Excel VBA XML
The full form of XML is eXtensible Markup Language which is much like an HTML file, is designed to store and transport the data from different programs. XML file stores the data which includes the splits and separators. We can create a VBA code by which we can import the data from the XML file into Excel. In order to import the data from the XML file to any other format, we need to set some rules which tells what kind of data and fields can be used in the XML file. To create a macro in VBA for the XML file, we do not mandatory need XML Notepad in our system. But if we have it will be easy for us to read the XML file for the data we need.
Although in Excel, we have a provision of importing the data of XML file but using VBA, we can read, import the XML file in Excel.
Types of Node in VBA XML
In XML, we have a variety of Nodes that constructively helps in reading and parsing the XML file into other sources such as Word or Excel. Each DocumentElement refers to some of the nodes lists below.
- Parent Node
- First Child
- Last Child
- Child Nodes
- Next Sibling
- Previous Sibling
All the above-mentioned nodes confirm the type as [XDoc.DocumentElement], where only Child nodes are the array type of [XDoc.DocumentElement].
In this example, we will see a very simple VBA Code to access the XML file saved in the individual system’s any location and load them into VBA. Usually, to import XML files in Excel using VBA, we have MSXML2.DOMDocument object to allow us to transverse the data through XML structure. But this may not be used in this example.
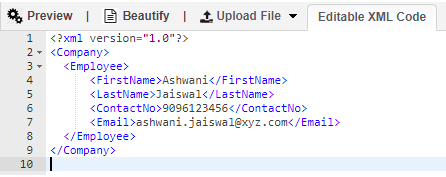
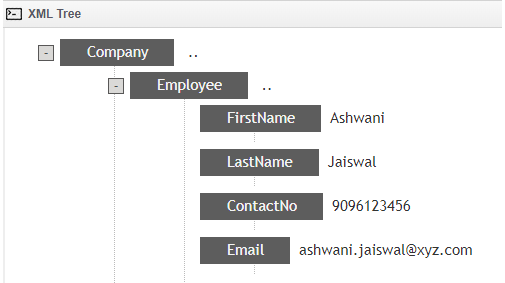
For this, we must have an XML file in which we can create a data structure in the form of Schema. Below is the screenshot of Company schema where under that we have Employee branch with the employee details like First Name, Last Name, Contact Number, Email ID.
Steps to Import & Add XML in Excel VBA
Below are the examples of XML in Excel by using the VBA Code.
Example #1
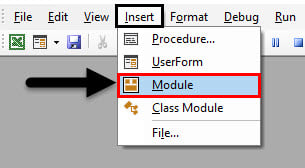
Step 1: First go to Insert menu tab in VBA and open a Module where we will be writing the code transverse data through XML as shown below.
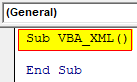
Step 2: Write the subprocedure in the name of VBA XML for the definition of the code.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() End Sub
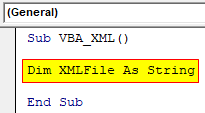
Step 3: As we already discussed, for the XML file we will require Object. So, Now define a variable using DIM as String which will be used for storing the File name.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim XMLFile As String End Sub
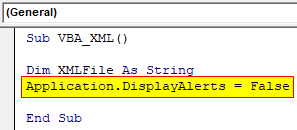
Step 4: Now we will use an application Display Alerts which is used for showing the alert message if the chosen path is incorrect.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim XMLFile As String Application.DisplayAlerts = False End Sub
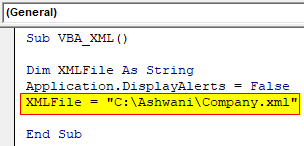
Step 5: Now we will put the link or location where we have kept XML file and assign it to the defined variable.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim XMLFile As String Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" End Sub
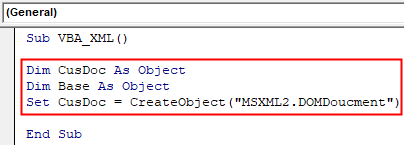
Step 6: As we discussed, we will get the first Object with MSXML2.DOMDoucment.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim CusDoc As Object Dim Base As Object Set CusDoc = CreateObject("MSXML2.DOMDoucment") End Sub
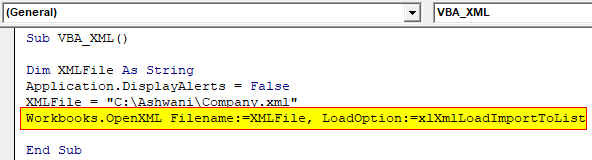
Step 7: To load the data of XML file in Excel, we need to open that XML file, using the name and location which we have stored in XML File variable and select the load option as Import to List as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim XMLFile As String Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Workbooks.OpenXML Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList End Sub
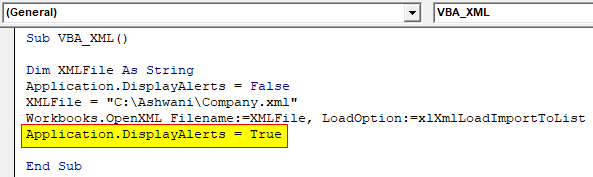
Step 8: At last, again use the Application option to display the alert as TRUE if there is any.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML() Dim XMLFile As String Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Workbooks.OpenXML Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
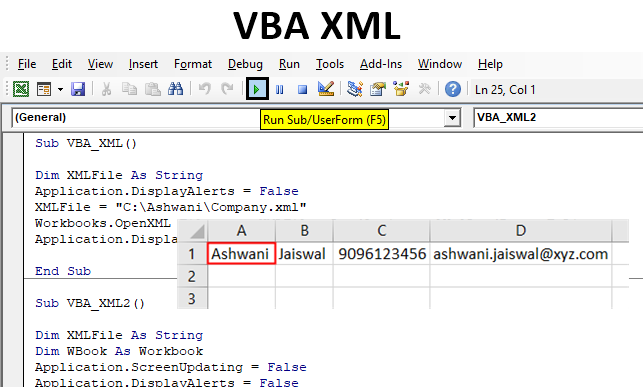
Step 9: Now we will compile the written code by pressing F8 functional key and run it, if there is no error found during compilation.
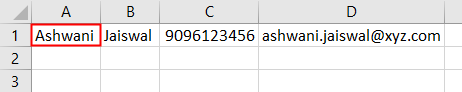
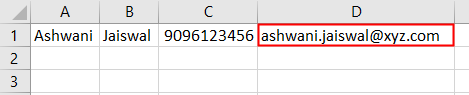
We will see, the data stored in the XML file is not imported in a new workbook as shown below. We can fetch any length of data of XML file into Excel using this simple VBA Code.
Example #2
There is another way to import the data of an XML file using the VBA Code which is simple too. For this, we can have another module of we can make the changes in the same module as well.
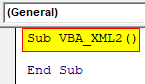
Step 1: For this again we would require a module and there write the subprocedure in the name of VBA XML.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() End Sub
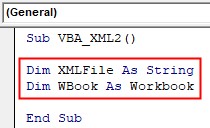
Step 2: Define a variable as String where we will be storing the file location and another variable for Workbook as shown below.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook End Sub
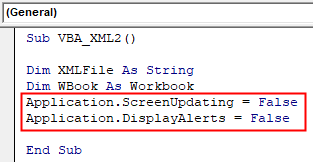
Step 3: Now similar to the previous example we will now use 2 Applications, one of Screen updating and other for Display Alerts as FALSE.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False End Sub
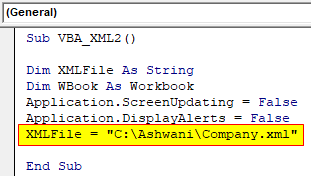
Step 4: Now in the defined variable XMLFile, we will assign the path of the XML file.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" End Sub
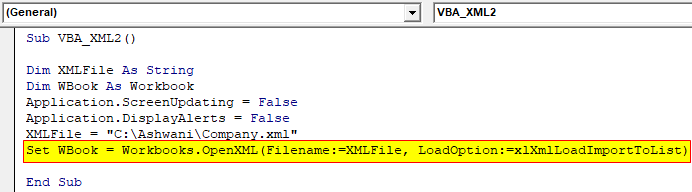
Step 5: Similar to example-1, we will now update set the code for Opening XML file with the path defined in XMLFile variable and load the data Import to list.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Set WBook = Workbooks.OpenXML(Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList) End Sub
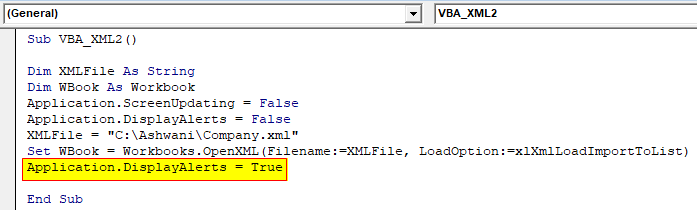
Step 6: Now again to put the Display alert application as TRUE.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Set WBook = Workbooks.OpenXML(Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList) Application.DisplayAlerts = True End Sub
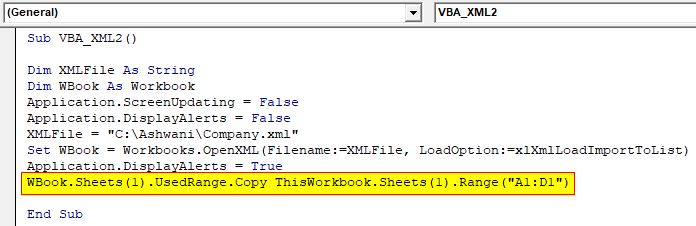
Step 7: Once the data is imported we will copy that into another workbook from the selected cell A1:D1 as per the number of headers available in the XML file.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Set WBook = Workbooks.OpenXML(Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList) Application.DisplayAlerts = True WBook.Sheets(1).UsedRange.Copy ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1:D1") End Sub
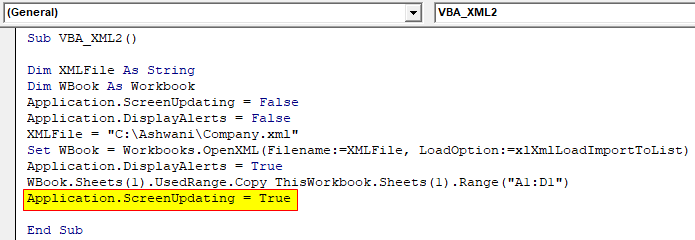
Step 8: At last close the code using Screen updating application as TRUE.
Code:
Sub VBA_XML2() Dim XMLFile As String Dim WBook As Workbook Application.ScreenUpdating = False Application.DisplayAlerts = False XMLFile = "C:\Ashwani\Company.xml" Set WBook = Workbooks.OpenXML(Filename:=XMLFile, LoadOption:=xlXmlLoadImportToList) Application.DisplayAlerts = True WBook.Sheets(1).UsedRange.Copy ThisWorkbook.Sheets(1).Range("A1:D1") Application.ScreenUpdating = True End Sub
Step 9: Now if we run this code, we will see the data from the XML file will get imported into a new Excel workbook as shown below.
Pros of VBA XML
- Even if you do not know how to create an XML file and work on it, using such VBA codes, we can extract the data into VBA Code or in Excel.
- We can parse a portion of XML Data or complete data into the VBA window by using node references.
Things to Remember
- Every node reference has its own value and meaning. Using the right note type is very important for every condition.
- XML to VBA is not limited to the code which we have seen in the above examples.
- We can extract any type of data using the code which we have seen in above-discussed examples. But keep the proper location and path which is easy to access.
- We can also extract the XML file data without opening it from the developer tab’s Source option. This will help us to get the data as it is into the Excel workbook.
- Save the written code Excel file in Macro enabled excel format, to avoid losing the code.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the VBA XML. Here we discuss Steps to Import & Add XML in Excel VBA and its different types of node along with practical examples and downloadable excel template. You can also go through our other suggested articles –