Introduction to Java
Java is a high-level programming language initially created by Sun Microsystems and discharged in 1995. It is a broadly helpful computer programming language that is simultaneous, class-based, object-oriented, and explicitly designed to get usage conditions expected under the circumstances. It is proposed to provide application designers with “write once, run anyplace” (WORA), implying that the aggregated Java code can continue executing all phases that support Java without the prerequisite for recompilation. Any equipment or programming condition where a program runs is a platform. Java earns a platform designation due to its inclusion of a runtime environment (JRE) and API. This article will cover the different versions of Java with their functionality.
Top 10 Versions of Java with Features
Below, we will learn different versions of Java with its various features:
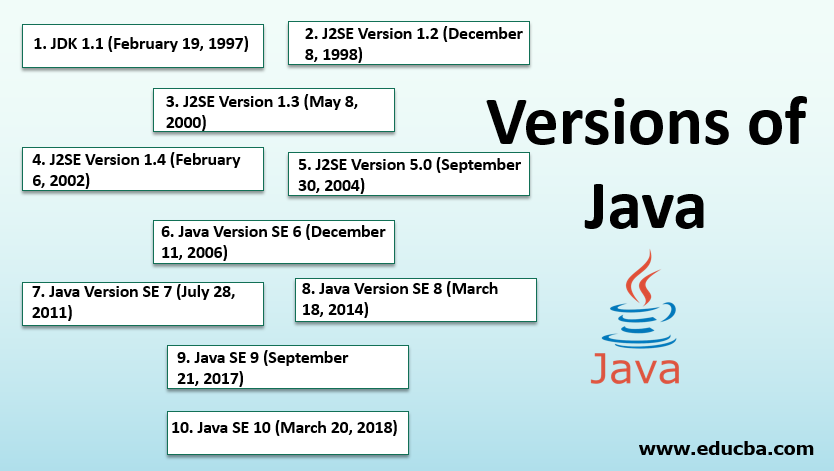
1. JDK 1.0 (January 23, 1996)
Features:
- Java programming language
- AWT (Abstract Window Toolkit)
- Applet support
- Basic I/O
- Networking support
- Standard library
- Security (sandbox model)
2. JDK 1.1 (February 2, 1997)
Features:
- The idea of the Inner Class
- JavaBeans
- JDBC
- RMI
- Reshaped AWT event model
- JIT (Just In Time) compiler: Used on Microsoft Windows stages, developed for JavaSoft by Symantec
- Internationalization and Unicode support beginning from Taligent
3. J2SE Version 1.2 (December 4, 1998)
Features:
- Collections structure.
- Java String memory map for constants.
- JIT (Just In Time) compiler.
- Jar Signer for marking Java Archive (JAR) records.
- Policy Tool for allowing access to framework assets.
- Java Foundation Classes (JFC) comprises Swing 1.0, Drag and Drop, and Java 2D class libraries.
- Java Plug-in
- Scrollable result sets, BLOB, CLOB, user user-characterized types in JDBC
- Audio help in Applets
4. J2SE Version 1.3 (May 8, 2000)
Features:
- Java Sound
- Jar Indexing
- Huge list of advancements for improving the Java area.
5. J2SE Version 1.4 (February 13, 2002)
Features:
- XML Processing
- Java Print Service
- Logging API
- Java Web Start
- JDBC 3.0 API
- Assertions
- API preferences
- IPv6 Support
- Regular Expressions
- Image I/O API
6. J2SE Version 5.0 (September 29, 2004)
Features:
- Generics
- Enhanced for Loop
- Autoboxing/Unboxing
- Typesafe Enums
- Static Import
- Metadata (Annotations)
- Instrumentation
7. Java Version SE 6 (December 11, 2006)
Features:
- Scripting Language Support
- JDBC 4.0 API
- Java Compiler API
- Pluggable Annotations
- Java GSS, Kerberos and LDAP support
- Incorporated Web Services
- Many more improvements
8. Java Version SE 7 (July 28, 2011)
Features:
- Strings in switch Statement
- Type Inference for Generic Instance Creation
- Different Exception Handling
- Backing for Dynamic Languages
- Attempt with Resources
- Java NIO Package
- Binary Literals underscore in literal
- Null Handling
9. Java Version SE 8 (March 18, 2014)
Features:
- Lambda Expressions
- Pipelines and Streams
- Date and Time API
- Default Methods
- Type Annotations
- Nashhorn JavaScript Engine
- Concurrent Accumulators
- Parallel operations
- TLS SNI
10. Java SE 9 (September 21, 2017)
Features:
- Modularization of the JDK under Project Jigsaw
- Given Money and Currency API
- Reconciliation with JavaFX
- Java usage of reactive streams
- More Concurrency Updates
- Provided Java Linker
- Programmed scaling and measuring
11. Java SE 10 (March 20, 2018)
Features:
- Local Variable Type Inference
- Exploratory Java-Based JIT Compiler incorporates the Graal dynamic compiler for the Linux x64 stage.
- Time-sensitive Release Versioning
- Parallel Full GC for G1
- Garbage collector Interface
- Extra Unicode Language-Tag Extensions
- Root Certificates
- String Local Handshakes
- Remove the Native-Header Generation Tool – Java
- Combine the JDK Forest into a Single Repository.
12. Java SE 11 (September 25, 2018)
Features:
- Local-variable syntax for lambda parameters
- Epsilon: A no-op garbage collector
- HTTP client (standard)
- Deprecating and removing older features
- Flight recorder
- ZGC: A scalable, low-latency garbage collector
- Single source-file launch
- Low-pause-time heap profiling
- Dynamic class-file constants
- Nest-based access control
- Launch single-file source-code programs
- Deprecate and remove the Applet API
- Deprecate and remove the CORBA modules
- Flight Recorder: A profiling tool for production environments
- Z Garbage Collector (ZGC): Low-latency garbage collector
- Implement HTTP/2
- Transport Layer Security (TLS) 1.3
13. Java SE 12 (March 19, 2019)
Features:
- Switch Expressions (Standard)
- Shenandoah: A Low-Pause-Time Garbage Collector (Experimental)
- Microbenchmark Suite
- Default CDS Archives
- Abortable Mixed Collections
- Promptly Return Unused Committed Memory
- One AArch64 Port, Not Two
14. Java SE 13 (Sepetember 17, 2019)
Features:
- Text Blocks
- Switch Expressions (Standard Feature)
- New Features in APIs
- File Systems
- Socket APIs
- Dynamic CDS Archives
- ZGC: Uncommit Unused Memory
- Reimplement the Legacy Socket API
- Deprecate and Remove RMI Activation
15. Java SE 14 (March 17, 2020)
Features:
- Pattern Matching for instanceof
- Records
- Switch Expressions Enhancements
- Text Blocks
- Foreign Function and Memory API (Incubator)
- Helpful NullPointerExceptions
- Packaging Tool (Incubator)
16. Java SE 15 (September 16, 2020)
Features:
- Sealed Classes
- Pattern Matching for instanceof
- Text Blocks
- Hidden Classes
- Foreign Function & Memory API
- Unix-Domain Socket Channel
- Z Garbage Collector (Experimental)
- Deprecations and Removals
- Preview Features
17. Java SE 16 (March 16, 2021)
Features:
- Records and Pattern Matching for instanceof
- Unix-Domain Socket Channel
- Foreign Function & Memory API (Incubator)
- Vector API (Incubator)
- Strong encapsulation of JDK internals
- New macOS rendering pipeline (Metal)
18. Java SE 17 (September 14, 2021)
Features:
- Sealed Classes
- Pattern Matching for switch
- Strong encapsulation of JDK internals
- Deprecating and removing older features
- Foreign function and memory API (Incubator)
- Unix-domain socket channel (Incubator)
19. Java SE 18 (March 22, 2022)
Features:
- Records
- Pattern Matching for a switch (Preview)
- Sealed Classes (Preview)
- Vector API (Incubator)
- Foreign Function and Memory API (Incubator)
- Deprecate the Applet API for Removal
20. Java SE 19 (September 20, 2022)
Features:
- Enhanced Pseudo-Random Number Generators
- Foreign Function and Memory API (Second Incubator)
- Enhanced Java Language Support for Pattern Matching
- Enhanced Java Language Support for Records
- Enhanced Vector API (Incubator)
- Enhanced Stream API – Enhanced Security
- Enhanced JFR (Java Flight Recorder) Events
- Enhanced JFR (Java Flight Recorder) Streaming
21. Java SE 20 (March 21, 2023)
Features:
- Enhanced Switch Expressions (Standard)
- Text Blocks (Second Preview)
- EdDSA (RFC 8032) and Edwards
- Curve Digital Signature Algorithm
- Unix-Domain Socket Channels
- Foreign Function and Memory API (Final)
- Dynamic CDS Archives (Experimental)
- Removal of the Java EE and CORBA Modules
22. Java SE 21 (September 19, 2023)
Features:
- HTTP Client (Standard) – Records (Second Preview)
- Sealed Classes (Final)
- Enhanced Pattern Matching for instanceof
- Enhanced Pseudo-Random Number Generators (Final)
- Strongly Encapsulate JDK Internals by Default (Preview)
- Removal of the Nashorn JavaScript Engine
Conclusion – Versions of Java
The Java programming language is object-oriented, class-based, simultaneous, verified, and universally helpful. Developers can create applications on your computer. Java projects are translated by the Java Virtual Machine (JVM), which runs on various platforms. This implies all Java programs are multiplatform.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “Versions of Java” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


