Updated May 24, 2023
Introduction to Advantages of Hadoop
Hadoop is the big data processing paradigm that can effectively handle the challenges of big data (like Variety, Volume, and Velocity of Data) as it has the property of distributed storage, and parallel processing, due to which it has multiple advantages like open source, Scalable, Fault-Tolerant, Schema Independent, High Throughput and low latency, Data Locality, Performance, Share Nothing Architecture, Support Multiple Language, Cost-Effective, Abstractions, Compatibility and Support for Various file system.
What is Hadoop?
Hadoop is a big data processing paradigm that provides a reliable, scalable place for data storage and processing. Doug Cutting created Hadoop and is considered the “Father of Hadoop.” Hadoop was the name of his son’s toy elephant. Hadoop had its roots in Nutch Search Engine Project. Hadoop is a processing framework that radically changed how we process and store data.
Compared to traditional processing tools like RDBMS, Hadoop proved that we could efficiently combat the challenges of Big data, like –
Variety of Data: Hadoop can store and process structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data formats.
The Volume of Data: Hadoop is specially designed to handle the huge volume of data in the range of petabytes.
The Velocity of Data: Hadoop can process petabytes of data with high velocity compared to other processing tools like RDBMS, i.e., processing time in Hadoop is very less.
Salient Features of Hadoop
- Hadoop is open-source in nature.
- It works on a cluster of machines. The size of the cluster depends on requirements.
- It can run on standard commodity hardware.
Advantages of Hadoop
In this section, the Advantages of Hadoop are discussed. Now let us take a look at them one by one:
1. Open Source
Hadoop is open-source, i.e., its source code is freely available. We can modify source code as per our business requirements. Even proprietary versions of Hadoop, like Cloudera and Horton Works, are also available.
2. Scalable
Hadoop works on a cluster of Machines. Hadoop is highly scalable. We can increase the size of our cluster by adding new nodes as per requirement without downtime. Adding new machines to the cluster is called Horizontal Scaling, whereas increasing components, such as doubling the hard disk and RAM, is called Vertical Scaling.
3. Fault-Tolerant
Fault Tolerance is the salient feature of Hadoop. By default, every block in HDFS has a Replication factor of 3. For every data block, HDFS creates two more copies and stores them in a different location in the cluster. If any block goes missing due to machine failure, we still have two more copies of the same block, and those are used. In this way, Fault Tolerance is achieved in Hadoop.
4. Schema Independent
Hadoop can work on different types of data. It is flexible enough to store various data formats and can work on data with schema (structured) and schema-less (unstructured) data.
5. High Throughput and Low Latency
Throughput means the amount of work done per unit of time, and Low latency means processing the data with no delay or less delay. As Hadoop is driven by the principle of distributed storage and parallel processing, the processing is done simultaneously on each block of data and independently. Also, the code is moved to data in the cluster instead of moving data. These two contribute to High Throughput and Low Latency.
6. Data Locality
Hadoop works on “Moving the code, not data.” In Hadoop, Data remains Stationary, and for data processing, code is moved to data in the form of tasks; this is known as Data Locality. As we deal with data in the range of petabytes, it becomes difficult and expensive to move the data across Network; Data locality ensures that Data movement in the cluster is minimum.
7. Performance
In Legacy systems like RDBMS, data processing typically occurs sequentially. However, in Hadoop, processing starts simultaneously on all the data blocks, enabling parallel processing. Due to Parallel processing techniques, the Performance of Hadoop is much higher than Legacy systems like RDBMS. In 2008, Hadoop even defeated the Fastest Supercomputer present at that time.
8. Share Nothing Architecture
Every node in the Hadoop cluster is independent of each other. They don’t share resources or storage; this architecture is known as Share Nothing Architecture (SN). If a node in the cluster fails, it won’t bring down the whole cluster as each node acts independently, thus eliminating a Single point of failure.
9. Support for Multiple Languages
Hadoop extends support for other languages like Python, Ruby, Perl, and Groovy, despite its primary development being in Java.
10. Cost-Effective
Hadoop is very Economical. We can build a Hadoop Cluster using normal commodity Hardware, thereby reducing hardware costs. According to the Cloud era, they suggest that Hadoop’s Data Management costs, which encompass hardware, software, and other expenses, are minimal compared to Traditional ETL systems.
11. Abstraction
Hadoop provides Abstraction at various levels. It makes the job easier for developers. The system divides a large file into blocks of equal size and distributes them across multiple locations within a cluster. While creating the map-reduce task, we need to worry about the area of blocks. We give a complete file as input, and the Hadoop framework processes various data blocks at different locations. Hive is a part of the Hadoop Ecosystem, an abstraction on top of Hadoop. The developers introduced Hive to resolve this issue because SQL developers across the globe couldn’t take advantage of MapReduce since MapReduce tasks are written in Java. We can write SQL-like queries on Hive, which triggers Map to reduce jobs. So, due to Hive, the SQL community can also work on Map Reduce Tasks.
12. Compatibility
In Hadoop, HDFS is the storage layer, and Map Reduce is the processing Engine. But, there is no rigid rule that Map Reduce should be the default Processing Engine. New Processing Frameworks like Apache Spark and Apache Flink use HDFS as a storage system. Even in Hive, we can change our Execution Engine to Apache Tez or Apache Spark per our Requirements. Apache HBase, which is NoSQL Columnar Database, uses HDFS for the Storage layer.
13. Support for Various File Systems
Hadoop is very flexible. It can ingest various data formats like images, videos, files, etc. It can process Structured and Unstructured data as well. Hadoop supports multiple file systems like JSON, XML, Avro, Parquet, etc.
Working of Hadoop
Below are the points that show how Hadoop works:
1. Distributed Storage and Parallel Processing
This is the driving principle of all the frameworks of the Hadoop Ecosystem, including Apache Spark. To understand the working of Hadoop and Spark, first, we should understand “Distributed Storage and Parallel Processing.”
2. Distributed Storage
Hadoop doesn’t store data in a single machine. Instead, it breaks that huge data into blocks of equal size, 256MB by default, and stores those blocks in different cluster nodes (worker nodes). It keeps the metadata of those blocks in the master node. Hadoop distributed File System (HDFS) is the name for storing the file in distributed locations in a cluster.
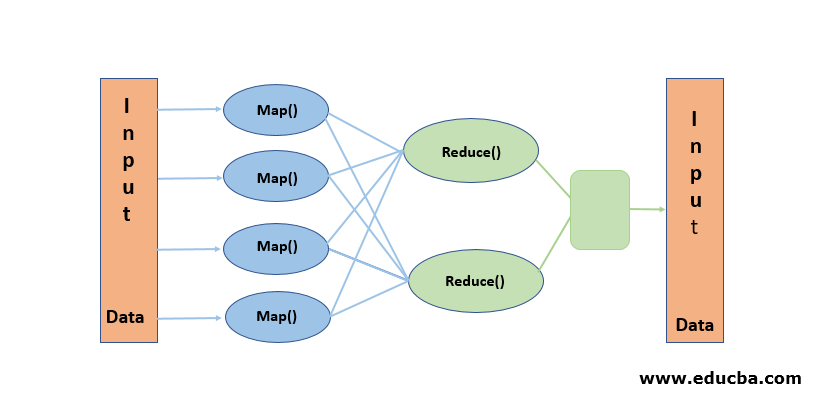
3. Parallel Processing
This Processing paradigm performs simultaneous processing on the data blocks stored in HDFS. Parallel Processing works on “Moving the code, not data.” HDFS maintains stationary data while moving the code to the data for processing. Simply put, if we break a file into 100 blocks, we create 100 copies of the job that travel across the cluster to the respective block locations. This allows simultaneous processing of the 100 blocks during the Map Phase. The Reduce Phase considers the output data from all the blocks and reduces it to generate the final output, making it the “Heart of Hadoop.”
Conclusion
In this Data age, Hadoop paved the way for a different approach to Big data’s challenges. When we say Hadoop, we don’t mean Hadoop alone; it includes Hadoop Ecosystem tools like Apache Hive, which provides SQL-like operations on top of Hadoop, Apache Pig, Apache HBase for Columnar storage database, Apache Spark for in-memory processing, and many more. Although Hadoop has disadvantages, it is highly adaptable and constantly evolving with each release.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Advantages of Hadoop. Here we discuss what is Hadoop, working, and the top advantages of Hadoop. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –