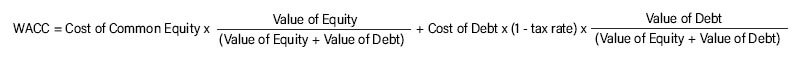Updated August 9, 2023
Part – 9
Our last tutorial taught us the basics for calculating the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). Now, we will proceed to understand it further.
Use the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) to determine the appropriate discount rate range. Principally, nominal free cash flows should be discounted by a nominal rate and the real flows by the real rate.
Definition of WACC
This WACC is the weighted average of the after-tax cost of a company’s debt and the cost of its equity. WACC analysis assumes that capital market investors (debt and equity) in any given industry require returns commensurate with the perceived riskiness of their investment.
What is the Weighted Average Cost Of Capital (WACC)?
One of the best and most commonly used measures of the riskiness of projected cash flows (and the best way to determine the correct range of discount rates) is the Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC). This WACC is the weighted average of the after-tax cost of a company’s debt and the cost of its equity. WACC analysis assumes that capital market investors (debt and equity) in any given industry require returns commensurate with the perceived riskiness of their investment.
WACC Definition of Formula
A simple overview of a company’s WACC calculation is as follows:
- There is no charge on the income statement, which reflects the cost of equity (as interest expense is associated with debt). The concept of taxation does not apply to equity.
- Not net debt, but rather the market value of debt.
The cost and proper weighting of each type of financing must be included in a WACC calculation. For example, if a portion of the company’s capital structure is preferred equity, its cost, and proper weighting must be factored into the WACC, debt, and equity cost.
Note that the cost of preferred equity is usually its dividend yield.
A company’s optimal capital structure typically includes a proportion of debt; debt is cheaper than equity, and the interest payments on debt are tax-deductible, resulting in a ‘tax shield’. Note that you should use a target level of debt to represent its optimal capital structure. The structure implied from a company’s balance sheet may differ from its long-term optimal capital structure. As such, the calculation may need to be adjusted over time if the capital structure changes.
Step 10 – WACC: Calculate the Cost of Debt
You can’t just go to a company’s annual report and capture their cost of debt for use in your WACC calculation. The cost of debt in the annual report is historical and may not reflect your choice of debt-equity mix in your WACC or future debt cost. You must find the company’s future cost of debt for the credit rating implied by the debt-equity mix in your WACC.
Method 1: Yield to Maturity Approach (Only for Public Debt)
Determine the Weighted average of current yields to maturity on all issues in the target capital structure. The yield to maturity incorporates the market’s expectations of future returns on debt and should be used instead of the coupon rate
Method 2: Credit Rating Approach
First, determine the credit rating the company would have given your assumed debt-equity mix. S&P, Moody’s, and other credit rating services publish ratio guidelines for different credit ratings. The rating guidelines change frequently, so check for the latest information. Once you have the credit rating, check Bloomberg for yield to maturity on publicly traded long-term bonds with the same credit rating.
The difference between a company’s cost of debt and the benchmark rate (LIBOR/Government Bond) is the Spread.
Method 3: Synthetic Rating Method
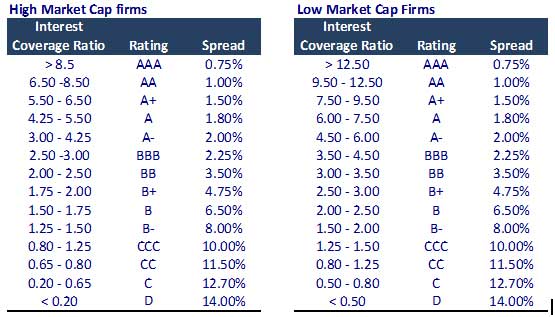
One must calculate the implied synthetic default spread if the company bonds are not listed.
Calculation of Synthetic Default Spread
- Calculate the interest coverage ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense.
- Derive the Synthetic default spread, as per the table below.
Method 4: Company Report Method (Spot Check!)
Find the interest rate on each debt from the annual/quarterly report. The cost of debt may be historical, but it may provide a good double-check.
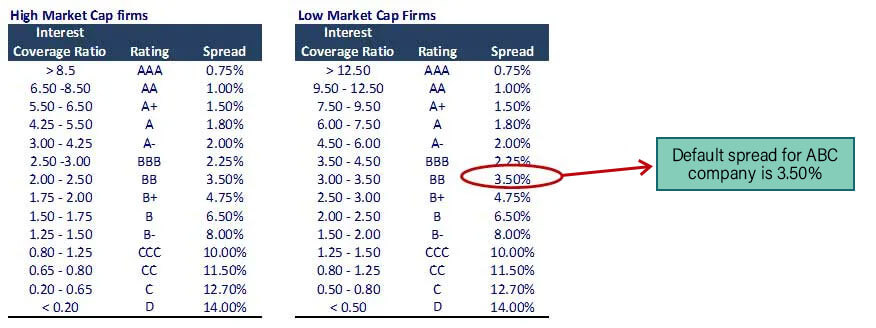
Cost of Debt Calculation for Company ABC
Using the synthetic rating method, we have an interest coverage ratio = EBIT / Interest Expense.
Interest Expense for ABC company (small cap $ 257 million) is 15. Interest coverage ratio = 50/15 = 3.33
Pre tax cost of debt = Risk-free rate + default spread = 5.0% + 3.50% = 8.50%
Post tax cost of debt = 8.50% × (1-33%) = 5.70%
What’s Next?
In this article, we have understood the concept of WACC. Next, we will look at the cost of equity.
Recommended Articles
Here are some further articles to learn more: