What is the Accounting Cycle?
An accounting cycle is a step-by-step process that businesses use to identify, analyze, and sort all payments made & received in an accounting period and finally document them in financial statements.
For example, Blooms & Co. company generates revenue of $5,000 at the end of the fiscal year. The company’s accounting cycle will include recording all the transactions, journal entries, general ledger, trial balances, reviewing & fixing errors, creating financial statements, and closing.
The business’s accounts must be organized as it contributes to maintaining overall efficiency and the bookkeeper primarily does it. Depending on the need for reporting, accounting cycle times will change. Though some businesses may give a greater emphasis on a quarterly or annual basis, most try to examine their performance on a monthly basis.
Key Highlights
- The accounting cycle is a financial process of recording and analyzing all the financial transactions made by a company during an accounting period.
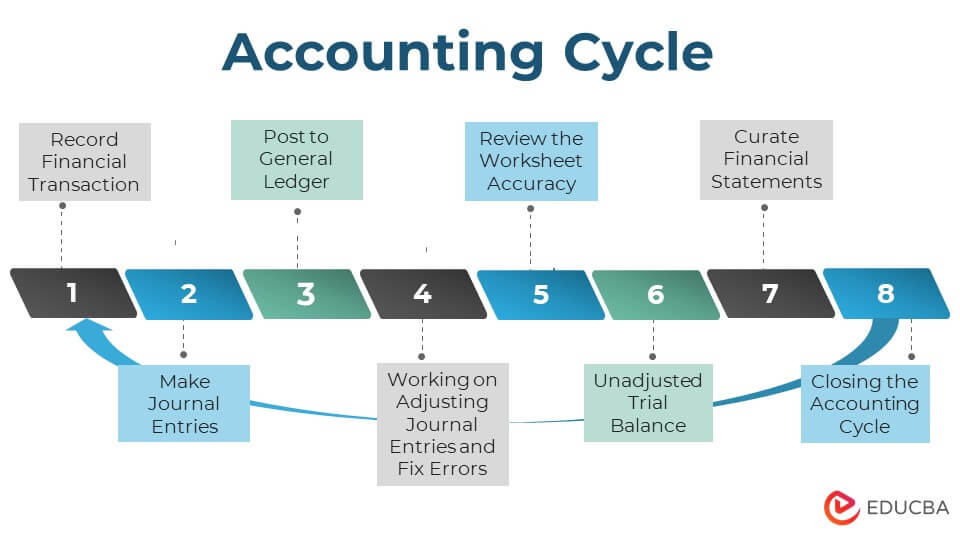
- The eight steps of the accounting cycle are as follows: recording the financial transactions, making journal entries, posting to the general ledger, unadjusted trial balance, reviewing the accuracy of the worksheet, working on adjusting entries, curating financial statements, and closing the accounting cycle.
- The closing of this cycle gives an insight into the financial health of a business and a scope for improvement.
- It helps in cost controlling, price determination, fixing the standards, and showing profit and non-profit activities.
Explanation
- The accounting cycle forms an integral base for the company’s financial statements.
- It is advised to follow some steps and rules of the accounting methods to maintain accuracy in the process.
- Adopting the latest computerized accounting methods makes it easier for companies to record and maintain uniformity in the accounting process.
- The bookkeeper actively maintains the accounting process in any company and accurately reflects the transactions and business of the company in its financial statements.
- The accounting cycle includes all types of entries like journal entries, T accounts, credits, and debit; it also makes sure to follow a particular method and adjust entries for any financial transaction.
Steps of the Accounting Cycle
There’s a specific set of steps that every business must follow in an accounting period. Below is a complete breakdown of the 8 steps of the accounting cycle:
Step #1 – Recording the Financial Transaction
- This is the first and important step where a bookkeeper records and analyzes all the financial transactions.
- In this stage, businesses go through every transaction that has affected their finances.
- Transactions can vary, and they might have various kinds like debt payoff, asset purchase, a loan taken, acquisition of any company, etc.
- Thus, it is important to identify the type of transaction to be recorded accurately in the accounting books.
Step #2 – Making Journal Entries
- The next stage is to document all financial transactions’ specifics as journal entries in either a physical book or an accounting application.
- The entries should be made in systematic and chronological order.
- It is important to ensure that all debits and credits eventually match, commonly known as double-entry accounting.
- In this, every transaction has two or more sub-ledger accounts that help manage and develop a balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow.
Step #3 – Posting to General Ledger
- Now is the time to record these journal entries into the ledger, with a summary of all the recorded transactions.
- In short, the General ledger provides a step-by-step breakdown of all the recorded accounting activities.
- A general ledger helps analyze the company’s financial positions and keep track of the liquidity through the cash account.
Step #4 – Unadjusted Trial Balance
- After the accounting period has ended, and all transactions have been discovered, documented, and posted, we determine the unadjusted trial balance.
- You may get a sense of each account’s unadjusted balance from the trial balance.
- Moreover, businesses rely on unadjusted trial balances to ensure that they maintain total debits and entire credit balances in their financial records.
Step #5 – Reviewing the Accuracy of the Worksheet
- The fifth step of the accounting cycle entails reviewing your worksheets to find entries that require correction.
- Recording every transaction as a credit or debit ensures that both the total and debit balances are equal.
- In accrual accounting, this step helps match revenue and expenses, apart from recognizing errors.
Step #6 – Working on Adjusting Journal Entries and Fix Errors
- In this step, we have to rectify any errors and irregularities discovered during the worksheet assessment by adjusting journal entries after the accounting period has ended.
- Before generating the final financial statements, the last stage requires double-checking everything using a newly adjusted trial balance.
Step #7 – Curate Financial Statements
- Once you have corrected all the account balances and made the necessary adjustments, it is time to create the financial statements.
- Such statements provide an overview of a company’s operations and performance over a certain time period, such as a monthly or quarterly interval.
- The income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement are businesses’ three major financial statements.
Step #8 – Closing the Accounting Cycle
- This is the last step, where the books of accounts are closed at a specified closing date.
- At the end of the accounting period, closing entries are made by settling expenses, revenues, and temporary accounts.
- After you close the accounting book, the financial statements generated give a comprehensive performance analysis for that particular time frame.
Example of Accounting Cycle with Excel Examples
Shakes & Bakes is a company established in Arizona. The company is significantly big in size and operations; thus, they have an accounting cycle. Let’s create and analyze the step-by-step process of the accounting cycle for the company.
Solution:
Below is the step-by-step process of the accounting cycle for Shakes & Bakes:
Step #1 – Recording the Financial Transaction
Shakes & Bakes is a company based in Arizona that receives a profit of $36,840 from the products it sells.
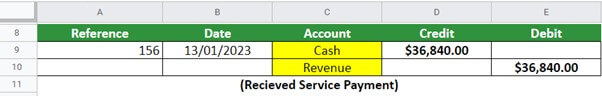
Step #2 – Making Journal Entries
As noted above, the company has made a profit of $36,840 through its services. This means that there will be an increase in both cash and revenue accounts. This implies the cash will be debited for $36,840 and revenue credited for $36,840.
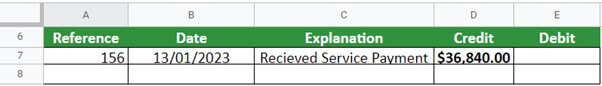
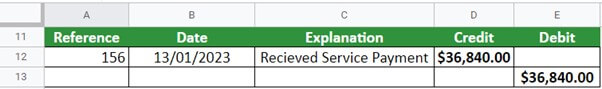
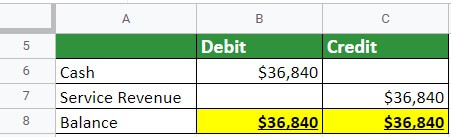
Step #3 – Posting to General Ledger
It’s time for the posting, wherein journal entries will be transferred to the general ledger. So, here’s how the previous entry would look in the ledger:
Cash:
Revenue:
Step #4 – Unadjusted Trial Balance
By assuming the end of the accounting period on the 31st of August, this is how the trial balance for Shakes & Bakes would look:
Step #5 – Reviewing the Accuracy of the Worksheet
If the total profit of Shakes & Bakes is $36,840, then the bookkeeper has to keep a record that no error is recorded in the account book.
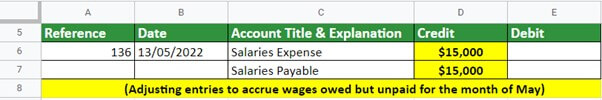
Step #6 – Working on Adjusting Entries
Let’s look at the adjusting wages of Shakes & Bakes for the month of May.
Step #7 – Curating Financial Statements
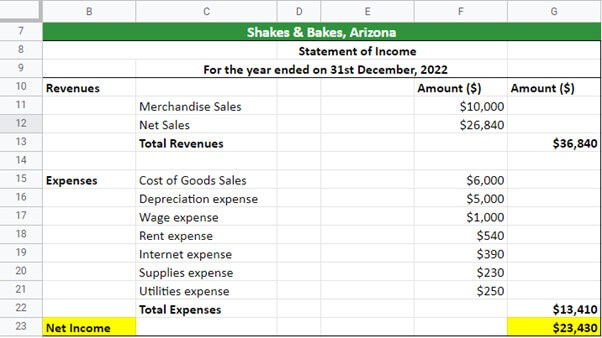
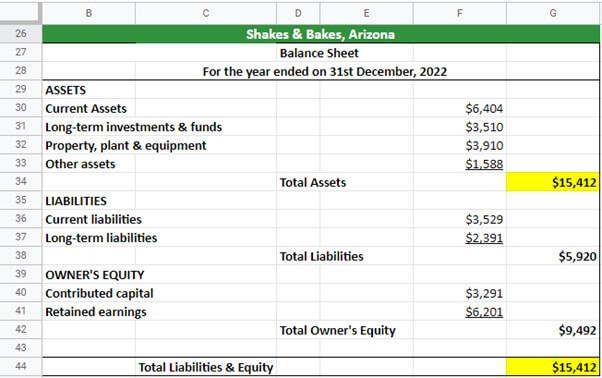
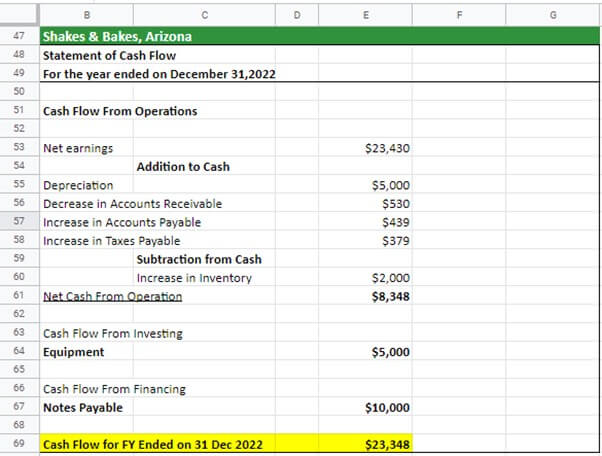
It’s time to look at all the financial statements of Shakes & Bakes, i.e., the income sheet, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
#1 Income Statement
#2 Balance Sheet
#3 Cash Flow Statement
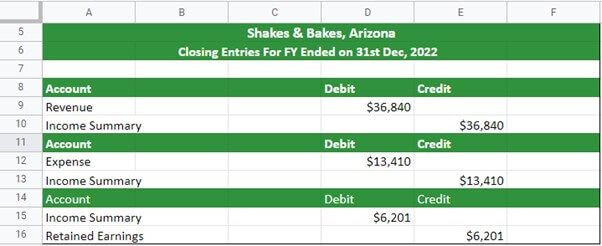
Step #8 – Closing the Accounting Cycle
Let’s see how the closing entries of Shakes & Bakes would look:
Purpose of Accounting Cycle
- The accounting cycle’s systematic approach helps record every important transaction in the accounting book.
- It helps the accounting team analyze all the financial statements with more accuracy and conformity. Also, the prepared accounting book is a base for creating financial statements.
- Businesses always have a check on the accounting cycle before making any important financial decisions such as cash, assets, loans, and debts.
- From a regulatory perspective, it is required for every business to file income tax returns.
- Moreover, this cycle helps businesses close their books for a particular accounting period.
What is the Cost Accounting Cycle?
The business performs the cost accounting cycle, which involves recording data, classifying data, determining the overall cost, determining the cost of the product, determining the sales price, controlling the cost, and making decisions.
The cost accounting cycle includes the following steps:
- Recording the cost data
- Classification of the cost data
- Determining the total cost
- Determining the product cost
- Determining the selling price of the product
- Cost control and
- The decision making
What is the Revenue Accounting Cycle?
The revenue accounting cycle plays a crucial role in business activities as it involves maintaining records of transactions from the sale of goods or services to the receipt of payment. It serves as a means to monitor and analyze the cash flow within a business.To understand it in a much better way, go through the below steps of the revenue accounting cycle:
- The customer has placed the sales order
- The sales order processing starts by making the products or goods ready for delivery
- The billing statements or the invoices are being prepared
- The delivery of the interest is being made to the customer
- The customer is collecting the delivery
- The accounts receivable is being recorded
- The customer pays the payment
Importance of Accounting cycle
#1 Cost controlling: This is the most efficient way for the business to foresee labor and inventory costs. With such references, the business can work on various techniques to control the high prices and achieve maximum profit.
#2 Price determination: This cost accounting technique helps the business to understand the fixed and variable costs of products. They have to ensure that the business economy is not suffering or that we are not paying extra for any product or service.
#3 Showing the profit or non-profit activities: This information helps the business to avoid non-profit activities and expand the profitable ones.
#3 Fixing the standards: With this technique, the business can measure the efficiency of the products and, therefore, can standardize their budget or estimates.
Difference between the Accounting Cycle and Budget Cycle
|
Accounting Cycle |
Budget Cycle |
| The accounting cycle records the business transaction in the accounting books. | The Budget cycle maintains the cost of the inventory and other related expenses and compares if the incurred costs align with the proposed budget. |
| The purpose of the accounting cycle is to maintain the books of accounts for the accurate recording of transactions. | The budget cycle’s purpose depends on the financial statements analysis. |
| The accounting cycle helps the business to showcase important information about the business finances to external people such as investors and stakeholders. | The Budget cycle is used for the internal management of the business. |
| The Accounting cycle focuses on the events during the specified timeframe and ensures that the financial transactions of that period are being recorded accurately. | The budget cycle associates the future performance of your business and helps in planning the future transactions of the business. |
Final Thoughts
Accounting Cycle is very important for every business looking for a seamless accounting process. This step-by-step process must be followed with utmost accuracy to avoid any errors. Moreover, it is the best way to record and analyze a business’s total profit during a particular period.
Using the accounting cycle accurately is very important. For instance, the Americanas’ shares saw a decline of 50% when the new management found accounting inconsistencies in the records.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q.1 Which step of the accounting cycle involves checking?
Answer: The fourth stage of the accounting cycle involves calculating a trial balance at the end of the accounting period. The company can know the unadjusted amounts in each account from a trial balance. After testing and analysis in the fourth stage, the unadjusted trial balance is taken to the fifth step.
Q.2 What are the 5 accounting cycles?
Answer: Following are the 5 accounting cycles. (1) Financial transactions, (2) Journal entries, (3) Posting to the Ledger, (4) Trial Balance Period, and (5) Reporting Period with Financial Reporting and Auditing.
Q.3 How has accounting changed with technology?
Answer: Nowadays, companies use machines and technologically advanced tools for accounting purposes. Technologically driven machines and equipment have improved work accuracy and even reduced manual labor.
Q.4 What is the operating cycle in accounting?
Answer: An operating cycle refers to the time a business needs to purchase items, sell them, and get paid for those sales. In other words, the time it takes for a business to convert its inventories into cash.
Q.5 Do all companies have an accounting cycle?
Answer: No, not necessarily all companies have an accounting cycle. Small businesses with low turnover do not abide by this kind of cycle for every fiscal year. Moreover, it will become very difficult to track transactions made or received by the company if one misses an accounting cycle.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the Accounting Cycle. Here we also discuss the introduction, the steps of the accounting cycle, and the difference between the accounting and budget cycles. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –