Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to YAML and JSON
JSON is abbreviated as JavaScript Object Notation which is easy to understand and self-describing. It is available in standard text format and used for saving and transporting the data. JSON helps to transmit data in web applications where the data is sent from server to client and can be viewed on the web page. YAML is used for scripting configuration files and can be incorporated with added programming languages. It is popular for data serialization language, human-readable language, and adaptive. The difference and comparison of JSON and YAML are described in the article.
Head to Head Comparison Between YAML vs JSON (Infographics)
Below are the top 8 differences between YAML vs JSON:
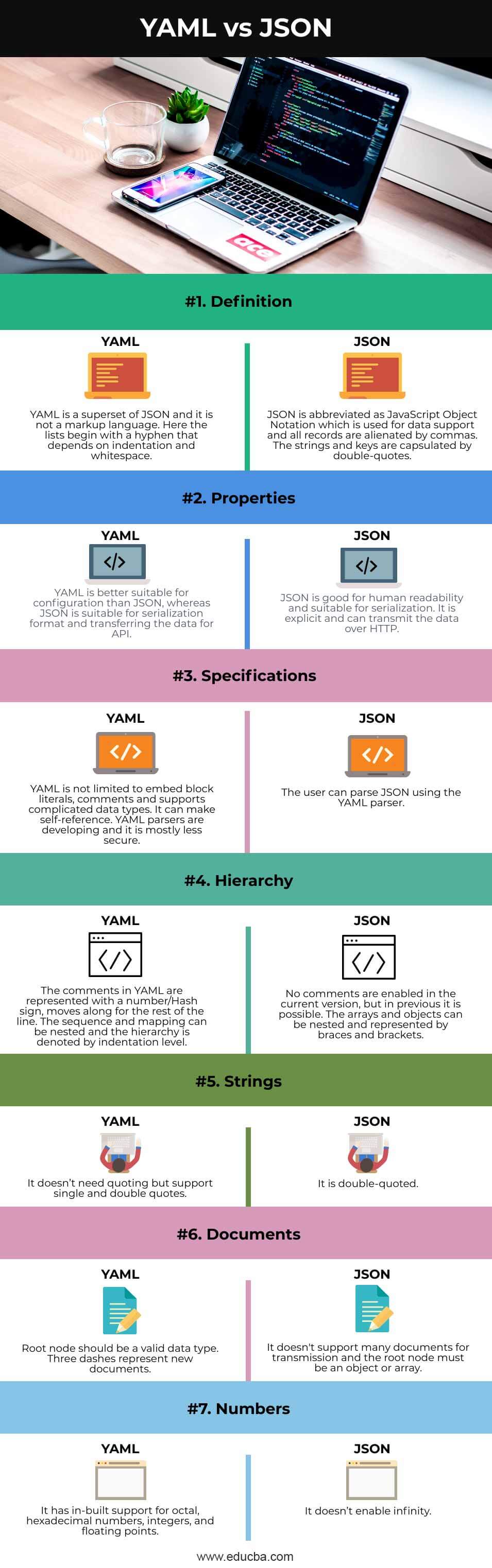
Comparison Table of YAML and JSON
| Features | YAML | JSON |
| Definition | YAML is a superset of JSON and it is not a markup language. Here the lists begin with a hyphen that depends on indentation and whitespace. | JSON is abbreviated as JavaScript Object Notation which is used for data support and all records are alienated by commas. The strings and keys are capsulated by double quotes. |
| Properties | YAML is better suitable for configuration than JSON, whereas JSON is suitable for serialization format and transferring the data for API. | JSON is good for human readability and suitable for serialization. It is explicit and can transmit the data over HTTP. |
| Specifications | YAML is not limited to embed block literals, comments and supports complicated data types. It can make self-reference. YAML parsers are developing and it is mostly less secure. | The user can parse JSON using the YAML parser. |
| Hierarchy | The comments in YAML are represented with a number/Hash sign, moves along for the rest of the line. The sequence and mapping can be nested and the hierarchy is denoted by indentation level. | No comments are enabled in the current version, but in previous it is possible. The arrays and objects can be nested and represented by braces and brackets |
| Strings | It doesn’t need quoting but support single and double quotes | It is double-quoted. |
| Documents | Root node should be a valid data type. Three dashes represent new documents | It doesn’t support many documents for transmission and the root node must be an object or array |
| Numbers | It has in-built support for octal, hexadecimal numbers, integers, and floating points. | It doesn’t enable infinity |
Definition YAML is a superset of JSON and it is not a markup language. Here the lists begin with a hyphen that depends on indentation and whitespace. JSON is abbreviated as JavaScript Object Notation which is used for data support and all records are alienated by commas. The strings and keys are capsulated by double quotes.
Properties YAML is better suitable for configuration than JSON, whereas JSON is suitable for serialization format and transferring the data for API. JSON is good for human readability and suitable for serialization. It is explicit and can transmit the data over HTTP.
Specifications YAML is not limited to embed block literals, comments and supports complicated data types. It can make self-reference. YAML parsers are developing and it is mostly less secure. The user can parse JSON using the YAML parser.
Hierarchy The comments in YAML are represented with a number/Hash sign, moves along for the rest of the line. The sequence and mapping can be nested and the hierarchy is denoted by indentation level. No comments are enabled in the current version, but in previous it is possible. The arrays and objects can be nested and represented by braces and brackets
Strings It doesn’t need quoting but support single and double quotes It is double-quoted.
documents Root node should be a valid data type. Three dashes represent new documents It doesn’t support many documents for transmission and the root node must be an object or array
Numbers It has in-built support for octal, hexadecimal numbers, integers, and floating points. It doesn’t enable infinity
The key difference between YAML vs JSON
- Promptness:
JSON is implementation-oriented and used widely as it has maximum native support due it is speed. But the YAML is the same as JSON but tends to pull more truckload. But when compared to JSON and YAML in terms of speed, JSON acts quicker. It is known that the YAML file is a smaller JSON because of its, and ” characters and it is possible to make YAML highly optimized and rapid in exceptional scenarios.
- Memory:
In terms of memory, both JSON and YAML occupy a similar data structure but the efficiency of the YAML parser is effective than the JSON parser and still, the argument goes on to know which memory efficient is.
- Accessibility:
Python programmers prefer YAML, whereas JavaScript programmers choose JSON. The syntax of JSON is easy to memorize and its meaning to every syntax is easily understandable. But in YAML doesn’t give a clear understanding to humans as its few edge cases and subtleties are quite complicated and extreme. Because some parsers are deployed in a certain specification, makes it harder to understand the real meaning of the provided expression in the given comment. There is no comments section JSON, which makes it a bit harder, but in practice, it can be avoided.
- Compatibility:
It is unimaginable to build a modern language without using the JSON library and its parser deploys anything minimum than the complete specification. YAML is not as global as JSON but it is widespread, and here every parser implies a different subset. But it is files are less interoperable. It is the potential to script YAML recursive structures that have an infinite loop in few converters. The YAML bomb can be possibly found in circular detection. As there are no references, it is difficult to serialize the complicated structures regarding objects in JSON. But it can be more performed more efficiently in YAML serialization and it enables the attacker to run arbitrary code in some coding environments.
- Internet:
JavaScript dominates the web in huge amounts as the response for the data format is overwhelming with the famous web APIs. When it comes to a team environment, it is not preferred to use YAML over JSON when scripting web programming in general applications. Many programmers, don’t know the existence of YAML and feel uncomfortable when using it over the internet. If the user is executing web programming he can go for JSON as there are many codes available on the internet when he struck with the next translation steps.
- Interoperability:
According to the developer perspective, the YAML uses the identification of space that is required for Python developers. There are excess parsers that are effective on both JSON and YAML. The format of YAML’s space is compact and tabs are not considered as spaces which makes the user difficult in editing and interpreting the keystrokes in space columns. A common error is YAML requires minimum punctuation and is more compressed than JSON which is a false assumption. The invisible whitespace is mandated to be in YAML but it is applied in fewer characters which should be properly interpreted with correct identification. But JSON doesn’t use whitespace as much as YAML but it denotes hierarchy and grouping which is easily trampled with unwanted whitespace eliminated for effective compressed transport.
Conclusion
YAML has multiple features and includes relational anchors and comments but it’s quite complicated and tough to understand and when you start to use it regularly it can be more readable and affordable than JSON. It is easy to script a well-defined JSON parser in a short time. The working of JSON is rapid and still, it is interoperable with high-end systems. Few duplicate keys are theoretically valid in JSON but become invalid in YAML.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to YAML vs JSON. Here we discuss key differences with infographics and comparison tables, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –