
Introduction to Throws Keyword in Java
Java throws is a keyword that is declared with the name of the method, with the exception name method is likely to raise while it is called. Declaring a keyword helps in exception handling and lets the compiler know that the particular method throws a checked exception, which must be declared at the compile-time, such as IOException or ClassNotFoundException. If one does not handle a checked exception using a try-catch block or throws keyword, the compiler throws a compile-time error. This keyword also helps the programmer develop an efficient application by knowing that the method throws an exception.
Syntax:
Access_specifierreturn_typemethod_namethrowsexception_nameHere,
- Access_specifier: This refers to the keyword that tells JVM from where the particular method can be accessed. E.g., private/public or protected.
- Return_type: This refers to the keyword that tells the datatype of the object being returned by the called method, e.g., int, Boolean, String, etc.
- Method_name: This refers to the method’s name that needs to be called.
- exception_name can be a built-in or custom exception that the process will likely raise while running the program flow.
E.g.:
public void my_method() throws MyExceptionHow does Throws Keyword Work in Java?
Errors and Exceptions are of great importance to one Java application. It helps to determine if something unsuitable occurred, such as a syntax error or input entered does not match the data. Besides, errors are unavoidable and just leads to compilation errors and stopping the application execution unpredictably; exceptions can be handled to some extent.
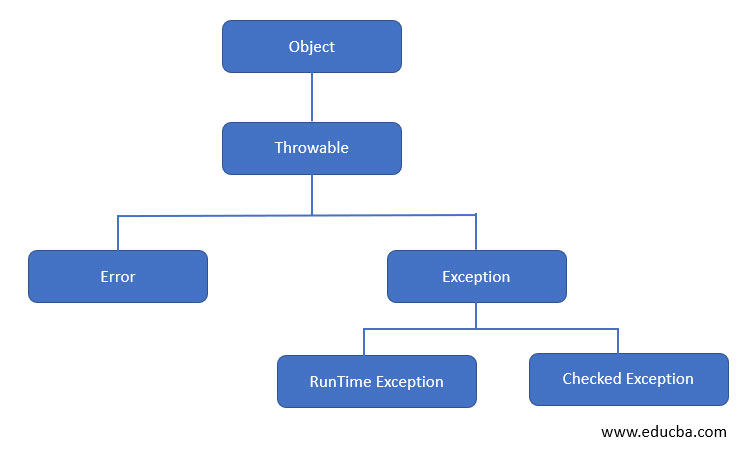
Handling an exception means that if they occur, how to stop the execution in a correct and decided manner.
There are two types of exceptions:
- Unchecked Exception: These types of exceptions are runtime exceptions that are not checked by the compiler if they are being handled in the code. Example- Arithmetic Exception, IndexOutOfBoundsException, etc. Using throws keyword for these exceptions is meaningless.
- Checked Exception: These are the types of exceptions that the compiler checks at compile time to see if they are being handled or not. Thus, if these are not handled, the compiler throws the error – Unhandled exception type. Example – IOException, ClassNotFoundException.
Two Ways Handle
Thus, there are two ways to handle a checked exception:
1. Try-catch
Using try-catch, one puts the statements that might raise an exception in a try block, and in case an exception is raised, control goes to statements in the catch block to execute them. In this way, we can control the application’s flow when an exception occurs.
Code:
//package Proc;
class MyCustomeException extends Throwable{
MyCustomeException(String s){
super(s);
}
}
public class prac1
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
try{
System.out.println("Now exception is being raised");
throw new MyCustomeException("Custom exception is thrown");
}
catch(MyCustomeException e){
System.out.println("Here exception is caught and handled");
}
}
}Output:

Explanation: In the above example, we declared a custom exception and threw it explicitly in the main method using the throw keyword. Once control enters the method control and throws an exception, it goes directly to the catch block, executes those statements, and exits the program.
2. Throws keyword
Declaring this keyword with the method’s name tells the compiler that the method can throw an exception. This keyword is mostly confused with the throw keyword, used to throw an exception on purpose in our code or while working with custom exceptions.
- Throws keyword-only lets us execute the statements in case an exception occurred. It can not be used to avoid the occurrence of an exception. Thus, it is used for exception handling.
- The throws keyword is often confused with a throw, used to throw an exception explicitly. And throws are used to handle it.
- If an exception occurs, row keywords help programmers to make the program run smoothly and efficiently.
Examples to Implement Throws Keyword in Java
We can use the throws keyword in 2 ways:
Example #1
First, we can use throws in the declaration for the method where an exception is being thrown.
Code:
//package Proc;
public class prac1
{
public static void main(String[] args)throws IllegalAccessException
{
System.out.println("Hello Everyone lets start our learning with throws keyword");
throw new IllegalAccessException("My Exception");
}
}Output:

Explanation: In the above example, we have used the throws keyword to handle the exception being thrown using the throw keyword. In case an exception is raised, it will not prevent the program’s abnormal termination; instead, it helps to convince the compiler. Also, it helps to inform the programmer that the method might throw an exception and needs exception handling.
Example #2
Second, we use a try-catch block while calling a method that is likely to throw an exception. We have made a custom exception here named MyCustomeException that is being thrown by the method throwsDemo.
Code:
//package Proc;
class MyCustomeException extends Throwable{
MyCustomeException(String s){
super(s);
}
}
public class prac1
{
static void throwsDemo() throws MyCustomeException
{
System.out.println("We are Inside the method");
throw new MyCustomeException("Custom exception is thrown");
}
public static void main(String[] args)throws IllegalAccessException
{
try{
System.out.println("Now exception is being raised");
throwsDemo();
}
catch(MyCustomeException e){
System.out.println("Here exception is caught and handled");
}
}
}Output:

Explanation: In the above example, one method throws a new exception. This is indicated using the throws keyword. But when the method is called in the main method, we can use a try-catch block or declaring a throws keyword with the main method to handle the exception.
Conclusion
Throws keyword is used for exception handling in Java, where one needs to handle the flow of the program when a checked exception occurs. This is different from the throw keyword and must only be used with the checked exception since it does not prevent the occurrence of an exception but helps the way that must execute if one occurs.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Throws Keyword in Java. Here, we discuss an introduction to Throws Keyword in Java, syntax, and how it works with programming examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –


