Updated July 6, 2023
Introduction to Tkinter Spinbox
The Tkinter Spinbox widget is an alternative to the Entry widget. It can replace ordinary entries where the user can choose from only a limited number of values. When there are a fixed number of values, and we want to select the values, we use a spinbox widget, a standard Tkinter entry widget variant. And it is very much like an ordinary widget except that it can specify the values to be allowed, which can be either a range or a tuple. This spinbox widget is available only in the versions of Python above 2.3.
Syntax of Tkinter Spinbox:
w = Spinbox(master, option,..)Where master represents the parent window, option is the list of options that can be used for the widget, and options are the key-value pairs that are separated by commas.
Tkinter Spinbox Widget
The most commonly used list of options for the widget are:
- active background: This option represents the slider and arrowhead colors when the mouse is placed over them.
- bg: This option determines the color of the slider and arrowheads when the mouse is not hovering over them.
- bd: The trough has three-dimensional borders that go all the way around it, and the width of these borders can be adjusted. It also represents the width of the three-d effect on arrowheads and sliders. By default, the trough has no borders around the perimeter of the trough, and the arrowheads and slider have a two-pixel border.
- command: This option calls the procedure whenever the scrollbar is moving.
- font: This represents the font to be used in the widget.
- fg: This represents the color of the text in the spinbox.
- cursor: This option appears when the mover is present over the scrollbar.
- disabledbackground: If you disable the widget, you can select the background color for use with this option.
- disabledforeground: Whenever the widget is disabled, this option represents the text color to be used.
- format: This option represents the string format, and there is no default value for this.
- from: Set the range by entering the lowest value in the spinbox.
- justify: This option has a default value of LEFT.
- repeatDelay: This option and repeat interval control the auto-repeat button, and both values can be represented in milliseconds.
- repeatInterval: This option and repeat delay control the auto-repeat button, and both values can be expressed in milliseconds.
- state: This option can be either NORMAL or DISABLED, or read-only. The default value for this option is NORMAL.
- textvariable: There is no default value for this option text variable.
- to: The spinbox allows you to set the lowest possible value you can select.
- validate: This option represents the mode of validation. The default value for this option is NONE.
- validateCommand: This option represents the callback of validation. There is no default value for this option.
- values: This option defines the valid values contained in the tuple for the widget. This option can override from, to, and increment.
- vcmd: This option specifies the callback of validation. There is no default value for this option.
- wrap: There is a wrapping of up and down buttons if the condition is true.
- relief: SUNKEN is the default value for relief.
- width: This option represents the width of the characters in the widget. Twenty is the default value.
- xscrollcommand: The option allows the user to scroll the spinbox horizontally.
Methods of Tkinter Spinbox
There are several ways to use spinbox objects, including:
- delete(startindex[,endindex]): When a specific character or a range of characters must be deleted, we used this method.
- get(startindex[,endindex]): When a specific character or a range of characters must be returned, we used this method.
- identify(x,y): You can identify the widget element using this method based on location.
- index(index): This method will return the absolute value of the provided index.
- insert(index,[,string]..): The specified index location is where the string is inserted using this method.
- invoke(element): To activate the spinbox button, use this method.
- selection_clear(): This method helps in clearing the selection.
- selection_get(): The function returns the selected text. This method will raise an exception if there is no selection currently.
- selection(‘range,’ start, end): This method selects the text within the specified start and end indices.
- selection(‘to,’ index): This method selects the text between the index and the anchor.
- selection(‘from,’ index): The given index specifies the position at which the selection anchor must be pointed. Set the selection anchor to zero at the start.
Example of Tkinter Spinbox
Below are the examples of Tkinter Spinbox:
Python program using Tkinter Spinbox to select from a list of numbers from one to sixty incremented by one.
Code:
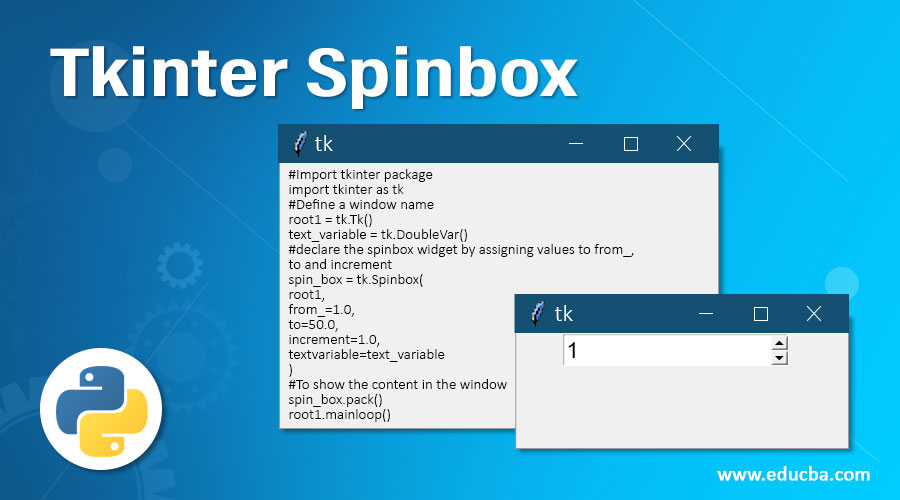
#Import tkinter package
import tkinter as tk
#Define a window name
root1 = tk.Tk()
text_variable = tk.DoubleVar()
#declare the spinbox widget by assigning values to from_, to and increment
spin_box = tk.Spinbox(
root1,
from_=1.0,
to=50.0,
increment=1.0,
textvariable=text_variable
)
#To show the content in the window
spin_box.pack()
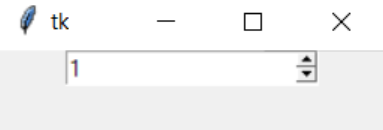
root1.mainloop()Output:
The Tkinter packages and libraries are imported to create a window, and a name is assigned in the code above. In our example, we call it tk. In our example, the values we are trying to keep fixed must be floating-point numbers or double; hence we declare a variable and assign it to double. We then define the spinbox widget with from_to values. Users can choose a value between 1.0 and 50.0, and each time they click the upward arrowhead, the value increases by 1. The output snapshot above displays the updated value. You can use the pack function to display content in the window.
Conclusion
This article has learned about the Tkinter spinbox, the syntax attributes, methods, and examples of the Tkinter spinbox. You can utilize various widgets provided by Tkinter to create personalized GUIs.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Tkinter Spinbox” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information,