Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to SQL REVOKE
REVOKE command in standard query language (SQL) is used to remove previously granted permissions or privileges to a user account on database objects. Therefore, we can consider REVOKE as a tool to restrict the ability of an already permitted role or user to perform select, insert, delete, alter statements, assign constraints like foreign keys, update a data record, etc., on the database objects.
REVOKE is a command antipodal to GRANT, which grants privileges on database objects to a user account or role. For example, in SQL, we can grant or revoke the following sets of privileges from a user.
You may consider it as a summary table for reference purposes.
| Privilege | Description |
| SELECT | The ability of the user account to perform SELECT statements and fetch records from the said database object. |
| DELETE | The ability of the user account to perform DELETE statements and delete or remove records from the said database object. |
| INSERT | The ability of the user account to perform INSERT statements and insert records in the said database object. |
| UPDATE | The ability of the user account to perform UPDATE statements and update records in the said database object. |
| ALTER | The ability of the user account to perform ALTER statements and add, delete or modify columns in the said database object. |
| TRUNCATE | The ability of the user account to perform TRUNCATE statements and delete the said database object. |
| TRIGGER | The ability of the user account to specify TRIGGER constraints like logon triggers to the said data objects. |
| REFERENCES | The ability of the user account to specify constraints like foreign keys that reference the said data objects. |
| ALL | The ability of the user account to perform all the above-mentioned statements except ALTER, i.e., SELECT, INSERT, DELETE, UPDATE, REFERENCES, etc. |
Having seen about the types of privileges we can grant a user account in SQL databases.
The syntax for REVOKE Command in SQL
The basic syntax for writing a REVOKE command in SQL is as follows:
REVOKE PRIVILEGES [, ...]
ON DATABASE_OBJECTS [, ...]
FROM ROLE
[ CASCADE | RESTRICT ]The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows:
- PRIVILEGES: This is the argument where we specify the privilege(s) that has to be removed for a user account. We may refer to the table mentioned above on privileges.
- DATABASE OBJECTS: Database objects can be anything like a specific table or all the tables in a schema.
- ROLE: Here, we specify the user account from which the privileges have to be removed. We can choose from an array of possibilities like PUBLIC, GROUP, or USER.
- CASCADE | RESTRICT: We can indicate if the revocation of the above privileges also revokes other privileges which derive from the former using the CASCADE keyword. Otherwise, we can restrict revocation to just the specified privilege.
It has been rightly said that learning is incomplete without kinesthetic learning.
Examples of SQL REVOKE
Given below are the examples of SQL REVOKE:
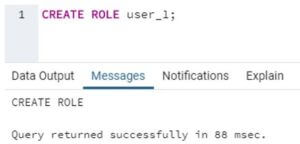
In order to illustrate the use of the REVOKE command, let us first create a user account and then grant it some privileges using the GRANT command. We will use the following SQL statement to create a new role called ‘user_1’. You may rename it to your preference.
Code:
CREATE ROLE user_1;Output:
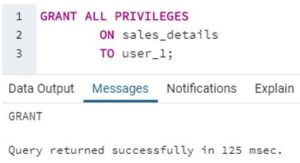
Now we have successfully created a new role, ‘user_1’ in the database. Now let us grant it some privileges using the GRANT command. We can use the following code_snippet to grant ALL privileges.
ALL keyword grants privileges such as SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE, TRUNCATE, REFERENCES, and TRIGGER.
Code:
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES
ON sales_details
TO user_1;Output:
Example #1
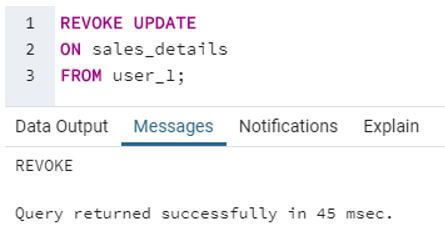
SQL query to illustrate revocation of UPDATE privilege from the user_1.
Code:
REVOKE UPDATE
ON sales_details
FROM user_1;Output:
In this example, we have successfully removed user_1’s ability to perform UPDATE statements on the sales_details table. So now, user_1 cannot update any record in the said table.
Example #2
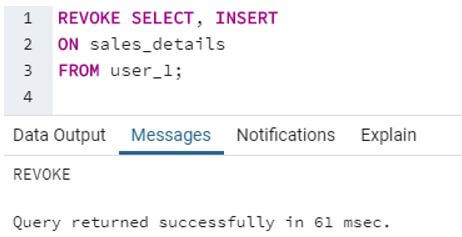
SQL query to illustrate revocation of SELECT and INSERT privileges from the user_1.
Code:
REVOKE SELECT, INSERT
ON sales_details
FROM user_1;Output:
Here, we have revoked user_1’s ability to perform SELECT and INSERT statements on the sales_details table. Ergo, user_1 will not be able to fetch records from the sales_details table. It will not also be able to insert new records in the table.
Example #3
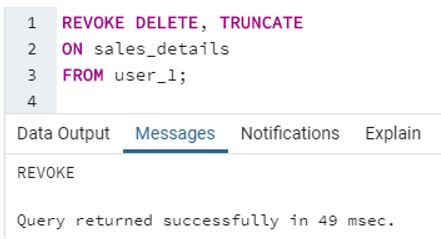
SQL query to illustrate revocation of DELETE and TRUNCATE privileges from the user_1.
Code:
REVOKE DELETE, TRUNCATE
ON sales_details
FROM user_1;Output:
In this example, we have revoked user_1’s ability to perform DELETE and TRUNCATE statements. That is, user_1 would not be able to delete one or more rows from the sales_details table.
Example #4
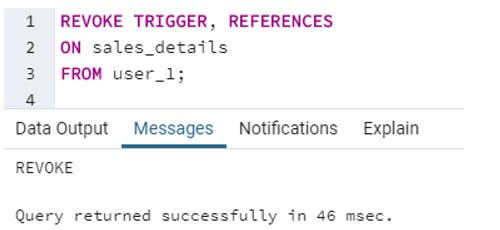
SQL query to illustrate revocation of TRIGGER and REFERENCES privileges from the user_1.
Code:
REVOKE TRIGGER, REFERENCES
ON sales_details
FROM user_1;Output:
Here we have removed user_1’s ability to perform TRIGGER and REFERENCE constraints on the sales_details table. Ergo, user_1 will not be able to make references such as foreign keys on the sales_details table. In addition, it will not be able to specify triggers.
Conclusion
The REVOKE command in SQL is used to remove already granted permissions or privileges to a user account on database objects like tables and schemas. It is useful for maintaining the integrity and security of the database.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL REVOKE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.