Updated May 10, 2023
Introduction to Cursor in MySQL
In this article, you will learn about MySQL cursor in stored procedures that control rows. Each row in the result set of a SELECT statement is processed separately by a cursor, which is responsible for iterating over the set of rows returned by the query. Thus, the cursor is a reserved SQL area from where information in a database can be retrieved. RDBMS stores a set of SQL statements as stored procedures with an assigned name for the purpose of reusing and sharing functions by multiple programs.
Features of MySQL Cursor
Below are the Features of MySQL Cursor:
- Read-Only: Using the cursor, you cannot modify any data in the primary table.
- Non-Scrollable: In MySQL, you can only fetch rows in the order they appear in the SELECT statement. It is not possible to fetch rows in reverse order, and you cannot skip or jump to a specific row in the result set.
- Asensitive: Cursors are of two kinds: asensitive and insensitive cursors. An asensitive cursor points to the actual data, whereas an insensitive cursor uses a provisional copy of the data. Thus, MySQL cursor is asensitive.
Types in MySQL
When you execute an SQL statement, the system generates a temporary workspace in the memory known as the cursor. A cursor holds a set of rows known as an Active set.
Cursors are of two types in MySQL:
1. Implicit Cursors
- Oracle automatically creates a cursor when executing SQL if no explicit cursor is specified.
- Users or programmers cannot control the information or programs in it
- Associated with INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE types of DML operation statements
- Attributes: SQL%FOUND, SQL%NOTFOUND, %ISOPEN, %ROWCOUNT
2. Explicit Cursors
- User-defined cursors help to gain more control over the context part.
- We define it in the declaration area of the SQL block.
- We create it on SELECT statements that return multiple records.
- Attributes: SQL%FOUND, SQL%NOTFOUND, %ISOPEN, %ROWCOUNT.
Syntax and steps for an explicit cursor:
CURSOR cursorname IS selectstatement;- Declaring the cursor to define a result set
- Opening the cursor to establish the result set
- Fetching the cursor to retrieve the data into local variables
- Closing the cursor when done
Cursor Actions in MYSQL
The Cursor in MySQL performs four actions, which are:
1. DECLARE: First, declare a cursor with a name associated with a SELECT statement.
DECLARE cursorname CURSOR FOR SELECTstatement;You should not declare the cursor before any variable declaration. otherwise, MYSQL may show an error.
2. OPEN: Next, open the cursor using the OPEN statement that initializes the result set and allocates memory for the cursor before the rows are fetched from the result set.
OPEN cursorname;3. FETCH: The FETCH statement is then used to access one row at a time and move to the next if available.
FETCH cursorname INTO variables_list;4. CLOSE: Disable the cursor that releases the memory allocated.
CLOSE cursorname;Note: Active voice: Each time you call the FETCH statement, it reads the next row in the result set. However, if there is no data found at the end of the set, you must use a NOT FOUND handler to handle this condition with the MySQL cursor.
Syntax:
DECLARE CONTINUE HANDLER FOR NOT FOUND SET variable_name = 1;Here, variable_name indicates the end of the result set. Let us also discuss the Cursor Attributes now. They are described below:
- %FOUND: If the recent operation fetches the record successfully, it returns ‘TRUE’; otherwise, ‘FALSE’.
- %NOTFOUND: It returns ‘FALSE’ if the record is retrieved but ‘TRUE’ if not.
- %ISOPEN: If the cursor is already opened, it results in ‘TRUE’; else, ‘FALSE’
- %ROWCOUNT: When DML operations are executed in a result set, it provides the count of rows.
Examples to Implement
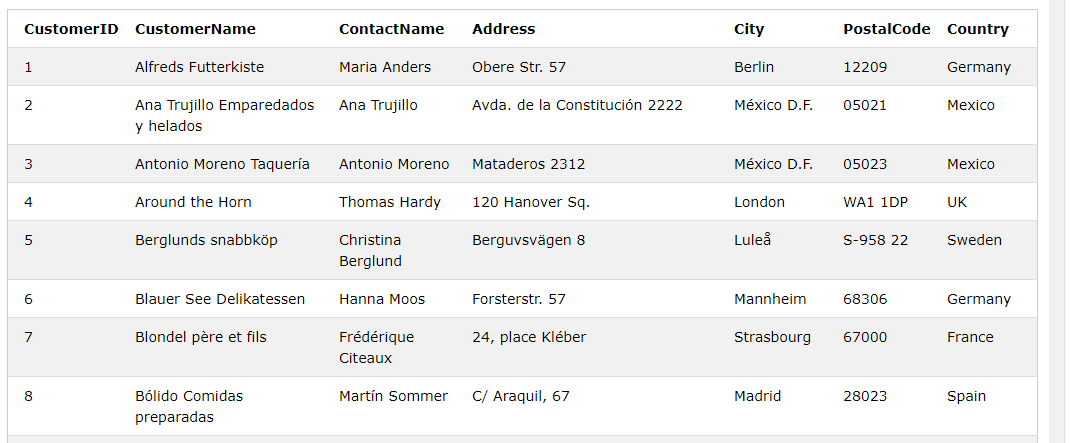
For example, let us take a table named ‘Customers’. Fetching its fields by query:
Code:
SELECT * FROM Customers;Output:
Following is an example to explain the concepts of cursors in MySQL:
Code:
DECLARE
CURSOR cust_record IS SELECT CustomerName FROM Customers;
cust_id Customers.CustomerID%TYPE;
cust_name Customers.CustomerName%TYPE;
cust_addr Customers.Address%TYPE;
BEGIN
OPEN cust_record;
LOOP
FETCH cust_record into cust_id, cust_name, cust_addr;
EXIT WHEN cust_record%notfound;
dbms_output.put_line(cust_id || ' ' || cust_name || ' ' || cust_addr);
END LOOP;
CLOSE cust_record;
END;
/Output:
*SQL Procedure Successfully Completed.
Importance of Cursors in MYSQL
Below are the important points of Cursor in MySQL:
- MySQL cursors are applicable in stored procedures, triggers, and stored functions. We can consider cursors as database objects that handle data or modify records in a database table on a row-by-row basis.
- Cursors are essential to return multiple rows when it processes rows individually for queries. At the same time, a trigger is a program code part that triggers automatically when particular events occur in a database table.
- Oracle generates a context or memory area that processes an SQL statement that holds all the information needed for handling the statement. Like, the number of rows processed in a result set, etc.
- In RDBMS, we perform various operations on a set of rows. For instance, we receive a result set when we execute the SELECT statement on a set of rows. But sometimes, the work may be with a row at a time, not with the entire result set needed by the application logic. MySQL uses the cursor as a significant function to accomplish this task in one way.
- A database cursor in computer science is a responsible control structure that allows traversal over the data in a database using the DECLARE, OPEN, FETCH, and CLOSE functions.
Conclusion
Just as on a computer screen, the cursor shows the current position; MYSQL Cursor is named so because it indicates the current position in the result set and returns a result set from a database. You cannot update it. It goes through the entire result set and shows everything found there. So, Cursor in MySQL is an important concept to be familiar with before moving on to their usages in ADO. But you can choose another alternative as a better choice if you want something more customized and able to skip rows in the result set. We can say that ‘Cursors Are Cool’, aren’t they? Writing this article supported me in studying and sharing some essential concepts on cursors that can further advance MySQL skills. I hope you like it; thanks for reading.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Cursor in MySQL” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.