Updated March 30, 2023
Introduction to XPath Sibling
Xpath Sibling is defined as a function for retrieving a web element that is a child of the parent element. The web element may be readily recognised or accessed using the sibling attribute of the Xpath expression if the parent element is known. In addition, a keyword called sibling can be used to retrieve a web element that is connected to another element.
Syntax of XPath Sibling
Given below is the syntax mentioned:
//node [attribute='value of attribute']//following-sibling:attributeExample:
Code:
//select[@id='fname']/following-sibling::*
//select[@id='fname']/following-sibling::select/Preceding-sibling syntax:
//select[@id='lname']/preceding-sibling::select/
//select[@id='lname']/preceding-sibling::*How does XPath Sibling Work?
If a simple XPath fails to locate a complex web element for our executable script, we must resort to the XPath 1.0 library’s functionalities. We may generate more specialised XPaths by combining the functions. One of such function is Sibling. The most important part of developing an automation script has always been locating a web element. The pain point of every automation test development process has always been finding the right, effective, and accurate locator.
Even the simple XPath solutions would not be very efficient because a simple XPath may return several elements in this scenario. Therefore, XPath in Selenium provides XPath functions that may construct effective XPaths to identify elements uniquely to overcome such problems. For example, the “XPath Axis” attributes in XPath leverage the relationship between multiple nodes to locate those nodes in the DOM structure.
Following and preceding siblings are just a few of the Axis that can be used in Selenium to discover elements on a web page using XPath. All siblings are referred to be the parent node’s children. So, we can use the following sibling if we’re referring to one of the children and want to browse to other children from the same parent who follow it.
1. following-sibling
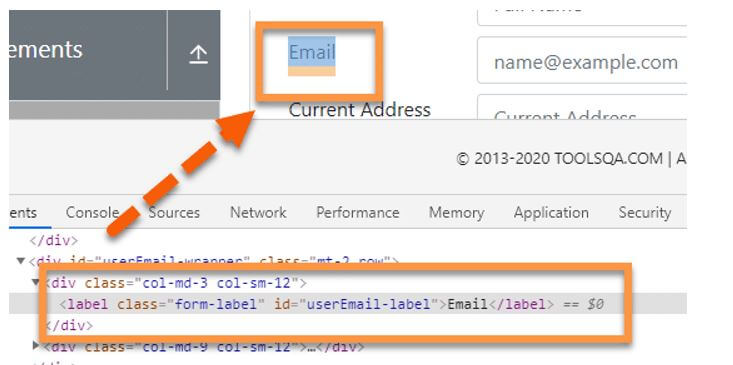
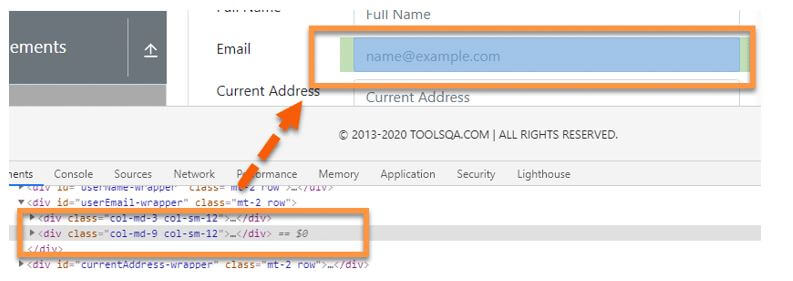
The Xpath sibling axis is similar to the axis that comes after it. Only sibling nodes, i.e. nodes on the same level as the current node, are recognised by following-sibling. For example, in the figure below, both highlighted “divs” are on the same plane, i.e., they are siblings; meanwhile, the “div” just over them seems to be the parent. Assume we’ve found the label “Email,” which is represented by the <div> element.
Xpath Example:
We can use the XPath following sibling axis to find this.
So, for this scenario, the XPath expression will be.
Code:
//div[@class='col-md-3 col-sm-12']/following-sibling::divOutput:
And we need to identify its sibling “div ” element, as shown below.
However, if numerous siblings have the same node, XPath will recognise all of the different elements.
Let’s take another case like:
For example, on the Facebook home page, the radio buttons for female and female text are siblings, as shown below. We can then simply discover the XPath of text “Female” at the same level by using the following-sibling axis.
Code:
//input[@id = ‘u_0_5’]//following-sibling::buttonUsing the “following-sibling” axis, the above formula identifies one input node.
2. preceding-sibling
The preceding-sibling axis shows all the nodes in the source document that have the same parent as the context node and occurs before it.
For the following test code:
Code:
<td>
<div class="btn-g">
<button class="btn ddd" title="withhold, Delete" name="delete" type="button">
<button class="btn ddd" title="cache" name="aaaa" type="button">
<button class="btn ddd" title=" Settings" name="bbb" type="button">
<button class="btn ddd" name="data" type="button">
<span class="class1"/>
Auro Water
</button>
</div>
</td>Examples of XPath Sibling
Below are the different examples of how the web driver takes sibling axes to find the exact XPath.
Example #1
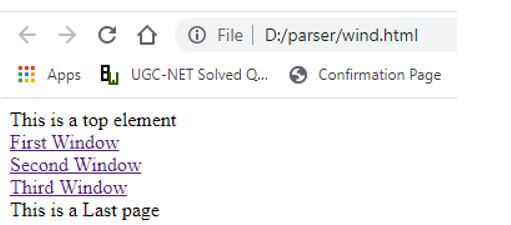
wind.html:
Code:
<html>
<head>
<title>Demo On Siblings -Xpath</title>
</head>
<body>
<form>
<header> This is a top element </header>
<div class="aab">
<a href="">First Window</a>
<div class="bbba">
<a href="">Second Window</a>
<div class="cca"> <a href="">Third Window</a> </div>
</div>
</div>
<footer> This is a Last page </footer>
</body>
</html>JavaScript:
Code:
List<WebElement>
sibElements = driver.findElements(By.xpath("//a[contains(text()," + "'Second Window.')]/parent::div//following-sibling::div[@class='cca']//a"));Here, the Firefox driver is invoked after the WebDriver API class ‘Firefox Driver’ is instantiated. The WebDriver object is then used to call and load the URL under test. We’re now utilising the WebDriver class’s’findElement’ method to find a list of web elements. We’re giving the XPath criteria to this procedure as input. As a result, we use the ‘following sibling function with the class ‘cca’ to choose the hyperlink with the tag ‘a’. This specific web element is listed in the list with the reference ‘sib Elements.’
Explanation:
- Three nested div blocks with the classes a, b, and c have been defined in the above HTML code.
- Each div block has a hyperlink and is labelled as “Inside div block 1,” “Inside div block 2,” or “Inside div block 3,” depending on which div block area it is contained in.
Output:
Example #2
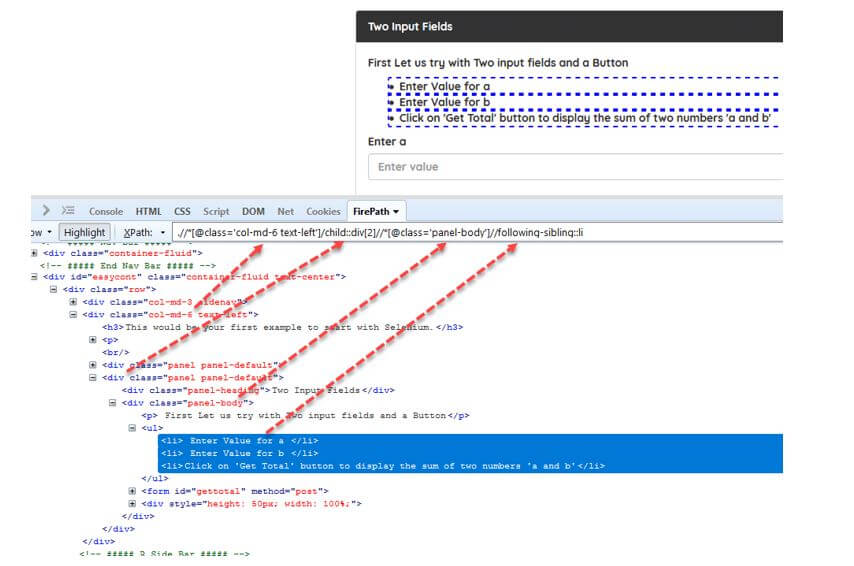
Simple example using Selenium.
Following-sibling XPath example.
Select the following siblings of the context node.
Code:
//*[@class='col-md-6 text-left']/child::div[2]//*[@class='panel-body']//following-sibling::liOutput:
The output that can be seen after running the above test script is as follows.
Example #3
Code:
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.Keys;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
public class Ances{
@Test
public void testAncestorInXpath()
{
WebDriver driver = new FirefoxDriver();
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("http://www.gmail.com/selenium/gmailhome/");
List<WebElement> dateBox = driver.findElements(By.xpath("//div[.//a[text()='SELENIUM']]/ancestor::div[@class='rt-grid-2 rt-omega']/following-sibling::div"));
for (WebElement webE : dateBox) {
System.out.println(webEl.getText());
} driver.quit();
}
}Explanation:
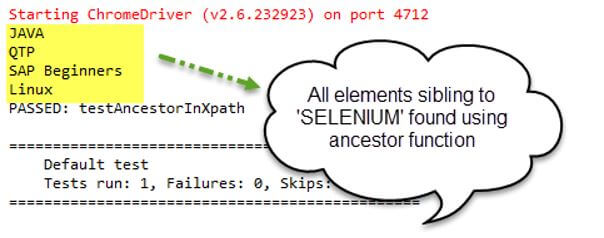
- Here the test is created to access the site Gmail. The sibling Div is specified using find elements, and the output is shown as.
Output:
Example #4
Code:
<ul class="right">
<li><a href="https://www.educba.com/feature">Home</a></li>
<li><a href="https://www.educba.com/Blogs">Automation</a></li> <li><a href="https://www.educba.com/product">Product</a></li>
<li><a href="https://www.educba.com/pricing">Pricing</a></li>
<li><a href="https://www.educba.com/support/">Support</a></li>
<li class="sign-out"><a href="https://accounts.educba.com/login">Login</a></li>
<li class="login"><a href="https://accounts.educba.com/login">Free Sign in</a>
</li>
</ul>XpathSib.java:
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class Xpathsib {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "path of chromeDriver");
WebDriver dr=new ChromeDriver();
dr.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(5, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
dr.get("https://www.educba.com/");
dr.manage().window().maximize();
dr.findElement(By.xpath("//li[@class='sign-up']//following-sibling::li")).click();
String cURL= dr.getCurrentUrl();
System.out.println(cURL);
driver.close();
}
}Explanation:
- One of the children has been mentioned in the DOM structure below, and we will travel to its siblings using the educba homepage links.
- Above is the code snippet incorporating Xpath in Selenium.
Output:
Conclusion
XPath Axes can be used to navigate the DOM tree and find dynamic web items. To write effective automation test scripts, Selenium Testers should understand each XPath axis and how to use it. Therefore, in this article, we have seen how to use sibling and their types in Xpath to give the desired result.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to XPath Sibling. Here we discuss the introduction; how does XPath sibling work? and examples, respectively. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –