Updated March 2, 2023
Introduction to Bug Life Cycle
In the Software Development Life Cycle, Bug Life Cycle, better known as Defect Life Cycle, is the defect or error created in an application during its lifetime. During the entire life cycle of software development, bugs or defects mainly happens in the application tools that the organization uses. It varies based on organizations and software development models. The defects are mainly found during testing purposes, and it also depends on project to project basis and various policies and terminologies that an organization follows.
What is Bug Life Cycle?
Before talking about the Bug or Defect Life cycle, understand what a bug or defect is?
A bug or defect is a code that restricts the user from using the application, behaving more unusually than expected. The bug mainly occurs when a programmer makes a fault during the stage of either designing or building an application. The flaw that is found by a tester while testing those applications is known as a defect or bug.
The tester is responsible for finding the number of bugs in the application and resolving it as early as possible to ensure that no bugs are left to prevent the applications and also quality products are produced for the client.
This is how the tester resolves a defect or bug by going through a chain of processes, and the whole process is known as the bug life cycle.
This is how a tester handles a defect, and the different states of a bug are described below.
Explain the Life Cycle of Bug
Bug Life Cycle is generally a cycle of bugs that goes through different stages throughout their life cycle.
The lifecycle starts with the new defect found by a tester while testing the application, and it goes on until the tester finds a specific solution and closes the bug so that it does not reproduce again.
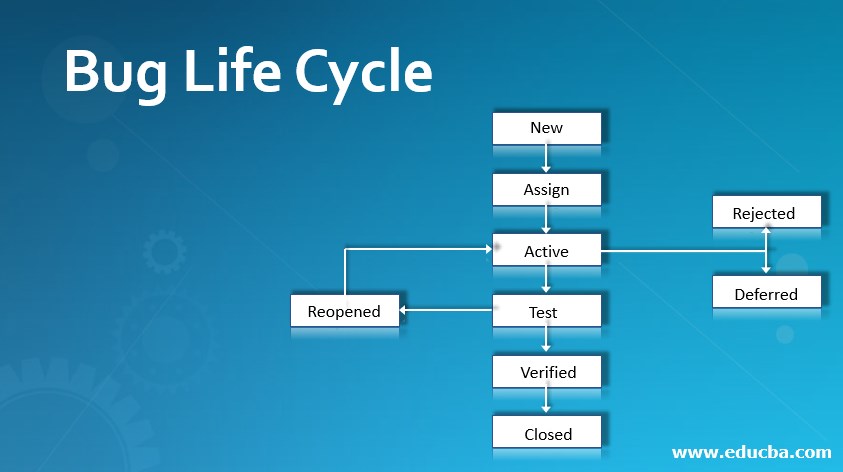
The above diagram shows the flowchart diagram of a bug that goes through the entire lifecycle. Now I will discuss the different stages. They are defined as below:
1. New
This is the first stage of a bug in its life cycle stages. Therefore, when a tester finds a bug while testing applications, it falls under the ‘New’ category, and proper validations and testing are done for the bug in the other stages of its life cycle.
2. Assigned
Here in this bug stage, the bug is identified, posted by the tester, approved by the testing lead, and finally assigned to the appropriate development team for working on it. Finally, the lead or manager of the testing team assigns the appropriate bug.
3. Active/Open
The developer in this phase starts analyzing the bug and finding a solution for fixing those bugs. Suppose the developer does not feel that this bug is appropriate for fixing. In that case, the developer may send the bug to one of the four other stages – Duplicate, Deferred, Rejected, or Not a Bug depending upon the particular reason.
4. Fixed
After the developer analyzes and makes necessary code changes to fix that bug, he marks the bug status as Fixed and passes it on to the testing team for further processing.
5. Pending Retest
After the developer fixes the bug, they assign that particular bug to the testing team for retesting from their end. The tester then works on the retesting part, and the flag is marked as ‘Pending Retest.’
6. Retest
At this stage, the tester starts working on retesting of changed code, and the developer verifies from the testing team whether the particular bug is accurately fixed or not as per the requirements given.
7. Verified
At this stage, the tester marks the fix status as ‘Verified’ when he feels that the bug has been fixed accurately and no more defects or issue is left after it is assigned to the developer team for retesting.
8. Closed
This is the last stage of the Bug Life Cycle. After the bug is fixed, the tester tests it again. The tester changes the bug’s status from ‘Verified’ to ‘Closed’ if they feel no more code is required and the bug has been resolved successfully. The closed stage means that the bug is free from any defects.
9. Rejected
The developer generally rejects the bug if they feel it is not accurate or genuine. The status of the bug then moves to ‘Rejected.’
10. Duplicate
If the same bug occurs again or the concept of the bug matches with the concept of another same bug, then the status is marked as ‘Duplicate‘ by the developer.
11. Deferred
The bug’s status is marked as deferred when it is of less priority and can be fixed in the next release. The deferred stage consists of several happenings of the bug-like low priority, less time to fixing the bug, or the bug that cannot do a major issue to the software product.
12. Not A Bug
The bug’s status is marked as ‘Not A Bug’ when there are little or no changes in the application product. In other words, the bug does not impact the program’s functionality, restricting the performance.
How does Bug Life Cycle Work?
The bug life cycle works the same way as discussed in the above stages. Firstly, the developer identifies the bug, then it moves to the tester for testing purpose, and based on the priority and importance of the bug that needs to be fixed, the tester marks the stages as per that and finally fixes the bug and develop an error-free software and delivers the same to the customer.
Conclusion
The bug life cycle plays an important role in the software development life cycle that depicts the harmful bugs, finds a solution for fixing them, and finally, provides bugless quality software to the client.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Bug Life Cycle. Here we discuss how Bug Life Cycle Works and explain the different stages in their entire life cycle. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –