Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SqlAlchemy ORM
The SQLAlchemy is one of the packages that can be facilitated efficiently for the programmers like python and java to communicate the databases. The library is mainly used for the ORM[Object Relational Mapper] tool that automatically converts the function calls to perform the SQL queries. It translates the Python classes to mapping the database tables on the relational databases system.
What is SqlAlchemy ORM?
The package can be made for the python programmers to communicate with the database system. Then most of the time, this library is used and mapping with ORM[Object Relational Mapper] tool, which automatically converts the function calls to SQL queries. It translates to the python classes on the database table with the relational database management system. The SQLAlchemy mainly provides the standard interface that enables the programmers to write the database agnostic codes through communication via various database engines. Specifically, the developers will understand before dealing with the SQLAlchemy applications.
Create SqlAlchemy ORM
The SQL database behaves like the object for all the divisions and collection classes based upon the sizes and vast performance of the abstraction tables and database rows. SQL Alchemy ORM comprises some parts; like the section, it will be more focused on the general reference of the SQL Alchemy core. It is more focused on the relational database model with additional SQLAlchemy on the Object Relational Model[ORM] component that is more focussed on the data models and classes developed by the programmers. In SQLAlchemy, ORM with the optional database object-relational mapping is more capable of providing the SQLAlchemy ORM, which builds upon the core. It also includes the setup layer allowing user-defined classes and methods to be mapped to each database table even though the SQL constructions and the Session object will be a more persistent mechanism for the database, especially in the SQL Expression language.
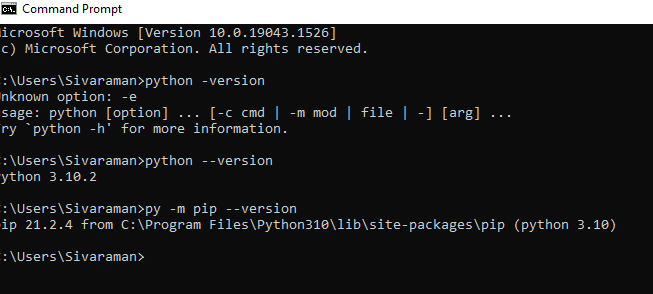
Moreover, it will be extended to allow n number of SQL queries that have to be written and invoked with user terms and defined objects. This concept will work most often with the ORM tools, and it will be discussed in each section with a light blue border on the left side. This user will utilize the CORE and ORM types. To create and install the SQLAlchemy ORM, we should install the python first on the machine,
https://www.python.org/. This official link will help install python on the device.
During the python install, use the Customized option to select the pip in the python package.
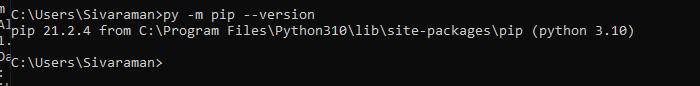
Next, we need to install the sqlalchemy to the python folder with the help of the below command like
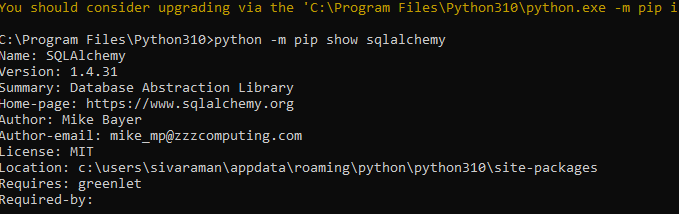
python -m pip show sqlalchemyfrom sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
basedirectory
engine = create_engine(connection path,echo=True)
session=sessionmakerThe above codes are the basic code for creating the SQLAlchemy ORM in the python script.
Mainly it needs the following types,
- Creating engine
- Creating session
- Creating table
These three requirements are needed for creating and using the SQLAlchemy in python scripts.
SqlAlchemy ORM Dialects
The dialect of the sqlalchemy will mainly communicate with several types, including DBAPI implementations with databases by using the dialect. It has some sections, including the material reference and unique comments for each backend usage and noted for various DBAPIs types. All dialects will necessitate the installation of the DBAPI drivers; it includes some Dialects types like
PostgreSQL
MySQL
SQLite
Oracle,
Microsoft SQL Server
The above databases perform the SQLAlchemy ORM in python using Dialect communication.
We can see the installed machine’s dialects for the above area or path. In addition, we see all the databases.
And inside, we see the required python files for each database configuration.
SqlAlchemy ORM Methods
It has n number of methods for utilizing the SQLAlchemy ORM using the select statement constructed by the Query object. It also provides the generative interface whenever we create and calls the return a new Query object. Mainly query objects are more initially generated by using the query() method with including and calculating the sessions,
Variable name=session.query(mapped class)Some of the methods are followed below,
- Add_entity(): This is one of the methods used to add the entity mapped with the database column results are returned.
- Count(): This method helps count the number of rows returned using the Query.
- Filter(): The SQL expressions are performed using the Query; at that time, the filter method applies the filter condition or criterion of the Query copy.
- Get(): We can get the primary key for the identifier to provide direct access to the user session map.
- Join(): We already know about the SQL joins, so when we use this method, the SQLAlchemy will create the SQL join against the Query object criterion and apply genuinely to return the results with the Query format.
SqlAlchemy ORM Class
The SQLAlchemy ORM Class is a user-defined python class that connects the database tables and creates instances of those specific classes. Each class has separate rows here; the class represents the instance or object that includes the system that transparently and synchronizes all the changes between the objects and related rows. Classes may be used as the declarative system, and it comes under the term of the base class, which maintains the tables corresponding to the base named it as the declarative base class. From sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base Using this import, we can declare and utilize the classes and objects.
Syntax:
Class _name(object):
def _method(parameter1, parameter2):
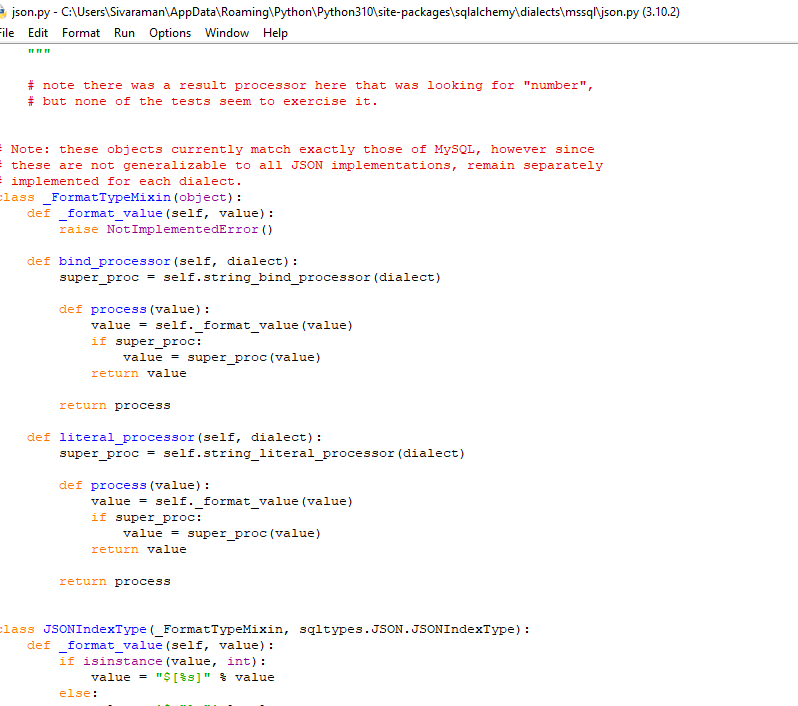
----some logic codes depends upon the requierment---The above screenshot is the primary class program that has already been created on the python dialects like MYSQL json.py program.
Conclusion
Many comparisons of the other ORM tools include the Relational database management system with the ORM object. But in each case, we use different technologies suited for more significant differences and specified with the user decisions to perform the operations in the programming language.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SqlAlchemy ORM” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.