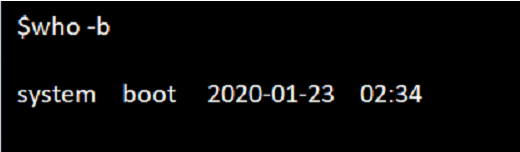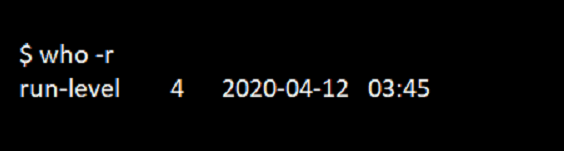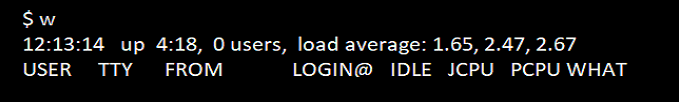Updated May 31, 2023
Definition of WHO Command in Unix
In Unix, “who” command allows to show or print the number of users who has been logged into your Unix computer system currently. The main usage of who command in Unix without command-line parameter is to show the name of the users who are logged in currently. Also, based on the Unix system, we can get the information to print the terminal and the time they have logged in. To print information about all the currently logged-in users, you use the who command.
Who command in Unix is used to determine the below information:
- Time at which the last system boot was done.
- Run the level of the current timestamp of the system.
- List of users who are logged in to the system and many more.
How does WHO Command Work in Unix?
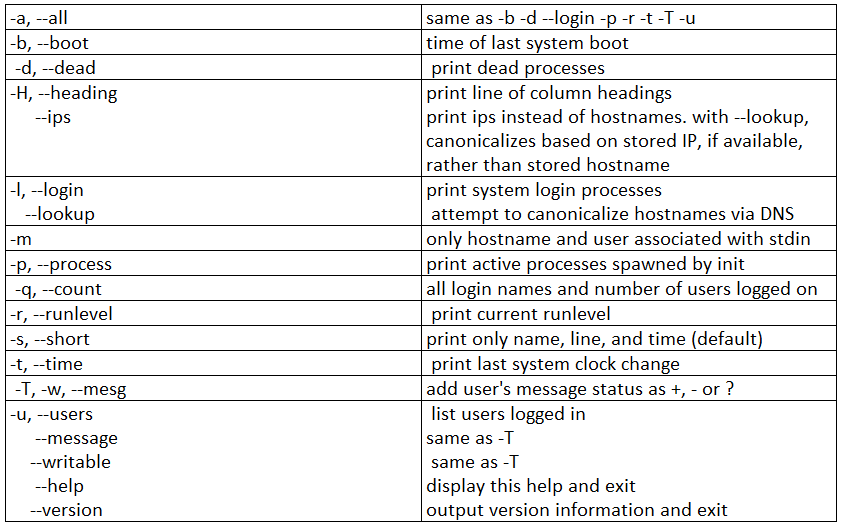
Usage: who [OPTION]... [ FILE | ARG1 ARG2 ]Description: Provides the information of the users who have logged in. Below are a few options and reports available with the ‘who’ command-line.
Syntax:
The syntax of who command in Unix is given below:
who [option]..[file] [am I ]Examples of WHO Command in Unix
Following are the examples are given below:
1. No Option
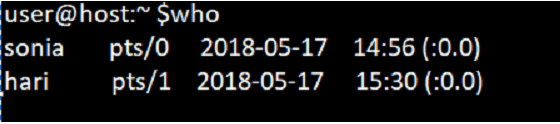
Who command without any input arguments will display the system’s information like user name, login time, the terminal of the user, and also the host name on the system.
Command:
whoOutput:
The above example gives the below information regarding the user:
- Name of the user who has logged in.
- line numbers in the terminal.
- time at which the user was logged in to the system.
- host name of the user who has logged in.
2. Option -H
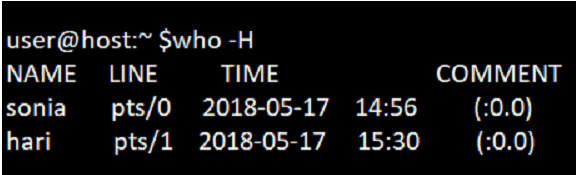
To display the headings of the columns in the who command, you use the option -H.
Command:
who -HOutput:
3. Option -q
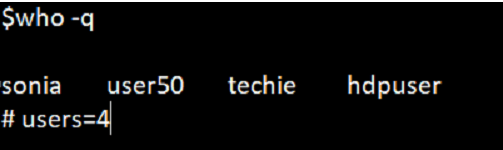
This option will allow to display the login names and total number of users logged on the system.
Command:
who -qOutput:
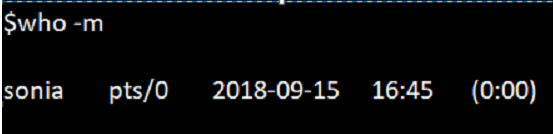
4. Option -m
To display only the hostname and user linked with stdin, we can use option -m, as shown below.
Command:
who -mOutput:
5. Option -b
We can see the user and the time of the last system boot. Using the -b option with the -c option in the who command will enable a listing of logged-in users in the output.
Command:
who -bOutput:
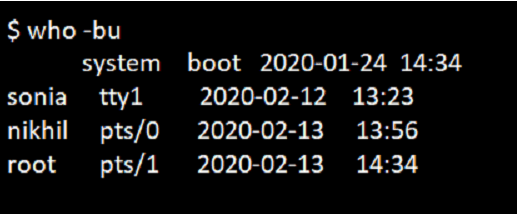
Command:
who -buOutput:
6. Option -r
To check the current processing run-level, we can use the -r option as below.
Command:
who -rOutput:
7. Option -d
This option will help to determine the dead processes in the system.
Command:
who -dOutput:
You can use the following command to check all active processes spawned by INIT.
Command:
who -p -HOutput:
8. To print the system’s username
We can display the current system’s username, which has logged in, by the following syntax.
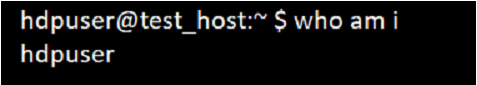
Command:
who am IOutput:
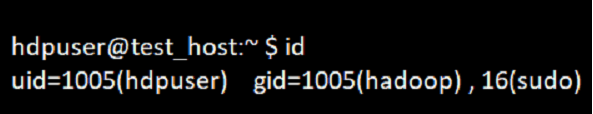
To print all the information regarding the current logged user.
Command:
idOutput:
9. Option w
‘w’ command gives us additional information regarding the current logged user. Username, current login time, number of idle days of the users, etc. example of this option is given below:
Command:
wOutput:
Conclusion
Without the command-line parameter, the who command in Unix shows the names of the users currently logged in. Also, based on the Unix system, we can get the information to print the terminal and the time they have logged in. The who command prints information about all the currently logged-in users.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “WHO Command in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.