processing segment of Big data platform. Hive holds its position for sequel data processing techniques. Like other sequel environments hive can be reached through sequel queries. The major offerings by hive are data analysis, ad-hoc querying, and summary of the stored data from a latency perspective, and the queries go a greater amount.
Hive Data Types
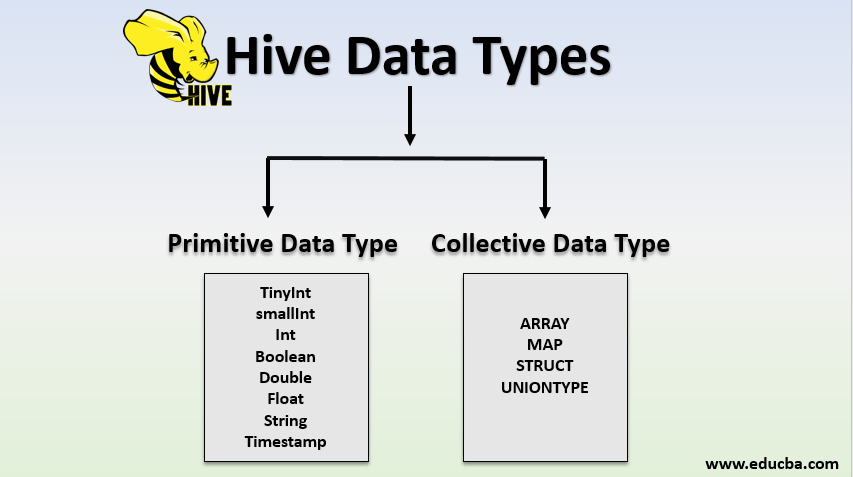
Datatypes are classified into two types:
- Primitive Data Types
- Collective Data Types
1. Primitive Data Types
Primitive means were ancient and old. all datatypes listed as primitive are legacy ones. the important primitive datatypes areas are listed below:
| Type | Size (byte) | Example |
| TinyInt | 1 | 20 |
| SmallInt | 2 | 20 |
| Int | 4 | 20 |
| Bigint | 8 | 20 |
| Boolean | Boolean true/False | FALSE |
| Double | 8 | 10.2222 |
| Float | 4 | 10.2222 |
| String | Sequence of characters | ABCD |
| Timestamp | Integer/float/string | 2/3/2012 12:34:56:1234567 |
| Date | Integer/float/string | 2/3/2019 |
Hive Data Types are Implemented using JAVA
Ex: Java Int is used for implementing the Int data type here.
- Character arrays are not supported in HIVE.
- Hive relies on delimiters to separate its fields, and hive on coordinating with Hadoop allows to increase the write performance and read performance.
- Specifying the length of each column is not expected in the hive database.
- String literals can be articulated within either double quotes (“) single quotes (‘).
- In a newer version of the hive, Varchar types are introduced, and they form a span specifier of (amid 1 and 65535), So for a character string, this acts as the largest length of value which it can accommodate. When a value exceeding this length is inserted, then the rightmost elements of that values have been truncated. Character length is a resolution with the figure of code points controlled by the character string.
- All integer literals (TINYINT, SMALLINT, BIGINT) are considered as INT datatypes basically, and only the length exceeds the actual int level it gets transmuted into a BIGINT or any other respective type.
- Decimal literals afford defined values and superior collection for floating-point values when compared to the DOUBLE type. Here numeric values are stored in their exact form, but they are not stored exactly as numeric values in the case of double.
Date Value Casting Process
| Casting Performed | Result |
| cast(date as date) | Same date value |
| cast(timestamp as date) | A local time zone is used to evaluate the Year/month/date values here and printed in the output. |
| cast(string as date) | A corresponding date value will be prompted due to this casting, but we need to ensure the string is of the format ‘YYYY-MM-DD’ Null will be returned when the string value fails to make a valid match. |
| cast(date as timestamp) | According to the current local timezone, a timestamp value will be created for this casting process |
| cast(date as string) | YYYY-MM-DD is formed for the year/month/date value, and the output will be of string format. |
2. Collection Data Types
There are four collection datatypes in the hive; they are also termed as complex data types.
- ARRAY
- MAP
- STRUCT
- UNIONTYPE
1. ARRAY: A sequence of elements of a common type that can be indexed, and the index value starts from zero.
Code:
array (‘anand’, ‘balaa’, ‘praveeen’);
2. MAP: These are elements that are declared and retrieved using key-value pairs.
Code:
‘firstvalue’ -> ‘balakumaran’ , ‘lastvalue’ -> ‘pradeesh’ is represented as map(‘firstvalue’, ‘balakumaran’, ‘last’, ‘PG’). Now ‘balakumaran ‘ can be retrived with map[‘first’].
3. STRUCT: As in C, the struct is a datatype that accumulates a set of fields that are labelled and can be of any other data type.
Code:
For a column D of type STRUCT {Y INT; Z INT} the Y field can be retrieved by the expression D.Y
4. UNIONTYPE: Union can hold any one of the specified data types.
Code:
CREATE TABLE test(col1 UNIONTYPE<INT, DOUBLE, ARRAY<VARCHAR>>)
Output:
Various Delimiters used in Complex Data Types are listed below,
| Delimiter | Code | Description |
| \n | \n | Record or row delimiter |
| ^A (Ctrl+A) | \001 | Field delimiter |
| ^B (Ctrl+B) | \002 | STRUCTS and ARRAYS |
| ^C (Ctrl+C) | \003 | MAP’s |
Complex Datatypes Example
Below are the examples of Complex Datatypes:
1. TABLE CREATION
Code:
create table store_complex_type (
emp_id int,
name string,
local_address STRUCT<street:string, city:string,country:string,zipcode:bigint>,
country_address MAP<STRING,STRING>,
job_history array<STRING>)
row format delimited fields terminated by ','
collection items terminated by ':'
map keys terminated by '_';
2. SAMPLE TABLE DATA
Code:
100 , Shan , 4th : CHN : IND : 600101 , CHENNAI_INDIA , SI : CSC
101 , Jai ,1th : THA : IND : 600096 , THANJAVUR_INDIA , HCL : TM
102 , Karthik , 5th : AP : IND : 600089 , RENIKUNDA_INDIA ,CTS : HCL
3. LOADING THE DATA
Code:
load data local inpath 'https://cdn.educba.com/home/cloudera/Desktop/Hive_New/complex_type.txt' overwrite into table store_complex_type;
4. VIEWING THE DATA
Code:
select emp_id, name, local_address.city, local_address.zipcode, country_address['CHENNAI'], job_history[0] from store_complex_type where emp_id='100';
Conclusion
Being a relational DB and yet a Sequel connects the HIVE offers all the key properties of usual SQL databases in a very sophisticated manner, making this one among the more efficient structured data processing units in Hadoop.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Hive Data Type. Here we discuss two types of hive data types with proper examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –