Updated December 15, 2023
Table of Content
- Introduction
- Syntax of Method Overriding
- How Overriding works in Java
- Examples of Method Overriding
- When to Apply Method Overriding
- Rules of Method Overriding in Java
Introduction to Method Overriding in Java
It is a feature that allows the child class or subclass to redefine or provide the specific implementation for the method already defined by one of the superclasses. The subclass method redefined in the subclass is called method overriding in java. Method overriding requires the child class to have a method with the same name, parameter list, and return type as a method in its parent class. In other words, they should share the same method signature. If these conditions meet, we say that the method in the child class overrides the method from its parent class.
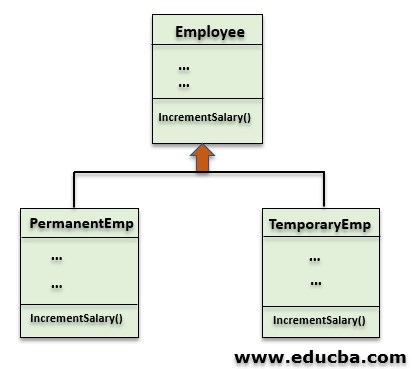
The Method overriding feature is used to perform the dynamic polymorphism in java. Another usage of Method overriding is to provide the specific implementation for the child class method, which is already provided in the parent class. We can understand the method overriding more clearly with the help of the below diagram.
As in the above example figure, the codePermanentEmp and TemporaryEmp classes inherit the class Employee. Both the codePermanentEmp and TemporaryEmp classes can reuse the Employee variables and methods. However, each class redefines the incrementSalary() method to calculate the salary increment according to the employee type. So both the classes override the incrementSalary() method. The subclass and the employee class must have the same method name, parameter list, and return type to meet the conditions for method overriding.
Syntax of Method Overriding in Java
Let’s see the syntax of method overriding in java:
class Superclassname
{
// variables
void methodA()
{
// method implementation code
}
}
class Subclassname1 extends Superclassname
{
// variables
void methodA()
{
// method specific implementation or re-implemented code
}
}
class Subclassname2 extends Superclassname
{
// variables
void methodA()
{
// method specific implementation or re-implemented code
}
}The keyword ‘extended’ signifies creating a new class derived from an existing one. Therefore, the methodA(), initially defined in the superclass, gets redefined in the subclasses.
The essential points to remember about the override method are:
- The overridden method allows more or equal, but not less, access modifiers to override the method.
- Private, Final, and static methods can not be overridden.
- Abstract methods must override the subclass of an interface or abstract class; otherwise, a compile-time error will be thrown.
How Overriding works in Java?
In method overriding, a subclass method with the same name as its parent’s is executed during runtime. Challenges arise when both classes use the same method name; the runtime call must correspond to either the child or parent class. The compiler determines this based on parameters, ensuring clarity in method invocation. The compiler of the language then decides this by taking into account the number of parameters, types of parameters, etc. Based upon which the function name to be called is determined. Method overloading and method overriding have been crucial concepts in the field of core java. It holds significance as the compiler needs to be clear as to which method to call.
Examples of Method Overriding in Java
Below are the example of method overriding in java to override a method of superclass –
Example #1
Next, we write the java code to understand the method overriding in java to override a method of the superclass with the following example –
Code:
class Employee{
float salary = 40000;
void incrementSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * 0.2)) );
}
}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.5;
void incrementSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Permanent Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * hike)) );
}
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee{
double hike = 0.35;
void incrementSalary()
{
System.out.println("The Temporary Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * hike)) );
}
}
public class p1
{
public static void main(String args[]){
Employee e =new Employee( );
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// based on an object it decide which class incrementSalary() method to be execute
e.incrementSalary();
p.incrementSalary();
t.incrementSalary();
}
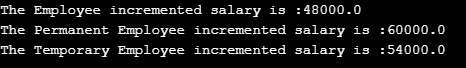
}Output:
As in the above code, PermanentEmp class and TemporaryEmp classes are the subclasses, and employee is the superclass inside subclasses; the method incrementSalary() is overriding from the superclass, as we can see in the code, the override method incrementSalary() has the same name, same signature and same return type as in the superclass Employee. In the primary method, we create objects of classes and determine which class’s incrementSalary() method to execute based on the object itself. This decision relies on dynamic polymorphism or late binding; it performs the same class method as the object belongs, which we can see clearly in the output.
Example #2
Let’s see an example of a method overriding in java to override the parameterized method of the superclass.
Code:
class Employee{
float salary = 40000;
void incrementSalary(double hike)
{
System.out.println("The Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * hike)) );
}
}
class PermanentEmp extends Employee{
void incrementSalary(double hike)
{
System.out.println("The Permanent Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * hike)) );
}
}
class TemporaryEmp extends Employee{
void incrementSalary(double hike)
{
System.out.println("The Temporary Employee incremented salary is :" +(salary + (salary * hike)) );
}
}
public class p1
{
public static void main(String args[]){
Employee e =new Employee( );
PermanentEmp p = new PermanentEmp();
TemporaryEmp t = new TemporaryEmp();
// based on an object it decide which class incrementSalary() method to be execute
e.incrementSalary(0.2);
p.incrementSalary(0.5);
t.incrementSalary(0.35);
}
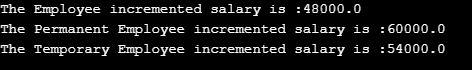
}Output:
In the above example, the PermanentEmp and TemporaryEmp classes override the incrementSalary(double hike ) method.
Example #3
Code:
class MyVehicle{
void run(){
System.out.println("It's a running vehicle");}
}
class MyCar extends MyVehicle{
public static void main(String args[]){
MyCar obj = new MyCar();
obj.run();
}
}Output:
The output is: It’s a running vehicle. I had to provide a specific implementation of the method run() provided in the subclass. Therefore, we could use the method overriding feature in the future.
Example #4
Code:
class MyVehicle{
void run(){System.out.println("My vehicle is running");}
}
class MyCar2 extends MyVehicle{
void run(){System.out.println("My car is running");}
public static void main(String args[]){
MyCar2 obj = new MyCar2();
obj.run();
}
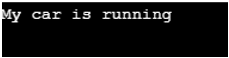
}Output:
Explanation : If we closely examine both examples, the third and fourth examples both involve extending the child class with the parent class. In the fourth case, MyCar2 extends MyVehicle. According to the definition of method overriding, the decision on which method to call is made at runtime, precisely when invoking the run() method. Upon calling the run() method in this example, the program first directs the call to the child class, as it already inherits all the properties of the parent class, making it fully sufficient. As the execution proceeds to the base class section and verifies the IS-A relationship through the “extends” keyword, it successfully generates the output: “My car is running.”
When to Apply Method Overriding?
Understanding Method overriding is crucial when a subclass aims to offer a specialized version of a method from its superclass. It’s frequently applied in inheritance, allowing customization or extension of inherited behavior. Let’s explore examples for better comprehension.
Example
Code
class Animal {
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Some generic sound");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal {
@Override
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Meow");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal {
@Override
void makeSound() {
System.out.println("Woof");
}
}
public class AnimalTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal cat = new Cat();
Animal dog = new Dog();
cat.makeSound(); // Output: Meow
dog.makeSound(); // Output: Woof
}
}
Output:
Explanation: In this example, the Animal class has a method makeSound(). The Cat and Dog classes extend Animal and provide their specific implementations of makeSound() using the @Override annotation. When we create instances of Cat and Dog but refer to them through the Animal reference, the runtime calls the respective subclass’s overridden method, demonstrating polymorphic behavior.
Rules of Method Overriding in Java
- The name of the method should be the same for both parents as well as child class.
- The parameter of the base class should be the same as that of the parent class.
- The relationship must be an IS-A relationship between the child class as well as the parent class.0000
Conclusion
Method override in java is a feature in which one superclass method redefines or again implements the subclass. To override a method, a child class must have the same name, the same parameters list or same signature, and the same return type as a method in its parent class; in this case, we use ‘temp_num’ to compare the result with the original number.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “Method Overriding in Java” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.