Updated March 17, 2023
Introduction to Spring Cloud
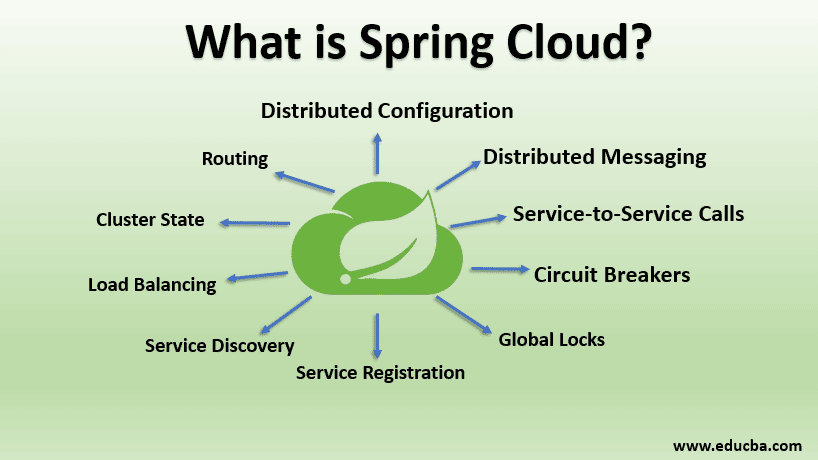
Spring Cloud is defined as an open-source library that provides tools for quickly deploying the JVM based application on the clouds, it provides an extensible mechanism and a better user experience than its competitors due to various features like Distributed configuration, Circuit breakers, Global locks, Service registrations, Load balancing, Cluster state, Routing, Load Balancing, etc, it is also capable of working with spring and different applications in various different languages
Features of Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud provides a better experience and an extensible mechanism that others. Major features of Spring cloud are:
- Distributed configuration
- Distributed messaging
- service-to-service calls
- Circuit breakers
- Global locks
- Service registration
- Service Discovery
- Load balancing
- Cluster state
- Routing
Why we should require Spring Cloud?
We face the following issues during the development of distributed microservices using Spring Boot:
- Performance issues: Different operational overheads affects performance badly.
- Complexity in deployment: DevOps skills are required.
- Redundancy: Distributed system often faces redundancy issues.
- Load–balancing: Workload distribution across various computing resources are improved by Load Balancing.
- Distributed system complexities: Complexities include bandwidth issues, network issues, security issues, latency issues, etc.
- Service directory tools: These tools let the processes and services in the same cluster talk to each other.
How does it work?
Below is the explanation of how Spring Cloud works:
- Spring Cloud Config provides client-side and server support for various configurations in distributed systems.
- It provides a centralized platform to manage various properties for all applications across different environments.
- Both server and client concept maps to the Property Source abstractions and Spring applications identically.
- They work properly with Spring applications and can be used with different applications in any language.
- It lets you manage and configure all the environments when applications are moving through deployment pipelines from development to testing.
- It also makes sure about all the necessities of an application when they migrate.
- To add and plugin alternative implementations with Spring Cloud Config is easy.
- The default value of spring.cloud.config.uri i.e. http://localhost:8888/ is being contacted by Spring Boot applications until Spring Config Client and Spring Boot Actuator are on the classpath.
- You may change the default value spring.cloud.config.uri can be set in bootstrap.[yml | properties] or in system properties.
Code:
@Configuration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@RestController
public class DemoApplication {
@Value("${config.name}")
String str = "Cloud";
@RequestMapping("/")
public String new() {
return "Spring " + str;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApp.class, args);
}
}- Local configuration or remote Config server can provide the value for name.
- You can try running your own server using a spring-cloud-config-server.
- To run the application on port 8888, you can set spring.config.name=configserver And the data then is served from sample repositories.
- To locate the necessary configuration data, you may need spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri
Set-Up Spring Cloud
Below are the steps to follow:
Step 1: Open the website https://start.spring.io/ and choose
Step 2: Select Spring Boot 1.4.X.
Step 3: Artifacts should be set to ‘config’.
Step 4: Add the config server’ module from the dependencies section.
Step 5: Click the Generate button to download a preconfigured project containing a zip file.
Step 6: You can also create a Spring Boot project by adding the dependencies to the POM file manually.
Step 7: These dependencies can be shared among all the projects.
Code:
<parent>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot </groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-parent </artifactId>
<version> 1.4.0.RELEASE </version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot </groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-starter-test </artifactId>
<scope> test </scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.cloud </groupId>
<artifactId> spring-cloud-dependencies </artifactId>
<version> Brixton.SR5 </version>
<type> pom </type>
<scope> import </scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId> org.springframework.boot </groupId>
<artifactId> spring-boot-maven-plugin </artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>Step 8: Dependencies for the ‘config server’ is below:
Code:
<dependency>
<groupId> org.springframework.cloud </groupId>
<artifactId> spring-cloud-config-server </artifactId>
</dependency>Step 9: The Application class should be added with the following to enable Config Server as mentioned in the previous example:
Code:
@SpringBootApplication
@EnableConfigServer
public class DemoApplication {
...
}Step 10: The ‘application properties’ should be added to src/main/resources.
Code:
server.port = 8888
spring.application.name = config
spring.cloud.config.server.git.uri = file://${user.home}/application-configStep 11: The Uri parameter is one of the most significant settings for the ‘config server’.
Step 12: On Windows, the Uri parameter is usually added to a relative path that resolves to
C:\users\<username>\. And on Linux, it is /users/<username>/.
Step 13: All the property files for various applications are stored in the above pointed Git repository.
Step 14: The folder ‘application-config’ should be then added to the folder cloud.config.server.git.uri.
Step 15: Navigate to that folder by using ‘cd’ command and then type git init.
Step 16: A Git repository will be initiated now, that lets you store and track your files.
Step 17: Run the config server to check whether it’s working.
Step 18: Type mvn spring-boot: run command in the command line to start the server.
Step 19: The following output will be seen as an indication for a successful server start:
Tomcat started on port(s): 8888 (HTTP)
Step 20: The config server manages the application properties in the servers.
Step 21: In the servers, each application’s properties should be configured in such a way that they should be able to talk back to the server.
Step 22: This process is a bootstrap process. Each of the applications should have a file called properties.
Step 23: It contains properties similar to application properties with few differences.
Step 24: The properties are initially loaded by a parent spring called Application Context.
Step 25: As it is critical, the config server will start the properties management of properties.
Step 26: The Application Context will also decrypt encrypted properties.
Step 27: These properties should be kept distinct.
Step 28: The properties initiate the config server and make it ready.
Step 29: The properties specify the properties for your application.
Step 30: Technically, the application properties can also be placed in properties.
Step 31: Though config servers are responsible for the management of application properties, we will still need the properties as they are available as default values and that is unavailable in config servers.
Conclusion
Various parts of Spring Cloud can be connected together into a functional Microservice application. This is a base platform that lets you build various complex applications. Spring Cloud lets you build powerful cloud applications. All the problems faced by distributed environments are solved by using Spring Cloud.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to What is Spring Cloud. Here we discuss the introduction, features, requirements, working, and step-by-step setup of Spring Cloud. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more-