Updated May 31, 2023
Introduction to VI Editor in Unix
VI Editor is a kind of text editor that is available in the UNIX operating system, and it is the default editor that comes with the UNIX operating system, which is used to create a new file or editing an existing file and offering rich, user-friendly features, which are available in almost all the UNIX distribution systems. The capabilities incorporated into the tool, which opens the door to the endless possibilities used to edit a file, renders the tool a unique position among all the editors, including pico, nano, vile, in UNIX, is termed as VI Editor in the UNIX operating system.
Modes of VI Editor in Unix
To have an easy working experience with the VI editor, we need to understand the different modes of operations of the VI editor.
They are divided into three main parts:
- Command Mode
- Insert Mode
- Escape Mode
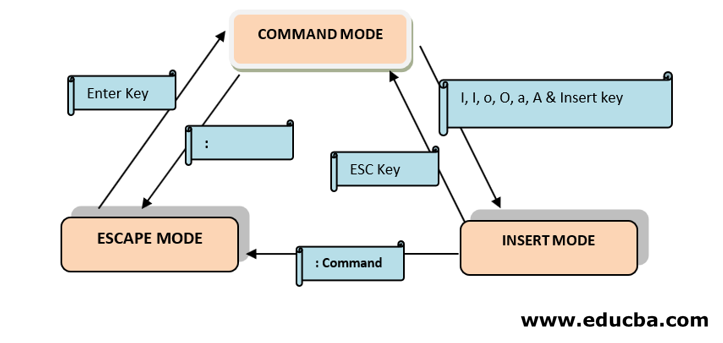
1. Command Mode
Command Mode is the first screen of the VI editor. It is case sensitive. Any character that is typed during this mode is treated as a command. These character are not visible on the window. We can cut, copy, paste, or delete a piece of text or even move through the file in this mode
[ESC] used to enter the Command Mode from another mode (Insert Mode)
2. Insert Mode
We can easily move from Command mode à Insert mode by pressing the ‘i’ or ‘Insert’ key from the keyboard. Characters typed in this mode are treated as input and add text to your file
Pressing ESC will take you from Insert Mode -> Command Mode
3. Escape Mode
Press [:] to move to escape mode. This mode is used to save the files & execution of the commands.
Fig : Blue Box Represents the various modes on the VI editor
Green Box Represents the keys/commands to move from one mode to another
Syntax of VI Editor in Unix
VI Editor has various features for easy editing in the Linux environment. The basic purpose of highlighting these commands and their syntax is to familiarize oneself with the availability of various features. We do not need to mug up all the commands. You can refer to the main pages for the details of the commands and the options.
Now let us get going on the same:
1. Open/ Create a File
This will create a file with the name ‘filename’ or open the file with the name ‘filename’ if it already exists.
Output:
2. Read-Only Mode
To open the file in read-only mode, use the following:
Output: At the bottom of the file, you will see ‘Readonly.’
3. Moving out of a file
| :q | Quit out of a file |
| :q! | Quit the file without saving the changes |
| :w | Save the content of the editor |
| :wq | Save the changes and quit the editor (*Combing the commands: q &: w) |
| ZZ | In command mode, this works similarly to wq |
4. Rename a File
:w newFileName – This will rename the file you are currently working into ‘new filename’. A command is used in Escape Mode.
5. Move within a file
To move around in a file without actually editing the content, we must be in Command mode and keep the below commands handy.
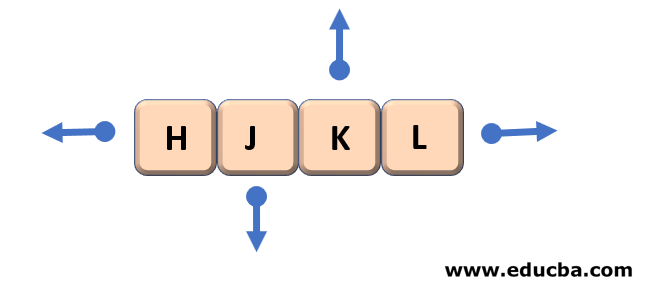
| h | Moves the cursor left one character position |
| l | Moves the cursor right to one character position |
| k | Moves the cursor one line up |
| j | Moves the cursor one line down |
**Arrows can help you remember the functionality of that key. It has no other significance.
Keyboard keys for movements within the editor.
Example: 2j will move the cursor two lines down from the current cursor location\
6. Inserting or Adding Text
Following is the command used to put the editor in the insert mode.
Once the ESC is pressed, it will take the editor back to command mode.
| i | Insert text before the cursor |
| I | Insert at the beginning of the current line |
| a | Append after the cursor |
| A | Append at the end of the current line |
| o | Open & places the text in a new line below the current line |
| O | Open & places the text in a new line above the current line |
7. Searching the Text
Similar to the find & replace command in the windows editor, we also have certain Search & replace commands available in the VI editor.
| /string | Search the mentioned ‘String’ in the forward direction |
| ?string | Search the mentioned ‘String’ in the backward direction |
| n | Move to the next available position of the searched string |
| N | Move to the next available position of the searched string in the opposite direction |
8. Determining the Line Number
Having the line number is very useful sometimes while editing the file. These commands are used in Escape Mode that is after pressing the [:] key
| :.= | Line Number of the current line |
| := | Gives the total number of lines |
| ^g | Gives the line number along with the total number of lines in a file at the bottom of the screen |
9. Cutting & Pasting Text
These commands allow you to copy and paste the text
| yy | Copy (yank, cut) the current line into the buffer |
| Nyy or yNy | Copy ‘N’ lines along with the current line into the buffer |
| p | Paste / Put the lines in the buffer into the text after the current line |
Conclusion
Due to the availability of the VI editor in all the Linux environment, learning the VI editor can be really useful. It can help us in creating and editing the scripts. We must be familiar with the commands along with the particular mode in which that command is to be used. This is not the end of the options available in VI editor keep exploring as the challenge comes your way.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “VI Editor in Unix” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.