Introduction to CIDR
Imagine a virtual postal system where every device linked to the Internet requires a unique address, similar to a home address, to receive and send data accurately. CIDR, standing for Classless Inter-Domain Routing, is a revolutionary addressing scheme that redefines how Internet Protocol (IP) addresses are allocated and managed. With CIDR, the days of traditional and inflexible IP address classes are gone! Instead, CIDR introduces a flexible and scalable system, using the available address space best and enabling seamless communication across the vast web of networks!
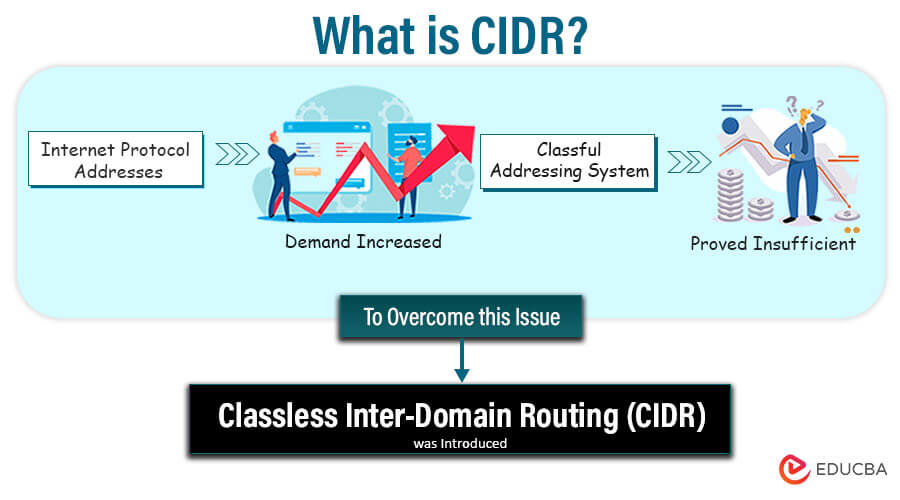
Table of Content
- Introduction to CIDR
- CIDR in a Nutshell
- Evolving IP Address Formats
- How does it Work?
- Examples
- CIDR Implementation in IPv6
- Significance of CIDR in IP Addressing
- CIDR Blocks and Prefix Lengths
- CIDR Subnetting
- Understanding Supernetting
- Comparison of CIDR in IPv6 over IPv4
CIDR in a Nutshell: Breaking Down the Basics
Before diving deeper into the wonders of CIDR, let’s break down the basics in bite-sized pieces:
- IP Addresses – The Internet’s GPS: Just as you need a GPS to navigate unfamiliar territories, devices on the Internet require IP addresses to find each other and communicate.
- IPv4 – The Old Guard: The most widely used version of IP addresses is IPv4 (Internet Protocol Version 4), represented in four sets of numbers (e.g., 192.168.0.1).
- IPv6 – The Future is Near: With the ever-expanding Internet, we needed more IP addresses than IPv4 could provide. IPv6 (Internet Protocol Version 6) came to the rescue with its vast pool of unique addresses, represented in eight sets of numbers (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334).
Evolving IP Address Formats: From Classful to Classless
IP addresses have evolved from the rigid classful addressing system to the more flexible classless addressing system. Let’s explore the different IP address formats:
Classful Addresses
In the early days of the internet, IP addresses were assigned using the classful addressing system. The address length was set at 32 bits with a fixed allocation of bits for the network and host portions. There were three main classes of IPv4 addresses under this system:
Class A:
- The first octet (8 bits) represents the network address.
- The remaining three octets (24 bits) represent the host address.
- Example: 44.0.0.1, where 44 is the network address, and 0.0.1 is the host address.
Class B:
- The first two octets (16 bits) represent the network address.
- The remaining two octets (16 bits) represent the host address.
- Example: 128.16.0.2, where 128.16 is the network address, and 0.2 is the host address.
Class C:
- The first three octets (24 bits) represent the network address.
- The last octet (8 bits) represents the host address.
- Example: 192.168.1.100, where 192.168.1 is the network address, and 100 is the host address.
Classless Addresses (CIDR)
As the demand for IP addresses increased and the classful system proved inefficient, the classless addressing system, also known as Classless Inter-Domain Routing, was introduced. It utilizes variable length subnet masking (VLSM) to allow for a more flexible allocation of network and host address bits in an IP address.
When utilizing CIDR, you use a subnet mask to identify the network segment of an IP address. The suffix value indicates the number of bits in the network address prefix. This allows network administrators to create subnets of different sizes, each with its own range of host addresses.
CIDR Notation Example:
Let’s consider the CIDR notation 192.0.2.0/24:
- The first 24 bits (192.0.2) represent the network address.
- The remaining 8 bits (0) are available for host addresses within the subnet.
- This means the subnet can have up to 2^8 – 2 = 254 usable host addresses.
In CIDR, the length of the network prefix can vary, allowing for more efficient use of IP address space and better allocation of addresses.
How does it Work?
CIDR, or Classless Inter-Domain Routing, works its magic by providing a more flexible and efficient method of allocating and managing IP addresses within computer networks. Unlike the old system of IP address classes (Class A, B, C, and so on), which had predefined boundaries and wasted precious IP resources, CIDR introduces a notation that allows for custom subnetting. Let’s dive into the essence of how CIDR works its wonders:
Embracing the Power of CIDR Notation
CIDR’s heart lies in its notation, which combines the network address with a slash followed by a number (IP_address/mask_bits). This seemingly simple chant holds the key to unraveling CIDR’s might!
- IP_address: This is the starting address of the network. It’s like the magical gate that leads to your subnet’s domain.
- Mask_bits: These are the essential ingredients to shape the subnet mask, which determines the size of the subnet. Think of them as the enchanted runes that define the boundaries of your network.
Taming the Subnetting Dragon
CIDR allows network administrators to create subnets of varying sizes based on the number of mask bits used. The more mask bits you have, the smaller the subnet and the more devices it can hold within its domain.
- Example 1: Suppose you possess an IP address of 192.168.1.0 along a subnet mask of 255.255.255.0 (equivalent to /24 in CIDR notation). This means you have 24 mask bits, and your subnet can accommodate 2^(32-24) – 2 = 254 devices.
- Example 2: Consider an IP address of 10.0.0.0 with a subnet mask of 255.255.255.240 (equivalent to /28 in CIDR notation). Here, you have 28 mask bits, which results in a subnet with 2^(32-28) – 2 = 14 usable IP addresses.
Supernetting: Weaving Subnets into One
Just as master wizards combine spells for more significant impact, CIDR allows supernetting – consolidating multiple smaller networks into a larger supernetwork. This helps optimize routing tables and simplifies the network landscape.
Example: Suppose you have two subnets: 192.168.1.0/24 and 192.168.2.0/24. Instead of listing them separately in routing tables, CIDR notation lets you represent them as 192.168.0.0/22. This single entry encompasses both subnets and streamlines routing!
Efficient IP Address Allocation
In the bygone era of rigid IP address classes, allocation was akin to dividing a potion among thirsty wizards. With CIDR’s fluid allocation, IP addresses are used more efficiently.
Example: Imagine you have a company with 500 employees. In the old ways, you might have needed a whole Class C network (256 addresses). But with CIDR, you can create a /23 subnet (512 addresses) and comfortably accommodate everyone!
Seamless Routing with CIDR
Like magical messengers, Routers need to traverse the vast network terrain swiftly and accurately. CIDR comes to their aid by summarizing multiple networks under one entry, reducing the complexity of routing tables.
Example: Instead of listing your subnets separately, CIDR lets you group them under a supernet. So, if you have subnets 10.0.0.0/24, 10.0.1.0/24, and 10.0.2.0/24, you can represent them all as 10.0.0.0/22.
CIDR is an alternative to traditional subnetting. It is also called classless Addressing. It consists of CIDR blocks; by this, it dynamically allocates the IP addresses on the requirement of the users based on certain rules. Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) handles the assignment of CIDR blocks.
CIDR block
This block contains IP addresses. This block consists of 3 basic rules.
Rule 1: In the CIDR block, the IP addresses that are allocated to the hosts should be continuous.
Rule 2: The block size should be of power 2 and equal to the total number of IP addresses.
Rule 3: The size of the block must be divisible by the first IP address of the block.
CIDR Notation
A CIDR IP address representation is the same as the IP address; it ends with a backward slash followed by a number. The n represents the number of network bits. It is called as IP network prefix.
The general way of representing the CIDR IP address is
a.b.c.d / n.
Examples
If we are given the CIDR representation, we can find the range of IP addresses. We can see this with examples.
Example #1
The CIDR representation is 21.19.35.40/24. Find the IP addresses of the CIDR block?
24 represents the number of bits used for the identification of the network.
The 5 bits are used for the identification of hosts.
The CIDR address is 21.19.35.40/24.
The first IP address is 21.19.35.0
The last IP address is 21.19.35.255
The total cost is 256.
Netmask is 255.255.255.0.
Example #2
The representation is 255.255.255.255/31. Find the IP addresses of the CIDR block?
31 represents the number of bits used for the identification of the network.
The 1-bit is used for the identification of hosts.
The CIDR address is 255.255.255.255/31.
The first IP address is 255.255.255.254.
The last IP address is 255.255.255.255.
The total cost is 2.
Netmask is 255.255.255.254.
We can find the CIDR block from the block of IP addresses.
Example #3
The IP address range is from 21.19.35.64 and 21.19.35.127. Find the CIDR block?
The IP address ranges are from 21.19.35.64 and 21.19.35.127.
Before proceeding further, the CIDR block rules mentioned above should be checked if they are satisfied; then, it is a CIDR block.
So the size of the block is 26. (i.e., 127 – 64 + 1 = 64)
Number of bits = 32 – 6 = 26.
CIDR block is 21.19.35.64/26.
Example #4
The IP address range is from 255.255.255.32 to 255.255.255.63. Find the CIDR block?
The IP address ranges are from 255.255.255.32 and 255.255.255.63.
Before proceeding further, the CIDR block rules mentioned above should be checked if they are satisfied; then, it is a CIDR block.
So the size of the block is 25. (i.e., 63 – 32 + 1 = 64)
Number of bits = 32 – 5 = 27.
CIDR block is 255.255.255.32/27.
CIDR Implementation in IPv6: Empowering the Vast Address Space
IPv6, the next-generation Internet Protocol, comes with a colossal address space that defies the limitations of IPv4. CIDR (Classless Inter-Domain Routing) finds new life within this vast realm, further empowering IPv6 with efficient subnetting, simplified routing, and optimized address allocation. Let’s explore how CIDR is implemented in IPv6, unleashing its magic on this futuristic addressing system.
1. IPv6 Address Format: Expanding Horizons
IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, presenting an astronomical number of unique addresses—approximately 3.4×10^38! The format comprises eight groups of four hexadecimal digits, separated by colons.
Example IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
2. CIDR Notation in IPv6: The Mighty Slash
Like in IPv4, CIDR notation in IPv6 involves appending a slash followed by the prefix length to an IPv6 address. The prefix length determines the number of bits in the network section of the address.
Example: 2001:0db8:85a3::/48
In this example, the first 48 bits are reserved for the network, while the remaining 80 bits are available for host addresses within the subnet.
3. Efficient Subnetting in IPv6
With the vast IPv6 address space, CIDR enables even more efficient subnetting. Network administrators can create subnets of varying sizes, optimizing address allocation based on the number of required hosts per subnet.
For instance, a large organization might allocate /48 blocks to different divisions, each with its own abundance of available subnets. You can allocate smaller subnets, like /64 or /96, to particular networks or departments.
4. Aggregation and Routing Advantages
CIDR’s aggregation capabilities are even more significant in IPv6 due to the sheer number of addresses. Aggregating multiple /64 or /48 blocks into larger supernets reduces the number of entries in routing tables, streamlining routing decisions and enhancing overall network performance.
IPv6’s hierarchical addressing structure and CIDR’s aggregation facilitate efficient routing across the global internet, making it a robust and scalable addressing solution.
5. Simplifying Network Management
CIDR’s implementation in IPv6 simplifies network management by providing greater flexibility and precision in addressing. Network administrators can allocate address blocks with the exact number of host addresses needed for each subnet, preventing address space wastage.
Additionally, VLSM (Variable Length Subnet Masking) in IPv6 allows for further customization of subnet sizes within a single network, accommodating various device counts and networking requirements.
6. Transitioning to IPv6 with CIDR
As the world embraces the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, CIDR remains a vital tool for efficient IP address management. It bridges the gap between the two protocols, allowing organizations to implement CIDR principles learned from IPv4 into their IPv6 networks.
7. IPv6 Security and CIDR
CIDR’s role in subnetting and network segmentation contributes to enhanced security in IPv6. Network administrators can implement targeted security measures and control access more effectively by allocating separate subnets for specific purposes or departments.
Due to the larger and more flexible address space in IPv6, CIDR is even more significant. Unlike IPv4 addresses, which are only 32 bits long, IPv6 addresses are 128 bits long, allowing for almost infinite unique addresses due to the vast address space.
Similar to IPv4, CIDR in IPv6 is done by utilizing variable-length subnet masks to create subnets of various sizes. IPv6 CIDR notation shows how many bits were used for the network portion of a 128-bit address. For instance:
IPv6 address: 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e:0370:7334
Subnet mask: /64
In this example, the network portion of the IPv6 address is represented by the first 64 bits, while the remaining 64 bits are set reserved for the host portion.
In IPv6, CIDR enables organizations to allocate exact and adequately sized subnets for their networks, resulting in effective address utilization. With the large number of accessible addresses in IPv6, subnetting becomes even more versatile and scalable, allowing modern networks to develop and become more sophisticated.
Significance of CIDR in IP Addressing
The significance are as follows:
1. Efficient Utilization of IP Address Space
CIDR’s flexible addressing scheme allows for variable-length subnet masking (VLSM), enabling network administrators to divide IP address space into smaller subnets of various sizes. This efficient allocation ensures that organizations can acquire only the necessary IP addresses, reducing wastage and making more addresses available for others.
2. End of IP Address Exhaustion Crisis
The internet faced a looming crisis due to the depletion of IPv4 addresses under the classful system. CIDR’s introduction came as a timely solution, alleviating the scarcity by allocating IP addresses more granularly. This extended the lifetime of IPv4 addresses and bought time for the gradual transition to IPv6, with its abundance of available addresses.
3. Simplified Subnetting and Routing
CIDR notation simplified subnetting and routing procedures, streamlining the management of large networks. Routers can make routing decisions more efficiently using a single CIDR notation to represent multiple subnets. This process also reduced the size of routing tables, making the routing process faster and more reliable.
4. Granular Control over IP Address Allocation
CIDR allows network administrators to precisely define their subnets, catering to the specific needs of different departments or divisions within an organization. This granular control ensures better security and easier management of devices and resources within each subnet.
5. Easy Address Aggregation
CIDR facilitates address aggregation, or supernetting, where multiple smaller subnets have been merged into larger supernets. This aggregation simplifies routing decisions and reduces the number of entries in routing tables, enhancing network performance and scalability.
6. Support for the IPv6 Transition
CIDR not only enhanced IPv4 addressing but also played an important role in the transition to IPv6. The principles of CIDR were adopted in the design of IPv6, allowing for a more efficient and flexible allocation of the vast IPv6 address space.
7. Addressing the Classful System Limitations
The classful addressing system imposed rigid boundaries on IP address allocation, leading to inefficiencies and address space wastage. With its classless approach, CIDR eliminated these limitations and provided a scalable and adaptable solution for the ever-expanding internet.
8. Facilitating Subnet-Based Security
Implementing CIDR notation enables administrators to implement more effective security measures at the subnet level. This allows for utilizing access controls and firewalls based on CIDR notation to protect or isolate specific groups of devices from certain network activities.
CIDR Blocks and Prefix Lengths
CIDR blocks indicate a range of IP addresses with the same prefix length. The prefix length determines the number of bits utilized for the network component of the IP address. Shorter prefix lengths suggest bigger subnets with more accessible host addresses, whereas longer prefix lengths denote smaller subnets with fewer available host addresses.
For example:
- A subnet with a CIDR block prefix length of /24 has 256 (2^8) available IP addresses. Out of these, 254 addresses can be utilized by hosts, excluding network and broadcast addresses.
- With 65,536 (2^16) available IP addresses, a CIDR block with a prefix length of /16 denotes a bigger subnet and offers greater address space.
CIDR blocks are required for Internet routing to be efficient. Network administrators can combine many smaller IP address blocks into bigger CIDR blocks, lowering the number of entries in routing tables. This aggregation optimizes routing and aids in controlling the growth of the global routing table.
CIDR Subnetting
Subnetting is a key concept in Classless Inter-Domain Routing) that allows network administrators to divide a big IP address block into smaller, more manageable subnetworks. It is required for effective IP address allocation and aids in network organization and security.
Subnetting Fundamentals
Subnetting is the process of dividing a single IP address block into multiple smaller blocks, each known as a subnet. It begins by borrowing bits from the IP address’s host section to construct a subnet mask, which defines the boundary between the network and host portions of an IP address.
It allows administrators to create distinctive broadcast domains, optimize network traffic flow, and improve security by isolating devices and services within smaller, self-contained subnets.
Subnetting is based on the idea of prefix lengths, expressed as “/X,” where X is the number of bits in the subnet mask set to 1. The prefix length defines the subnet’s size and the number of possible host addresses within each subnet.
Subnet Mask Calculation
Network administrators calculate the number of subnets and the number of hosts necessary in each subnet to accomplish subnetting. They compute the proper subnet mask based on these requirements.
The steps in the process are as follows:
- Determine the number of subnets needed.
- Determine the host addresses required per subnet (including network and broadcast addresses).
- Find a nearby power of 2 equal to or greater than the number of subnets and hosts required.
- Calculate the subnet mask using the number of bits taken from the IP address’s host section. In CIDR notation, the subnet mask is frequently expressed as “/X,” where X is the number of bits set to 1. Additionally, you can use a subnet calculator tool.
For example, suppose a network has 8 subnets, each requiring 30 host addresses. In that case, the subnet mask is calculated to give adequate address space for the needed hosts in each subnet while minimizing IP address wastage.
Understanding Supernetting
Supernetting, also known as route aggregation, aggregates numerous smaller contiguous IP address blocks into a single bigger block. This is accomplished by utilizing a common prefix for all smaller subnets. As a result, the routing table is simplified since individual routes are replaced with a single route entry that covers all aggregated subnets.
Instead of advertising separate routes for numerous smaller subnets (e.g., 192.168.1.0/24, 192.168.2.0/24, and 192.168.3.0/24), a network administrator might supernet these subnets into a larger block (e.g., 192.168.0.0/22). The /22 prefix length covers all of the smaller subnets, reducing the size of the routing table and improving routing efficiency.
When an organization has a high number of small subnets, supernetting is especially useful since it minimizes the number of entries in the global routing table, resulting in quicker and more efficient routing across the Internet.
Comparison of CIDR in IPv6 over IPv4
| Aspect | IPv6 | IPv4 |
| Address Length | 128 bits | 32 bits |
| Address Notation | Hexadecimal (e.g., 2001:0db8:85a3:0000:0000:8a2e) | Dotted-decimal (e.g., 192.168.1.1) |
| Address Space | 2^128 (approximately 3.4 x 10^38 addresses) | 2^32 (approximately 4.3 billion addresses) |
| Address Assignment | Developed for effective hierarchical allocation. | Classful and classless allocations are less efficient. |
| Routing Efficiency | A hierarchical structure allows for better routing. | Although there is a hierarchical structure, address space is limited. |
| Network Topology | Simplified and streamlined for easy maintenance. | More complicated and can result in address exhaustion. |
| Subnetting | Because of the larger address space, subnetting is considerably easier. | Smaller address spaces may need more frequent subnetting. |
| Address Configuration | SLAAC (Stateless Address Autoconfiguration) is used. | DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) is used. |
| Address Types | This includes link-local, site-local, global unicast, multicast, and so on. | restricted to multicast and unicast addresses. |
| Security | Secure communication is supported via built-in IPSec. | Security features added afterward (e.g., VPN, TLS) |
Conclusion
Congratulations, explorers of the digital frontier! Discover how CIDR facilitates efficient communication and conserves IP addresses. Mastering CIDR notation and subnetting empowers you to navigate the interconnected world. Next time you email, stream, or surf, remember CIDR’s seamless magic. Venture forth with this knowledge and embrace the wonders of the digital realm. Your innovative ideas might revolutionize the Internet’s future.
FAQ
Q1. What is the difference between CIDR and traditional IP addressing?
Ans: Traditional IP addressing relied on fixed and rigid class-based allocation, leading to address wastage. Conversely, CIDR allows flexible and precise allocation through subnetting, optimizing address usage, and simplifying routing.
Q2. Is IPv6 related to CIDR?
Ans: Indeed! CIDR paved the way for the adoption of IPv6 as the depletion of IPv4 addresses became imminent. IPv6, with its vast address space, relies heavily on CIDR principles to manage addresses efficiently.
Q3. How does CIDR affect Internet routing?
Ans: CIDR reduces the size of routing tables by aggregating multiple smaller subnets into larger blocks. This simplifies routing decisions, making the Internet’s backbone more manageable and efficient.
Q4. Can CIDR help conserve IPv4 addresses?
Ans: Absolutely! CIDR’s efficient allocation and aggregation practices help conserve the dwindling pool of available IPv4 addresses, ensuring they are used wisely.
Q5. Can CIDR be used with both IPv4 and IPv6 addresses?
Ans: Absolutely! While CIDR was initially introduced for IPv4 addresses, it also works like a charm with IPv6 addresses! So whether you’re working with the old, familiar IPv4 or the futuristic IPv6, CIDR has your back!
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “What is CIDR?” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,


