Updated April 18, 2023
Introduction to TypeScript Interface Default Value
Entities have to confirm to a syntactical contract called interface. Here, a syntax gets defined by the interface which every entity has to follow. Methods, properties and events are defined by the interface and also are the members of the interface. Only the members are declared in the interface. The deriving class is responsible for defining the members. An interface even provides a standard structure to the deriving class which it has to follow. In this article, the topic has been explained with its working and different examples. The examples would help the readers in the implementation.
Syntax:
To declare an interface, an interface keyword is used. Below syntax shows how to declare an interface in TypeScript−
interface interface_name {
…………
}Now within this declaration syntax of interface different objects can be defined whose default values are mentioned for example as,
interface EDUCBA {
courseName:string,
courseDuration:number,
courseCode:number,
loginAccess: number,
supplementaryCourse: string,
greetings: ()=>string
}
Moving further these default values are given data as,
var course1:EDUCBA = {
courseName:"Data Science",
courseDuration:22,
courseCode: 22435,
supplementaryCourse: "Data Analyst",
loginAccess: 10,
greetings: ():string =>{return "Heyoo! We have Updated your Learning Course"}
}
In last it is called as,
console.log("Earlier Course ")
console.log(course1.courseName)
console.log(course1.courseDuration, "Hours")
console.log(course1.courseCode)
console.log(course1.supplementaryCourse)
console.log(course1.loginAccess, "Weeks")
console.log(course1.greetings())Examples of TypeScript Interface Default Value
Below are some different examples:
Example #1
Code:
interface EDUCBA {
courseName:string,
courseDuration:number,
courseCode:number,
loginAccess: number,
supplementaryCourse: string,
greetings: ()=>string
}
var course1:EDUCBA = {
courseName:"Data Science",
courseDuration:22,
courseCode: 22435,
supplementaryCourse: "Data Analyst",
loginAccess: 10,
greetings: ():string =>{return "Heyoo! We have Updated your Learning Course"}
}
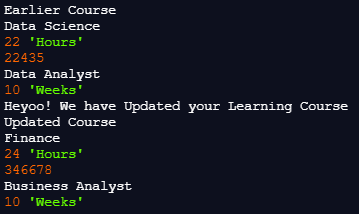
console.log("Earlier Course ")
console.log(course1.courseName)
console.log(course1.courseDuration, "Hours")
console.log(course1.courseCode)
console.log(course1.supplementaryCourse)
console.log(course1.loginAccess, "Weeks")
console.log(course1.greetings())
var course2:EDUCBA = {
courseName:"Finance",
courseDuration:24,
courseCode: 346678,
supplementaryCourse: "Business Analyst",
loginAccess: 10,
greetings: ():string =>{return "Heyoo!! Welcome"}
}
console.log("Updated Course ")
console.log(course2.courseName);
console.log(course2.courseDuration, "Hours");
console.log(course2.courseCode);
console.log(course2.supplementaryCourse);
console.log(course2.loginAccess, "Weeks")Output:
Example #2
Code:
interface EDUCBA
{
(pricePaid: number,
courseName: string,
allotedTo: string,
loginID: number,
): void;
};
function newData
(
pricePaid:number,
courseName:string,
allotedTo: string,
loginID: number,
):void {
console.log(" Price Paid by You: INR = " + pricePaid)
console.log(" You choosed = " + courseName)
console.log(" Alloted to = " + allotedTo)
console.log(" Credentials to Login = " + loginID)
}
function updatedData
(
pricePaid: number,
courseName:string,
allotedTo: string,
loginID: number,
):void {
console.log(" Price Paid by You: INR = "+ pricePaid)
console.log(" You choosed = " + courseName)
console.log(" Alloted to = " + allotedTo)
console.log(" Credentials to Login = " + loginID)
}
let hi: EDUCBA = newData;
hi(19999,
'Data Science',
"Rahul Sharma",
345623);
hi = updatedData;
hi(26500,
'Finance',
"Rohit Khattar",
556879032);Output:
Example #3
Code:
interface MobilePhone {
modelName: string;
modelNumber: number;
operatingSystem: string;
company: string;
price: number;
discount: number;
preBooking: string;
}
let Information = (type: MobilePhone): void => {
console.log(
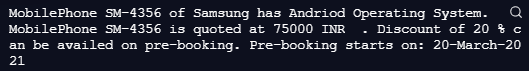
'MobilePhone ' + type.modelName + ' of ' + type.company + ' has ' + type.operatingSystem + ' Operating System.'
);
};
let Information1 = (type: MobilePhone): void => {
console.log(
'MobilePhone ' + type.modelName + ' is quoted at ' + type.price + ' INR ' + ' . Discount of ' + type.discount + ' % can be availed on pre-booking' + ". Pre-booking starts on: " + type.preBooking
);
};
let Info = {
modelName: 'SM-4356',
modelNumber: 7823095467,
operatingSystem: 'Andriod',
company: 'Samsung',
price: 75000,
discount: 20,
preBooking: '20-March-2021'}
Information(Info),
Information1(Info);Output:
Conclusion
On the basis of the above article, we understood the concept with different examples and working. The examples would help the beginners in understanding the concept and implementing it according to their requirements.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “TypeScript Interface Default Value” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.