Updated March 23, 2023
Introduction to PowerShell Run Command
PowerShell Run Commands this article is all about the PowerShell Run Commands which every IT Professional and System Administrator should be aware of.
- PowerShell Run Commands are essential to know about for getting your things done seamlessly and smoothly through PowerShell.
- PowerShell commands are referred to as cmdlets (Command-Let).
- These commands can be used by the users to perform various management tasks from monitoring to managing servers, testing and debugging scripts and other administrative tasks.
Basic PowerShell Run Commands
Let us walk through some of the very basic and important PowerShell commands to understand their uses in carrying out various tasks.
These commands are helpful in retrieving information in various formats from different data sources like file or folder system, registries, etc.
1. Get-Help
- This PowerShell command is the very basic command every Administrator or developer should be aware of.
- It is helpful in getting help with other commands, in simple terms, to get the information about other commands.
The syntax for this command is:
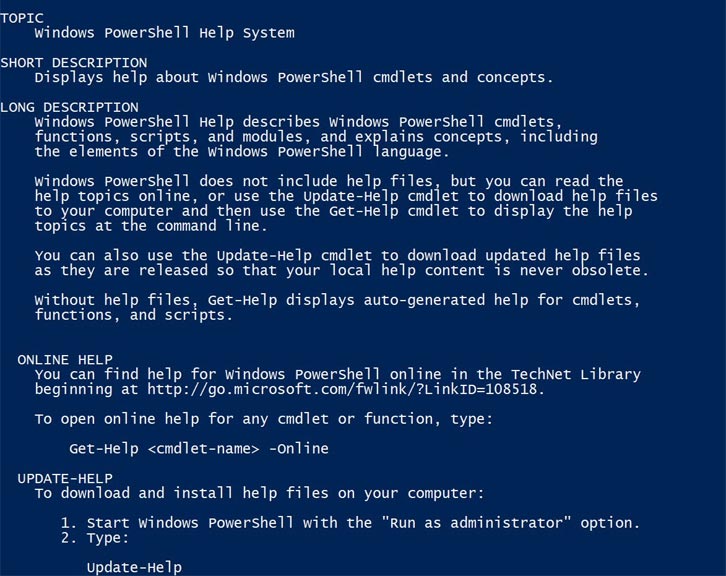
Get-Help
Output:
Windows will display the entire information about how to get help from PowerShell with other commands.
Let us see how this command works for a particular command or cmdlet for which we want information.
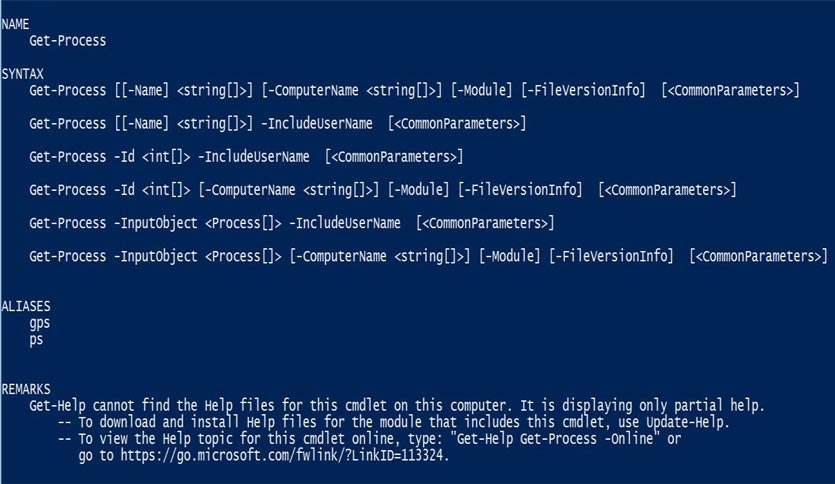
Get-Help Get-Process
Output:
The above command displays the complete information about the cmdlet “Get-Process” with full command syntax.
To view any help document, you can type Get-Help followed by the exact name of the help file.
For example,
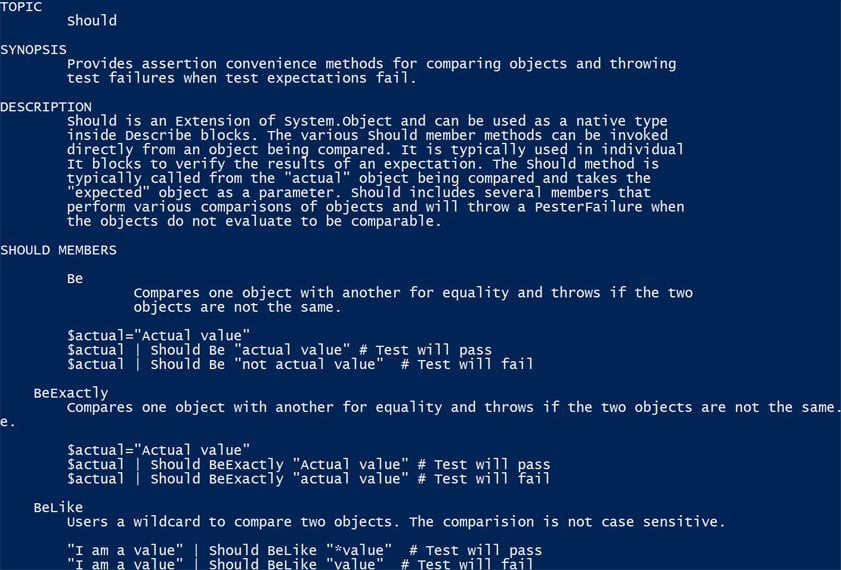
Get-Help about_should
Should is a help file and the above syntax is for getting the information about this help file.
Output:
The file’s content with a complete description along with examples get displayed on the screen.
2. Get-Command
This cmdlet is used to get the full list of commands (types Alias, Function and Script) available to you for use in the current session.
The syntax for this cmdlet is VERB-NOUN
where,
VERB refers to Get, Set, Add, Clear, Read and Write
NOUN refers to files, servers, storage and various other items in the system.
Example:
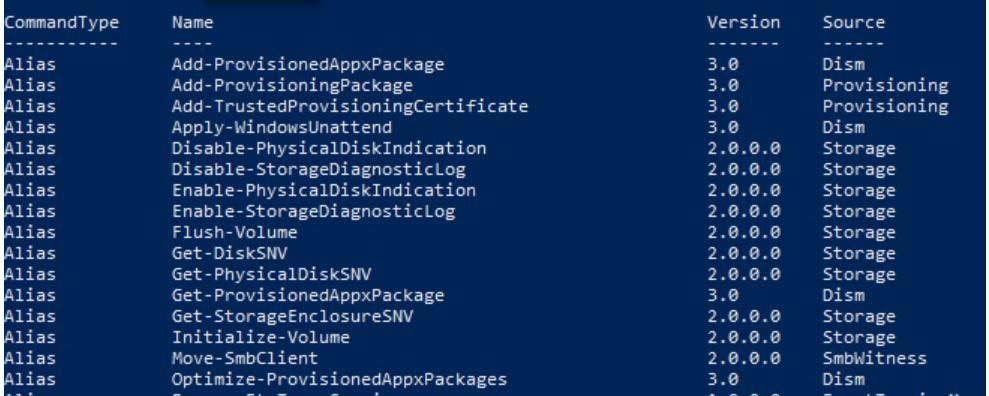
Get-Command
Output:
- Specifically, if you want to get the list of only Alias type, the cmdlet would be
Get-Command -CommandType Alias
- For Function type, the cmdlet would be
Get-Command -CommandType Function
- For Scripts, the cmdlet would be
Get-Command -CommandType Script
3. Get-Execution Policy
- Microsoft by default restricts users from executing scripts in PowerShell environment for security reasons.
- In order to use scripting, users need to change the default setting or default policy.
For this, one should first be familiar with the execution policies for running the scripts. The cmdlet for this is given below
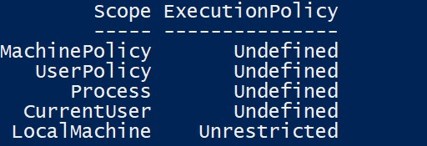
Get-ExecutionPolicy -List
Output:
This displays a list of execution policies with their scopes.
This list shows that for Local Machine, Execution Policy has been changed to Unrestricted.
4. Get-Process
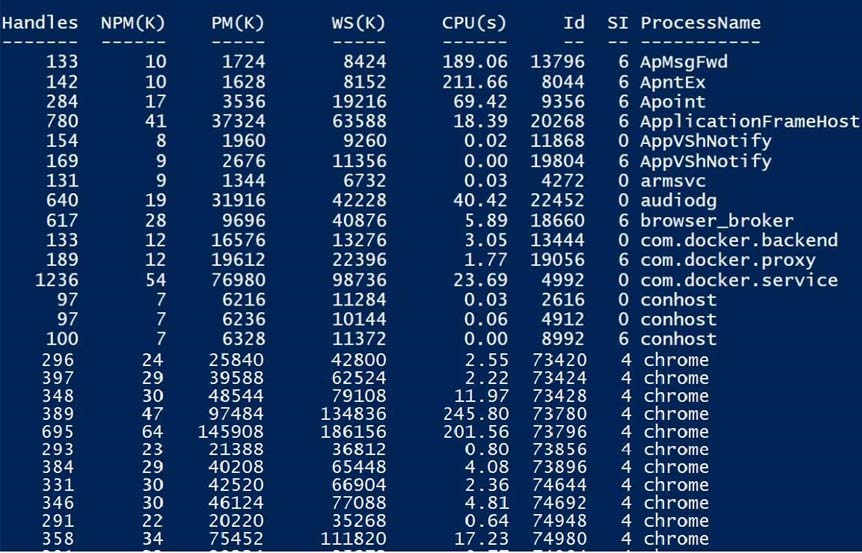
- This cmdlet displays a list of all currently running processes on the local machine If no parameter is passed, this cmdlet will return all the active processes on the system.
Example:
Get-Process
Output:
- For a particular process, you can specify process name or process Ids (Id).
Example:
Get-Process -id 0
This cmdlet will display the process with Id 0, that is, Idle process.
Output:
Note: If there is no process with the specified Id, it means that either the Id is wrong or that particular process has exited.
For example,
The below cmdlet searches for a process with Id 99.
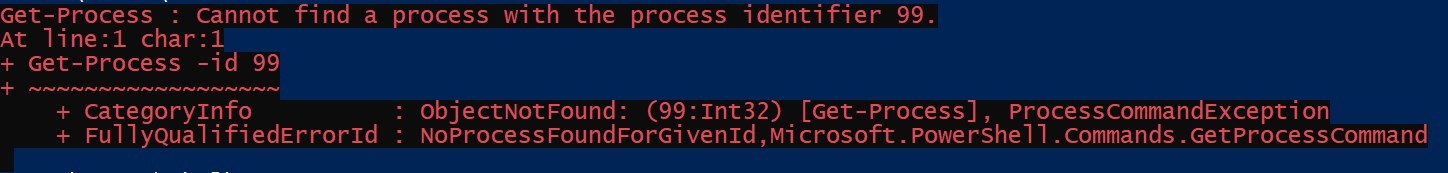
Get-Process -id 99
Output:
This throws an error stating that no process was found with Id 99.
- You can use “Stop-Process” to stop a running process by specifying its Name or Id.
For example,
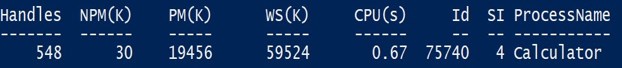
There is a process “Calculator” running in your local machine.
Get-Process -ProcessName Calculator
To stop this process, you can type the following cmdlet
Stop-Process -ProcessName Calculator
This will terminate the running instance of Calculator.
5. Get-Service
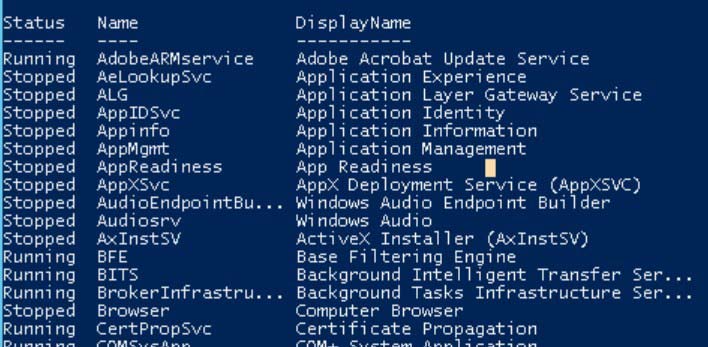
- This cmdlet returns all the services on your local machine whether running or stopped.
- If no parameter is passed with this cmdlet, all the services of your local machines are returned.
Example:
Get-Service
Output:
All the services, Running and Stopped, are returned.
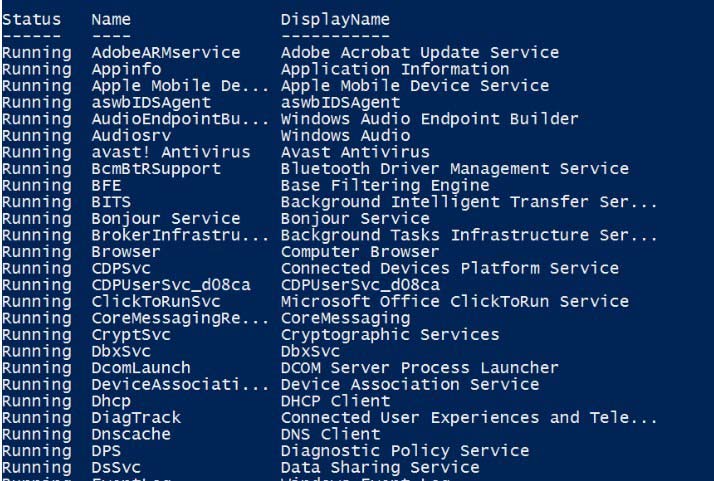
To get the services that are running, type in the following cmdlet.
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status –eq “Running”}
Output:
You can also get the properties of the service using Get-Member cmdlet.
Get-Service | Get-Member
Output:
This cmdlet displays the properties and methods of the objects generated as an output of Get-Service cmdlet.
(|) pipe operator’s role here is to send the output of Get-Service cmdlet to Get-Member cmdlet.
6. Where-Object
- It is used to select objects having particular values from a list of objects passed to it.
Example:
Get-Service | Where-Object {$_.Status -eq 'Running'}
This cmdlet will simply take a collection of objects and will pass it to the pipe operator for filtering to return a list of services whose status is “Running”.
7. ConvertTo-HTML
- This cmdlet is helpful when you want to create a report out of the information about a system.
- To do this, simply use the pipe(|) operator to provide the output from one command to ConvertTo-HTML.
- ConvertTo-HTML basically converts Microsoft .NET Framework objects into HTML to be displayed in a web browser.
For example,
You can create a web page and display the PowerShell aliases.
Get-Alias | ConvertTo-Html | Out-File Display_Alias.htm
invoke-item Display_Alias.htm
This will display all the aliases on a web page.
- You can also export the information in a .csv file
Get-Alias | ConvertTo-Html > Display_Alias.htm
invoke-item Display_Alias.htm
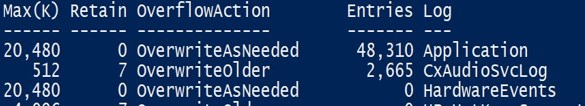
8. Get-EventLog
- Using this cmdlet, you can get event logs from your local computer as well as a remote computer.
- To get a list of event logs in your local system
Get-EventLog -List
Output:
Conclusion
- This article walked you through the very basic but very essential commands to work in PowerShell.
- Here, we tried to understand the purpose and uses of various PowerShell commands.
- These are extremely helpful for monitoring and troubleshooting purposes as well as managing various administrative tasks.
- PowerShell commands are all about cmdlets which are easy to remember and execute.
- Once you get the hold of at least basic PowerShell commands, you can make the most out of the PowerShell as it will massively simplify your daily manual tasks.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to PowerShell Run Command. Here we discuss the Basic PowerShell Run Commands along with the respective examples and the outputs. You can also go through our other suggested articles to learn more –