Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to Buffer Overflow
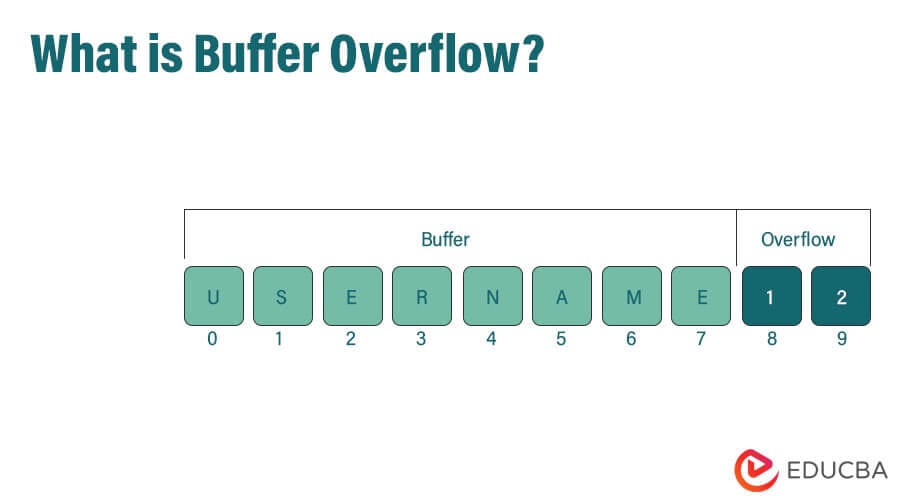
Buffer Overflow (or Buffer Overrun) is a state in which a computer application attempts to store more data in the buffer memory than its size permits. This can result in data being stored in adjacent storage, potentially overwriting existing data and leading to data loss or even a system crash. It is a common programming mistake and hackers often exploit this vulnerability to gain access to unsolicited data.
What’s Buffer Memory?
A buffer memory, also known as a buffer, is a sequential portion of the RAM that temporarily holds data while it is being transferred from one device to another, typically an input or output device. It compensates for differences in the speeds at which the devices operate. For example, while the latest i7 processor can execute a print command in nanoseconds, an outdated printer may not have such a fast processor. Therefore, the documents are held in the buffer memory and transferred to the printer at a speed it can accept. This frees up the CPU’s RAM for other tasks.
Buffer Overflow Attack
Once a vulnerability has been identified in the system, hackers are bound to exploit it and launch attacks through a buffer overflow. How does a hacker execute such an attack, and what are the consequences?
In a buffer overflow attack, the extra data includes instructions that are intended to trigger damaging activities such as corrupting files, changing data, sending private information across the internet, etc. An attacker injects surplus data into the buffer by taking advantage of any program that is waiting for certain user input.
Buffer overflow attacks can be primarily classified into two types:
- Stack-based: When the attack is on stack-based memory allocation. This is simpler to exploit and thus more susceptible to attacks.
- Heap-based: When the attack is on heap-based memory allocation. This is not easy to exploit and thus far less frequent.
The languages most vulnerable to buffer overflow attacks are C, C++, Fortran, and Assembly. They use stack-based memory allocation techniques.
Buffer Overflow: The Cure
Once data has been corrupted, there is no simple cure to restore it to its original state. Moreover, the intensity of the attack largely determines the appropriate course of action. If the attack is small-scale and only affects a portion of an isolated machine’s memory, a simple system format may be sufficient to remedy the situation. However, if the attack is widespread and has compromised data across multiple machines, formatting the entire network will not be effective unless the program injecting the malicious code is fixed.
Prevention is Better than Cure
It is the responsibility of developers to check for buffer overflows in our code. Handling buffer overflows in the code itself can prevent the security of the system from being prone to such attacks.
There are some simple precautionary steps that can help prevent buffer overflows:
- Using exception handling to detect buffer overflows and prevent code execution in the event of one.
- Allocate large enough size to buffers to properly handle un-intended large volumes of data.
- Avoid using library functions or third-party methods that are not bound-checked for buffer overflows. Common examples of such functions to avoid are gets(), scanf(), strcpy(), especially in C/C++ language.
- Code testing should account for such vulnerabilities and rigorously test the code to identify and fix bugs that may lead to overflow.
- Modern programming languages, operating systems, and code compilers have evolved to automatically detect buffer overflows and stop the command execution in such cases. This has become the most reliable way to detect buffer overflows automatically.
Try it Yourself
Disclaimer: The following program is for demonstration purposes only and should not serve to cause harm in any way. Any resemblance to malicious code is purely coincidental. Additionally, modern operating systems come with buffer-attack-preventive measures.
Below is a C program that could potentially cause a buffer overrun. The choice of language is C because more advanced programming languages have been developed to deal with buffer overruns during compile time. However, even modern C compilers have certain checks in place to avoid detecting buffer overflows. If such an overflow were to occur, you would receive an error message indicating a buffer overrun detection.
Code:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
char mybuffer[8];
// copy the user input to mybuffer, without any bound checking
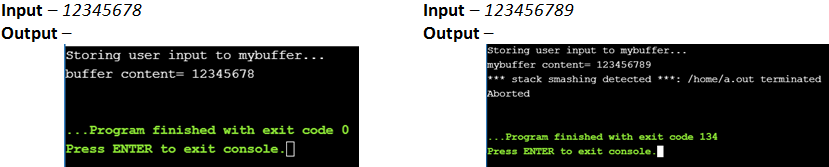
printf("Storing user input to mybuffer...\n");
strcpy(mybuffer, argv[1]);
printf("mybuffer content= %s\n", mybuffer);
return 0;
}
Output:
What happens when the program receives the command-line argument “123456789”? The compiler will detect the buffer overflow, causing the program to generate an error. Modern compilers and operating systems have an additional layer of protection in the form of variables called “Canaries”. These variables are initialized to certain values during compile time and stored in adjacent memory units to the buffer. When the buffer overflows, the extra data flows into the adjacent memory and corrupts the value of the Canaries. As soon as a corrupt Canary comes under detection, the system aborts the execution.
Another example in C++ Language:
Code:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
char buf[8];
cin>>buf;
return 0;
}
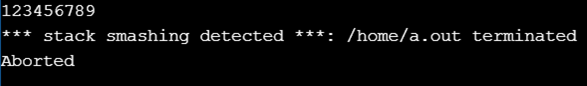
Input: 123456789
Output:
Conclusion
Buffer overflow makes a system vulnerable to hackers and allows them to take control of the system. Buffer handling is paramount during the writing and testing of the code, as it ensures the code is secure and immune to attacks.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further articles for increasing understanding: