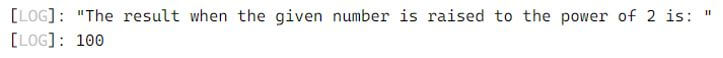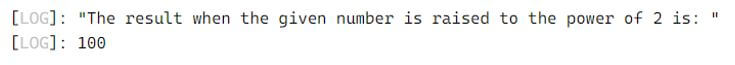Updated April 10, 2023
Introduction to TypeScript JSDoc
The Application Programming Interface documentation generator for TypeScript is JSDoc. In which the documentation comments are directly added to the source code on the right side of the code itself and there is a JSDoc tool to scan the source code and generate the HTML documentation and the purpose of JSDoc is to document the TypeScript library and by using JSDoc modules, classes, namespaces, methods, method parameters etc. can be documented and each comment in a JSDoc should begin with /** and end with */ otherwise the comment will not be recognized by the JSDoc parser and those beginning with /* or /*** will be ignored by the parser.
Syntax to declare a comment in TypeScript class:
** comment1
*comment2
*comment3
*commentn
*/Where comment1, comment2, comment3, commentn are the comments to be included in a TypeScript program.
Working of JSDoc or Comments in TypeScript
- The Application Programming Interface documentation generator for TypeScript is JSDoc in which the documentation comments are directly added to the source code on the right side of the code itself.
- There is a JSDoc tool to scan the source code and generate the HTML documentation.
- The purpose of JSDoc is to document the TypeScript library and by using JSDoc modules, classes, namespaces, methods, method parameters etc. can be documented.
- Each comment in a JSDoc should begin with /** and end with */ otherwise the comment will not be recognized by the JSDoc parser and those beginning with /* or /*** will be ignored by the parser.
Examples of TypeScript JSDoc
Given below are the examples of TypeScript JSDoc:
Example #1
TypeScript program to demonstrate JSDoc or the comments section to describe the functionality of the program along with the parameters using which we compute the power of a given number and display the output on the screen.
Code:
/** defining an anonymous function using arrow function to compute the power of a number and display the result as the output on the screen
*/
let power = (firstnum:number, secondnum:number) : number => {
return Math.pow(firstnum, secondnum);
}
console.log('The result when the given number is raised to the power of 2 is: ');
console.log(power(10,2));Output:
In the above program, the comments section is described between the symbols /** and */. Then we are defining an anonymous function using arrow function to compute the power of given number and display the result as the output on the screen.
Example #2
TypeScript program to demonstrate JSDoc or the comments section to describe the functionality of the program along with the parameters using which we compute the power of a given number and display the output on the screen.
Code:
/**
*Computes the power of a given number
*@constructor
*@param {number} firstnum – The number whose power raised to 2 must be found
*@param {number} secondtnum – The number 2 to which the given number must be raised to.
*/
function power(firstnum:number, secondnum:number)
{
let result = Math.pow(firstnum, secondnum);
return result;
}
console.log('The result when the given number is raised to the power of 2 is: ');
console.log(power(10,2));Output:
In the above program, the comments section is described between the symbols /** and */ in which we have defined that there is a function using @constructor and the parameters are defined with their datatypes using @param. Then we are defining a function using to compute the power of given number and display the result as the output on the screen.
Example #3
TypeScript program to demonstrate JSDoc or the comments section to describe the functionality of the program along with the parameters using which we compute the square root of a given number and display the output on the screen.
Code:
/**
*Computes the square root of a given number
*@constructor
*@param {number} firstnum – The number whose square root must be found
*/
function squareroot(firstnum:number)
{
let result = Math.sqrt(firstnum);
return result;
}
console.log("The square root of the given number is:\n", squareroot(4);Output:
In the above program, the comments section is described between the symbols /** and */ in which we have defined that there is a function using @constructor and the parameters are defined with their datatypes using @param. Then we are defining a function to compute the square root of a given number and display the result as the output on the screen.
Example #4
TypeScript program to demonstrate JSDoc or the comments section to describe the functionality of the program along with the parameters using which we compute the factorial of a given number and display the output on the screen.
Code:
/**
*Computes the factorial of a given number
*@constructor
*@param {number} firstnum – The number whose factorial must be found
*/
var fact:number = 1;
function factorial(firstnum:number)
{
for(let u =firstnum; u>=1; u--)
{
fact = fact * u;
}
return fact;
}
console.log("The factorial of the given number is:\n", factorial(5);Output:
In the above program, the comments section is described between the symbols /** and */ in which we have defined that there is a function using @constructor and the parameters are defined with their datatypes using @param. Then we are defining a function to compute the factorial of a given number and display the result as the output on the screen.
Rules and Regulations for JSDoc or Comments
Given below are the Rules and Regulations for JSDoc or Comments in TypeScript:
- A comment in TypeScript should begin with the symbol /**.
- A comment in TypeScript should end with symbol */.
- Comments beginning or ending with other symbols are not recognized by the JSDoc parser.
- A function must be represented within the comment section by using @constructor.
- The parameters must be represented along with their data types within the comment section by using @param followed by their data type in curly brackets.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript JSDoc” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.