Updated February 14, 2023
Introduction to XPath Functions
XPath functions are implemented using the CDC replication engine for the event server. The XPath function is uniquely defined by using the name, so creating a different function with the same name is impossible. Still, we can use different types of signatures, so the XPath function overloading is not permitted. XPath function will accept arguments of various kinds, which defines the signature of the argument type.
What are XPath Functions?
XPath defines each function with specifications by using a standard format. The function name is the qname defined and adhered to in syntactic conversions. The XPath function name is composed of English words and separated by the word using hyphens. We can use abbreviations only when there is precedent in other programming languages. If the name of the function contains the name of the data type, then it will have inter-capitalized spelling used in a function name.
When we pass argument ID in another type, the argument is converted into a string as if we are calling the function of the string. The string function will splitted into the list of whitespace-separated tokens. If the result in the node set contains the elements in the same documents as per the context node, it is equal to the token list.
XPath Functions Types
There are different types of XPath functions available.
Below is the type of function which was available in XPath as follows:
- Node function
- Numeric function
- String function
- Boolean function
There are four types of XPath functions available; also, this function contains its subtypes as follows:
1. Boolean Function
XPath Boolean function is used to convert the arguments into the Boolean.
Below is the XPath boolean function as follows:
- Not
- True
- False
- Long
Example:
Code:
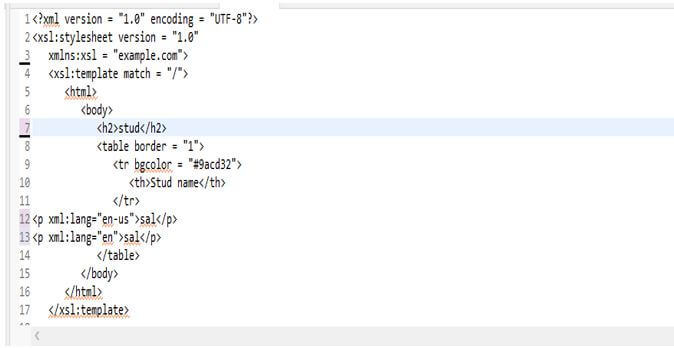
<p xml:lang="en-us">sal</p>
<p xml:lang="en">sal</p>Output:
2. Node Function
The XPath node function provides the node-related function as follows:
- Node – This function is used to return the value of the node.
- Text – This function returns the text value of a specific node.
- Comment – It is used to return the particular comment node.
- Last – This function is used to total context size from a given context.
- Position – This function is used to return the position of an element.
- Name – This function will return the last expression string name.
- Local-name – This function will return the previous expression string local name.
Example:
Code:
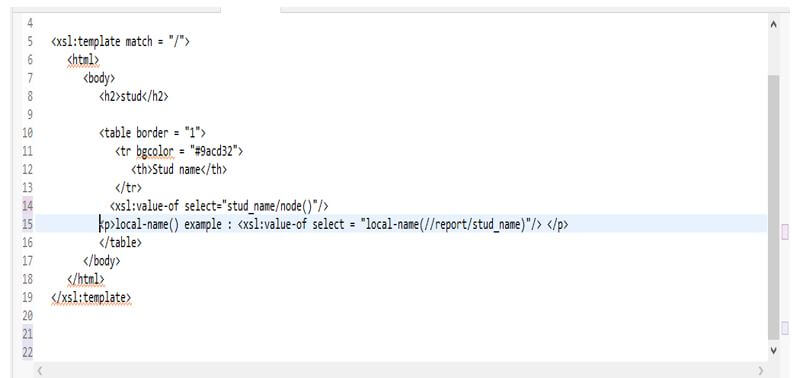
<xsl:value-of select="stud_name/node()"/>
<p>local-name() example : <xsl:value-of select = "local-name(//report/stud_name)"/> </p>Output:
3. Numeric Function
XPath numeric function provides the following numeric function as follows. Below is the numeric function available in XPath as follows.
- Count
- Sum
- Div
- Number
- Floor
- Round
- Ceiling
Example:
Code:
<p>01.35 number : <xsl:value-of select = "number('01.35')"/> </p>
<p>01.35 value : <xsl:value-of select = "floor(01.35)"/> </p>Output:
4. String Function
XPath string function provides the following string function as follows. Below is the string function available in XPath as follows.
- String
- Concat
- Start-with
- Contains
- Substring
- String-length
- Substring-after
- Substring-before
- Normalize-space
Example:
Code:
<p>starts-with() example : <xsl:value-of select="starts-with('String XPath function.','String')"/> </p>
<p>contains() example : <xsl:value-of select="contains('String XPath function.','XPath')"/> </p>Output:
XPath Functions Purpose
Each XPath function in the function library is specified using a prototype; it will also give the return type, the function’s name, and the argument type. If the type of argument is followed with the question mark, then the type of argument is optional, or otherwise, we require this argument. The function will select the element as per the unique ID. When our argument ID is the node set type, our result is the union of each node’s string value into the node-set argument.
Each function contains a different name; as per the function, we can pass one or more arguments to the function. After passing the argument, it will change the behavior of a function. Using the function, we can obtain the result. The function is essential and valuable in XPath.
Example of XPath Functions
The below example shows the XPath function as follows. In the below example, we are creating the project of XPathFunction. In the below example, we are making the template of the project name as XPath function into spring boot.
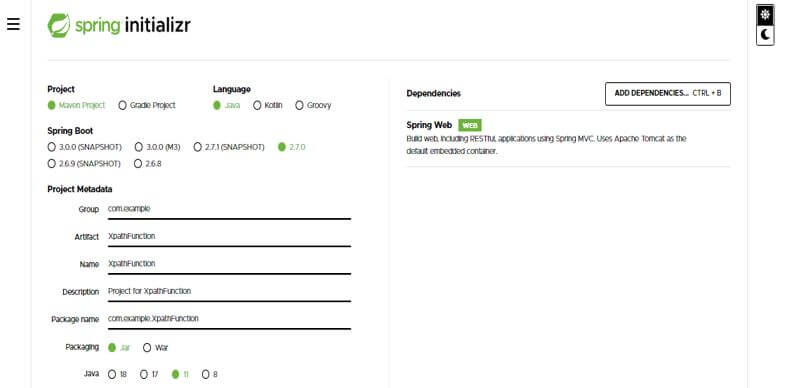
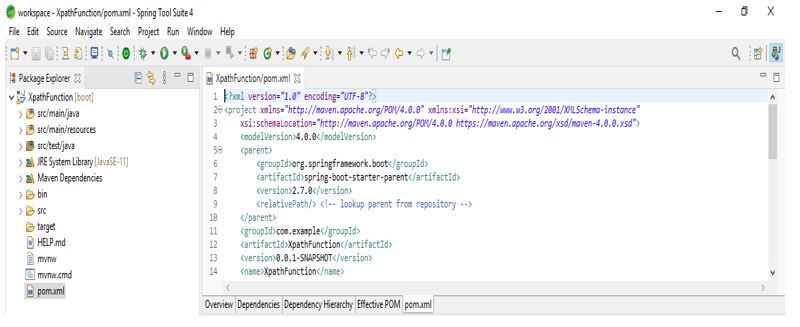
1. While creating the project into the XPath function using spring boot, we provided the group’s name as com.example, artifact name as XPathFunction, project name as XPathFunction, and selected java version as 11.
Group – com.example
Artifact name – XPathFunction
Name – XPathFunction
Spring boot – 2.6.7
Project – Maven
Java – 11
Package name – com.example. XPathFunction
Project Description – Project for XPathFunction
Dependencies – Spring web
Packaging – Jar
2. In the figure below, we can extract the project name as XPathFunction and open this project using the spring tool suite.
3. In the below step, we are checking the structure of the XPath Function project. Also, we are seeing the project dependency, which was added to the pom.xml file. Also, we are checking all the structures of the XPath Function example project.
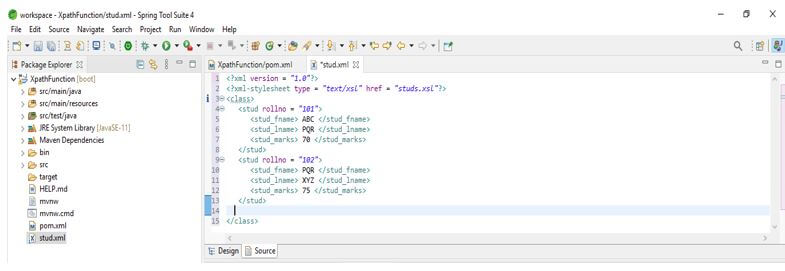
4. Now, we are creating the xml file for an example of the XPath Function. We are making a file name stud.xml.
Code:
<?xml version = "1.0"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type = "text/xsl" href = "studs.xsl"?>
<class>
<stud rollno = "101">
<stud_fname> ABC </stud_fname>
<stud_lname> PQR </stud_lname>
<stud_marks> 70 </stud_marks>
</stud>
<stud rollno = "102">
<stud_fname> PQR </stud_fname>
<stud_lname> XYZ </stud_lname>
<stud_marks> 75 </stud_marks>
</stud>
</class>Output:
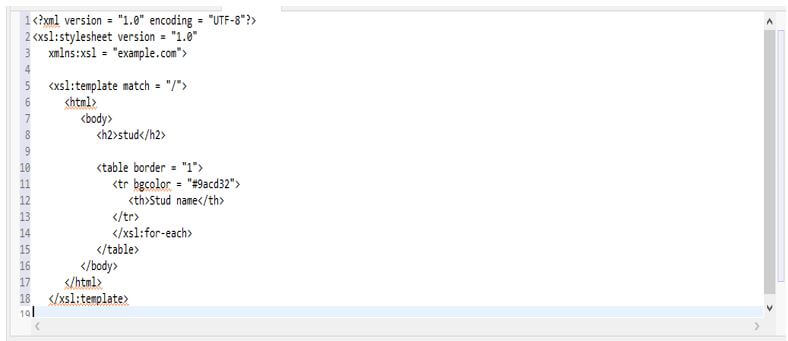
5. Now, we are creating the xsl file for an example of the XPath Function. We are building a file name as a stud.xsl.
Code:
<?xml version = "1.0" encoding = "UTF-8"?>
<xsl:stylesheet version = "1.0"
xmlns:xsl = "example.com">
<xsl:template match = "/">
<html>
<body>
<h2>stud</h2>
<table border = "1">
<tr bgcolor = "#9acd32">
<th>Stud name</th>
</tr>
</xsl:for-each>
</table>
</body>
</html>
</xsl:template>Output:
Conclusion
XPath defines each function with specifications by using a standard format. The function name is the qname defined and adhered to in syntactic conversions. XPath functions are implemented using the CDC replication engine for the event server. XPath function is uniquely defined by using the name.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XPath Functions. Here we discuss the introduction, XPath function types, purpose, and example. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –