Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction to Crontab in Unix
A utility that is always running while executing specific commands at pre-defined times is called Crontab. We use the crontab file when there are tasks that are to be executed repeatedly. The CRON daemon executes shell commands specified in the crontab file at specific dates and times. In simple terms, crontab works in the same manner as alarms on our phones. If we set the alarm to 6 A.M every day, the alarm rings on its own at the specified time every morning. Crontab is based on the same principle; this way, Unix ensures that we do not forget important events. This article will teach you about Crontab in Unix.
The syntax of Crontab is as follows:
minute(s) hour(s) day(s) month(s) weekday(s) command(s)- Crontab provides six fields. The first five fields in the schedule determine the execution timing for the statement, and they are indeed integer fields.
- The minute field in the cron expression specifies the exact minute for executing the command, accepting values from 0 to 59
- The hour field indicates the number of hours in which the command runs, storing a value between 0 and 23, as implied by its name.
- The command runs on the number of days specified by the value in the day field of the cron expression, which ranges from 1 to 31.
- As its name suggests, the month field stores a value between 1 and 12, indicating how many months have passed since the command was last issued.
- The weekday field in the cron configuration contains a value ranging from 0 to 6, indicating the number of days when the command is executed, as its name suggests.
- The sixth field executes the Bourne shell command.
- Using an asterisk (*) in the first five fields denotes that all possible values are allowed.
- Using a comma (,) denotes a list of values.
- You can indicate a range of values by using a hyphen (-).
- Using a separator (/) denotes a step value.
Working of Crontab in Unix
Red Hat Enterprise Linux runs the tasks of the system to update the system based on a pre-configuration. Red Hat Enterprise Linux consists of automated task utilities like cron, at, batch, etc.
Crontab is a utility that runs while executing specific commands at pre-defined times. If we want to run a table of commands on the desired schedule, we use crontab. These tables of commands can be managed using the command crontab. Crontab is the abbreviation for the cron table. The scheduler cron executes the jobs, hence the name cron table. The term “cron” is derived from the Greek word for time, which is “Chronos.”
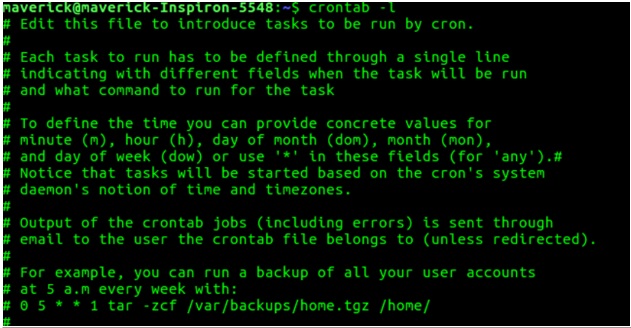
For instance, you can set up a cron job to automatically run a file on a weekly, monthly, or daily basis. If you need to take a database backup every day, you can use a cron job to execute a script specifically designed for that purpose. There is no need for manual running of the script. For example, to run the backup of user accounts at 5 A.M. Every week, the following command, shown in the below snapshot, must be used.
Crontab drives the cron daemon through the installation, uninstallation, and listing of tables. Every user owns a separate crontab, and they are files in /var. It is advisable to avoid direct editing of the files in /var. When calling a user’s crontab, the -u option must be used. If you omit the -u option, the crontab will execute for the user who is running the command.
The following options can be used with the crontab command:
- Crontab -a filename: To install the crontab file, you provide the filename.
- Crontab -e: Use the option crontab -e to edit the crontab file. If the crontab file doesn’t already exist, a new file will be created.
- Crontab -l: This option displays the crontab file.
- Crontab -r: This option removes the crontab file.
- Crontab -v: The option crontab -v shows the timestamp of the last edit made to the crontab file.
Cron uses an algorithm to schedule the jobs internally.
The algorithm works as follows:
1. When initiating the cron, it searches all the account holders’ home directories to locate the file named “. crontab”.
2. Determine the schedule for executing the command within the found crontab file.
3. In an event list, the five fields store the specified time and the commands to be executed, queuing them together.
4. Next, it enters the main loop:
- As the task enters the queue, check the task and determine how long it runs in the future.
- The period it runs in the future is the period it sleeps.
- The user has certain privileges if he creates the task. After verifying the time, the user executes the task in the background when the cron awakes.
- Find out when to run the command the next time and then place the command back in the queue of the list of events.
There are different options to set up a cron job on different servers. Servers not supporting cron cannot have a cron job set up. However, it is possible to set up a cron job on certain servers through the control panel. Easycron is one of the solutions for servers that cannot support cron.
Examples
- Crontab to run a command every day at 3.15 P.M.
15 15 * * * /path/to/script/script.sh- Crontab is to run the same script at the same time only on Monday.
15 15 * * 1 /path/to/script/script.sh- Crontab is to run the same script simultaneously on Monday and Thursday.
15 15 * * 1,4 /path/to/script/script.sh- Crontab will run the same script simultaneously on Monday and Tuesday.
15 15 * * 1-2 /path/to/script/script.shConclusion
The most useful utility in the Unix operating system is Crontab. We can execute the commands at a specified time using crontabs. We refer to these commands as cron jobs. They have a wide range of applications, like running scheduled backups, monitoring disk space, running system maintenance tasks, etc.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Crontab in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.