Updated March 23, 2023
What is UNION Operator in Oracle?
The UNION operator in oracle database combines the result set which is returned by two or more Oracle SELECT statements into a single result set by removing the duplicate rows between various SELECT statement that are under the UNION operator and also the SELECT statement that is present within the UNION operator also should have the same number of fields with same data types in the result set returned by the SELECT statement.
Points of Concentration:
- The queries are all executed independently, but their output is merged.
- Only the final query ends with a semicolon ‘;’
Syntax:
SELECT col_1, col_2, ..., col_n FROM TableName WHERE condition(s)
UNION
SELECT col_1, col_2, ..., col_n FROM TableName WHERE condition(s) ;
Description:
- Col_1/2/n: The column(s) or calculation as per your requirement.
- Table Name: As per your requirement
- WHERE: It’s optional, depends on your requirement
Example:
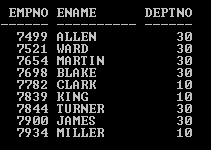
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno=10
UNION
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno=30
ORDER BY 1;
Output:
Rules and Restrictions of Oracle UNION Operator
Before implementing of UNION operator, one must know some important rules and restrictions of the UNION operator which are listed below:
- The result sets of the queries must have the same number of columns.
- The data type of each column in the second result set must match the data type of its corresponding column in the first result set.
- The two SELECT statements may not contain an ORDER BY clause, but the final result of the UNION operation can be ordered.
- The column used for ordering can be defined through the column number.
- To sort the final result set, the SELECT statement can contain an ORDER BY clause but the last SELECT statement only can contain the ORDER BY clause.
Implementations of UNION Operator with Examples
In this section, we’ll see the implementation of a UNION operator and its behavior. For that, we will use the below table (Emp) with 14 records throughout the examples to understand the UNION operator behavior.
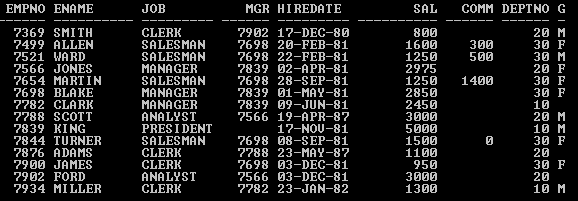
Query:
SELECT * from Emp;
Output:
1. UNION Operator without any Condition
Query:
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp
UNION
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM emp;
Output:
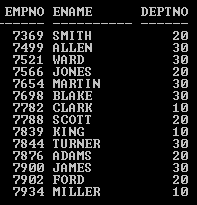
In this SQL SELECT statement with UNION operator, we got the same 14 records in which the EMP table consists because each SELECT statement generated an individual set of results but during the merge of the result sets, the UNION operator eliminated the duplicate records.
2. UNION Operator with WHERE Clause
Query:
SELECT ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
UNION
SELECT ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30;
Output:
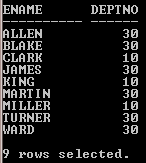
In this example, both the SELECT statements created a separate result set based on condition respectively and the UNION operator merged both the sets and displayed a final result with nine records in a single set which falls under deptno 10 & 30.
3. UNION Operator with Different Number of Columns
Query:
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
UNION
SELECT ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30;
Output:
![]()
As UNION operator Rules and Restrictions says that the result sets of all SELECT statements must have the same NUMBER of columns. But in this example first SELECT statement having three columns but the second SELECT statement having two columns. That’s why OUTPUT showing an incorrect number of result columns error.
4. UNION Operator with Invalid Column Name
Query:
SELECT dname, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
UNION
SELECT ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30;
Output:
![]()
Because the column name “Dname” does not exist in the Emp Table. That’s why got an invalid identifier.
5. UNION Operator with Mismatch Data Type
Query:
SELECT ename, hiredate, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
UNION
SELECT ename, job, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30;
Output:

UNION operator Rules and Restrictions says that the data type of each column in the second result set must match the data type of its corresponding column in the first result set. But in this example, column numbers are the same in both the result sets but the data type is mismatching with the result sets. First SELECT statement result set consisting column “Hiredate” which is DATE data type but the second result set consisting column “Job” which is VARCHAR2 data type it’s not matching. That’s why OUTPUT showing data type error.
6. UNION Operator with ORDER BY Clause
Query:
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
ORDER BY empno
UNION
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30 ;
Output:
![]()
In this example output throwing an ERROR even if the column number and data type criteria is matching with both the result sets. WHY THE ERROR?
In this example ORDER BY clause used by the first SELECT statement to sort the result set. But we can only use the OREDER BY clause in the last SELECT statement.
Query:
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 10
UNION
SELECT empno, ename, deptno FROM Emp WHERE deptno = 30
ORDER BY empno;
Output:
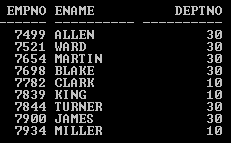
In this example OREDER BY clause used by the last SELECT statement to sort the result without any error.
TIP: In the ORDER BY clause, you can also use column position number instead of the column name. In some cases, UNION operation is costlier than other operations (join, subquery, etc.)
7. UNION Operator with NULL Column
Query:
SELECT Deptno, SUM(Sal) SalSum FROM Emp GROUP BY Deptno
UNION
SELECT NULL, SUM(Sal) FROM Emp;
Output:
Conclusion
UNION Operator performs VERTICAL Join and eliminates duplicate records. If you are looking for unique records, use UNION but column(s) number and data type must be the same.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to the UNION operator in Oracle. Here we discuss rules and restrictions along with various examples of UNION operators. You may also look at the following articles to learn more –

