Updated October 18, 2023
Table of Contents
- Difference Between Debit vs Credit
- Debits and Credits in Accounting
- Debit and Credit Example
- Infographics
Difference Between Debit and Credit
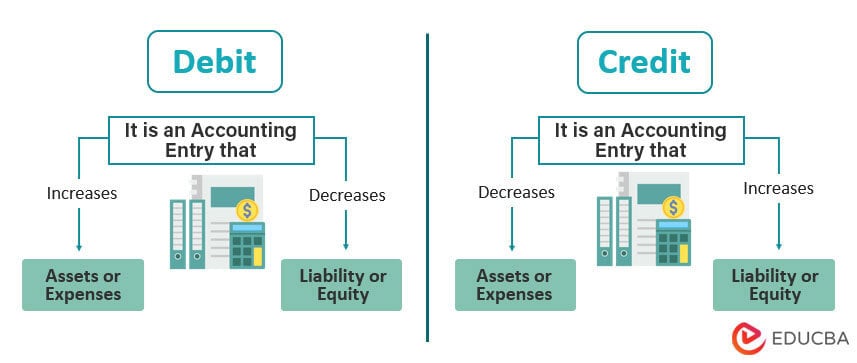
In debit vs credit, debit (dr) refers to an accounting entry that reflects an increase in assets or a decrease in liabilities or equity. In contrast, credit (cr) represents an entry that reflects a decrease in assets or an increase in liabilities or equity.
Debits and Credits in Accounting
Debits and credits form the foundation of the accounting system. These entries make up the data that companies use to prepare financial statements, such as the balance sheet and income statement. Every accounting transaction involves at least one debit and one credit.
What is a Debit?
In simple terms, a debit indicates incoming money/value. Basically, a debit is when an account (your own account or someone else’s account) receives value. It is a debit entry only if your asset account receives value. Therefore, while analyzing your own accounts, you must only consider asset accounts like cash, bank, inventory, and property.
What is a Credit?
In simple terms, a credit indicates outgoing money/value. Basically, a credit is when value is taken out of an account (your own account or someone else’s account). It is a credit entry only if your asset account loses value. Thus, while analyzing your own accounts, you must only consider your asset accounts.
Let’s take an example to understand these terms in a better way.
Imagine you are out shopping with a friend. You both are carrying around shopping carts and adding items to them. Adding items to the cart signifies debit, and removing items from the cart signifies credit.
Let us understand how by answering these 4 questions below:
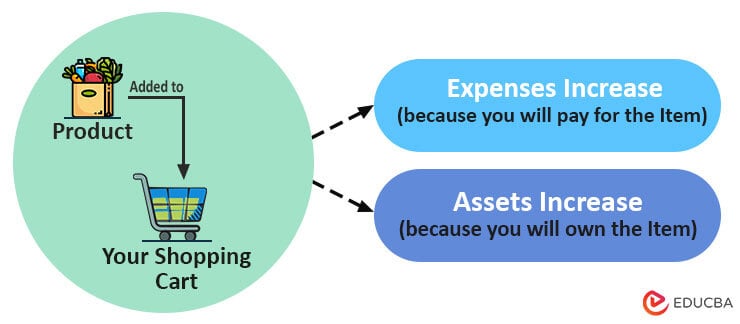
1. How does debit indicate an increase in assets?
Now, for each item that you add to the cart, you will have to pay money to buy the item, but you also get to take the item home. Here, we can see that when you spend money on the item, your expenses will increase. However, when you take the item home, your assets (things you own) will also increase. This is how assets and expenses increase in Debit.
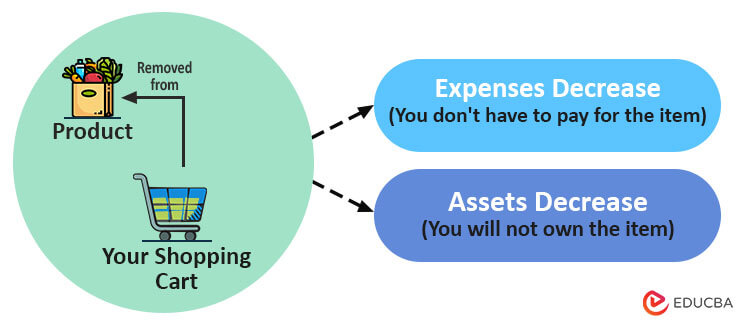
2. How does credit indicate a decrease in assets?
Now, let’s say you are at the checkout counter with a shopping cart full of items. Before paying, you decide to remove a few items from the cart. Now, for every item you remove from the cart, you are saving money. But at the same time, you own one less item than you did before. So, this is how assets and expenses decrease in Credit.
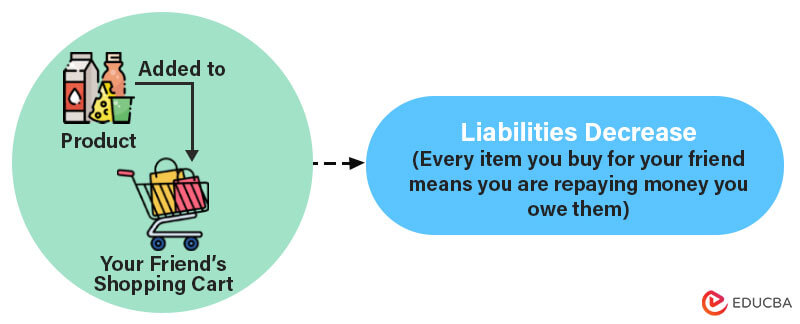
3. How does debit show a decrease in Liabilities?
Let’s go back to the start. Imagine you borrowed some money from that friend a few days back. Now, you decide that you will repay the money you owe (borrowed money) by buying some items for them. So, you start putting items in the friend’s shopping cart. Here, for each item that you put in their cart, i.e., each item that you buy for them, the amount of money you owe them decreases. This is how liabilities decrease in debit.
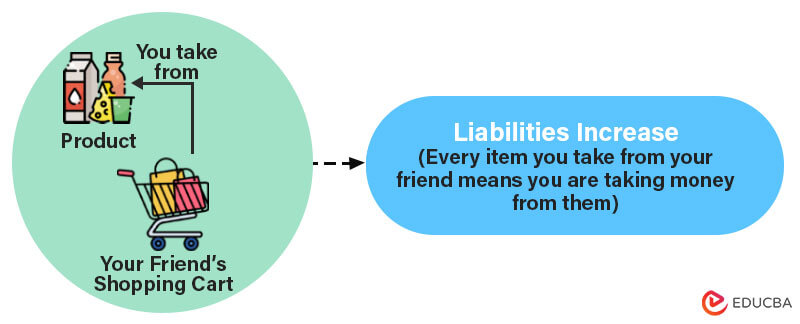
4. How does credit show an increase in Liabilities?
Imagine you and your friend have finished shopping and paid for everything in your respective shopping carts. However, in the parking lot, you realize that you forgot to buy something important. Your friend kindly offers to let you take that item from their cart. When you take an item from your friend’s cart, it’s like borrowing something they already paid for. As a result, you now owe your friend money, which increases your liabilities. This is how liabilities increase in credit.
Debit and Credit Example
Let’s have a look at some examples to understand the concept of debit vs credit in a more simpler way:
For example, Timms & Co is a company that receives inventory worth $1,000 from the supplier on 11 September 2023, which increases the company’s assets. So, the inventory account is debited by $1,000, reflecting the purchase of inventory.
Now, after a month, on 11 October 2023, the company has to pay the supplier for the inventory purchases. So, when Timms & Co. pays the supplier in cash, the cash account is credited with $1,000, reducing the company’s cash balance. This credit entry represents the outflow of cash from the company due to the purchase.
The double-entry journal entry will look like this:
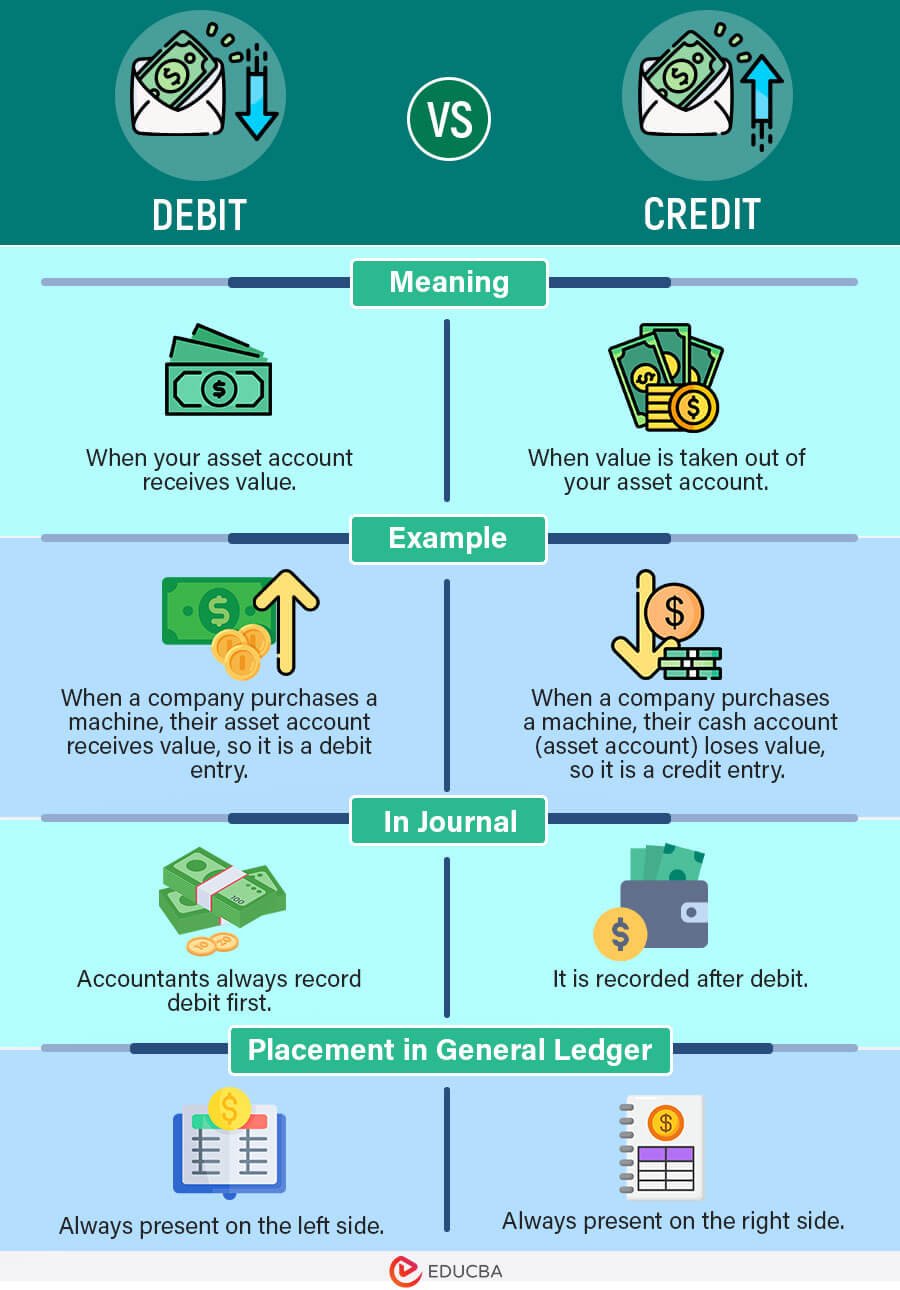
Debit vs. Credit Infographics
Below image shows the top difference between Debit and Credit.
Final Thoughts
Debits and Credits are fundamental to the dual entry system, where one account cannot exist without another. They are interdependent, meaning that debiting one account results from crediting another account and vice versa. Moreover, recording each transaction separately can be difficult in an accounting book, so businesses use the double-entry method. This method ensures that every transaction has an equal impact on both sides of the accounting equation.
Recommended Articles
This guide incorporates the concept of debit vs credit in accounting. It explains the differences with the help of an infographic and examples. You may also look at some similar articles to learn more –