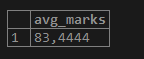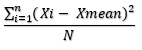Updated May 15, 2023
Introduction to MySQL Aggregate Function
Mainly in the data query language, we use these aggregated functions with SELECT statements. An aggregate function performs a calculation on multiple values and returns a single value like the sum of all values, maximum, and minimum among certain groups of values.
Example: If we have to calculate the total sales of a product in a month, then we have to use the ‘SUM’ function to add up all the sales values. Similarly, using the ‘MAX’ and ‘MIN’ functions, we can get the highest and lowest sale of that particular month. Aggregate functions ignore NULL values except for the ‘COUNT’ function. The count function returns the total number of observations. The HAVING clause is used along with GROU BY for filtering queries using aggregate values.
Top 11 MySQL Aggregate Function
Here are some MySQL aggregate functions which are explained below:
- AVG() Function
- COUNT() Function
- Sum() Function
- Max() Function
- MIN() Function
- DISTINCT() Function
- GROUP_CONCAT() Function
- VAR() Function
- STDEV() Function
- BIT_AND() Function
- BIT_OR() Function
| Section | Name | Marks |
| Sec-A | Stewart | 90 |
| Sec-B | Vince | 86 |
| Sec-C | John | 94 |
| Sec-A | Michelle | 78 |
| Sec-C | Robin | 60 |
| Sec-A | Sara | 86 |
| Sec-B | Peter | 92 |
| Sec-C | Ian | 89 |
| Sec-A | David | 76 |
1. AVG() Function
This is an average function. Its function calculates the average value for a set of values. It ignores null values in the calculation.
For getting average marks from all the students.
Query:
SELECT AVG(marks) AS avg_marks FROM student;Output:
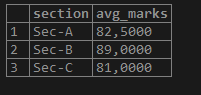
If we want the average mark of students for each section, we can use AVG() with the GROUP BY function.
Query:
SELECT section, AVG(marks) AS avg_marks FROM student GROUP BY section;Output:
2. COUNT() Function
The COUNT() function returns the value of the total number of observations/total number of values in a set of values.
If we perform this function in the above set of examples for getting the number of students,
Query:
SELECT COUNT(name) AS total_students FROM student;Output:
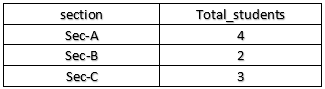
To get the student count in each section,
Query:
SELECT section, COUNT(name) AS total_students FROM student GROUP BY section;Output:
3. Sum() Function
The SUM() function returns the sum of all values in a set. To get the sum of marks of all the students,
Query:
SELECT SUM(marks) AS total_marks FROM student;Output:
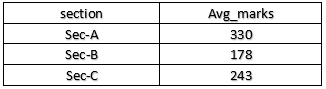
The sum of marks of all students section-wise,
Query:
SELECT section, SUM(marks) AS total_marks FROM student GROUP BY section;Output:
4. Max() Function
The max() function returns the maximum value in a set of values. To find the highest scorer in the exam from the student database, the below query can give us the desired output:
Query:
SELECT name, MAX(mark) AS highest_mark FROM student;Output:
In the same process, we can determine the maximum mark secured from each section.
Query:
SELECT section, name, MAX(mark) AS highest_mark FROM student GROUP BY section;5. MIN() Function
MIN() function returns the lowest value from the set of values. This doesn’t consider the null values. Lowest scorer among the students,
Query:
SELECT name, MIN(mark) AS lowest_mark FROM student;Output:
This also can be used with the GROUP BY function.
6. DISTINCT() Function
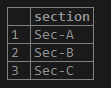
This function is used mainly with the COUNT function to get the number of unique values in the set of values. We can also use this DISTINCT function to get the unique values.
Query:
SELECT DISTINCT (section) FROM student;Output:
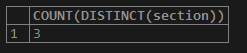
The query for using DISTINCT with COUNT() function.
Query:
SELECT COUNT(DISTINCT(section)) FROM student;Output:
7. GROUP_CONCAT() Function
This is used to concat all the string values of one attribute and merge them into one index.
Query:
SELECT GROUP_CONCAT(name SEPARATOR ';') FROM student;Output:
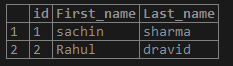
Like this GROUP_CONCAT(), we also use another function CONCAT(), which merges two sets of string values into a new column.
Example:
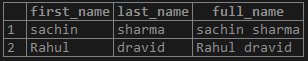
If, in this name database, we use the function CONCAT(),
Query:
SELECT first_name, last_name, CONCAT(first_name,’ ‘,last_name) as full_name FROM name;Output:
8. VAR() Function
This variance function returns the population standard variance of the specified column.
Variance is a measurement of the spread between the numbers in a dataset. It is calculated by how far each number is from the mean and, therefore, from each number of the set.
Variance:
Query:
SELECT VAR(mark) AS variance FROM student;Output:
9. STDEV() Function
Standard deviation is the measure of the amount of variation or dispersion of a set of values. This expresses how much the group members differ from the group’s mean value. This is calculated by taking the square root of the variance.
This function returns the population standard deviation of the specified column.
Query:
SELECT STDEV(mark) AS std_deviation FROM student;Output:
10. BIT_AND() Function
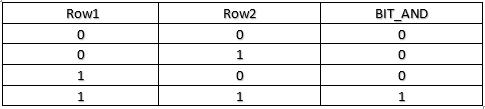
This function returns the bit-wise AND of specified rows. This returns the same data type, whichever is passed through argument.
If every row has 1 in the bit position, only it will return 1. Otherwise, it returns 0.
Query:
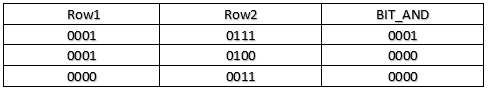
SELECT BIT_AND( CAST(row_value VariableBIT) ) FROM student.list('0001,0111,0100,0011');Output:
11. BIT_OR() Function
Returns the bit-wise OR of the specified expression for each group of rows.
Query:
SELECT BIT_OR( CAST(row_value AS VariableBIT) )
FROM student.list('0001,0111,0100,0011');The result of 0111 is determined as follows:
- A bitwise OR is performed between rows 1 (0001) and 2 (0111), resulting in 0111.
- Bitwise OR is performed between the result from the previous comparison (0111) and row 3 (0100), resulting in 0111.
- A bitwise OR is performed between the result from the previous comparison (0111) and row 4 (0011), resulting in 0111.
Conclusion
Those aggregated functions are essential from the analysis perspective and in the extraction process. Specifically, aggregated functions play significant roles when we give a condition in a query or while using a Windows function. Some functions like LIMIT, RANK, etc., and GROUP BY clause always comes with aggregated functions.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “MySQL Aggregate Function” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.