Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL EXECUTE
EXECUTE command in standard SQL is used to execute stored procedures and query strings in database servers. For the uninitiated, a stored procedure is a SQL code that can be saved and reused later. A stored procedure can be system defined or user-defined. EXECUTE command helps in context switching by allowing for executing commands on different servers and by different users.
Syntax and Parameters
The basic syntax for writing EXECUTE command in SQL is as follows :
---Executing a stored procedure
EXECUTE | EXEC <stored_procedure_name> <stored_procedure_parameter>
{WITH {RECOMPILE | RESULT SETS} | AT <server_name>| AS <username>}
--- Executing a query string
EXECUTE | EXEC ('query string')
{WITH {RECOMPILE | RESULT SETS} | AT <server_name>| AS <username>}The parameters used in the above-mentioned syntax are as follows:
- Stored_procedure_name: Stored procedure name
- Stored_procedure_parameter: Parameter name along with value or just parameter value
- Server_name: Name of the other server on which you wish to execute the command
- Username: Name of the user or login on the current server which you want to impersonate
- Query string: SQL statements written within single quotes
Examples of SQL EXECUTE
Following are the examples are given below:
1. Execute on Command Strings
Consider the “cities” table given below. We will be using this table to query a row from it using EXECUTE command.
| id | country | city |
| 1 | India | New Delhi |
| 2 | U K | London |
EXECUTE ('SELECT country, city FROM cities WHERE id = 1');2. Execute on Stored Procedures
As mentioned earlier, stored procedures are pre-saved commands in SQL. In this section, we will learn to create a stored procedure and then use the EXECUTE or EXEC command to execute it.
Consider the following SQL script. Here we have first created a dummy table called “students” with fields such as id, name, course, type of service, and student location. After creating the table, we have inserted a few records into it to work with. Once we have created a dummy table, we created a stored procedure to search student details based on his or her id.
USE Test_db
Create Students Table:
CREATE TABLE students(
[id] [int] NOT NULL,
[name] [varchar](100),
[course] [varchar](255),
[service] [varchar](50) CHECK (service IN('premium', 'Free')),
[city] [varchar](50)
)
GOInsert Values in Students Table:
INSERT INTO students VALUES(1,'Mathew Perry','Data Science','Free','New York'),
(2,'James Lakers','Data Science','Premium','Santa Monica'),
(3,'Rahul Kumar','Full Stack Development','Premium','New Delhi'),
(4,'Portia David','SQL Basics','Free','Perth'),
(5,'Naina Reddy','Frontend Development','Premium','Bangalore')
GOCreating a Stored Procedure on Students Table:
CREATE PROCEDURE [Studentsearch]
(@student_id int)
AS
BEGIN
SELECT id,name,course,service,city FROM students WHERE id = @student_id
END
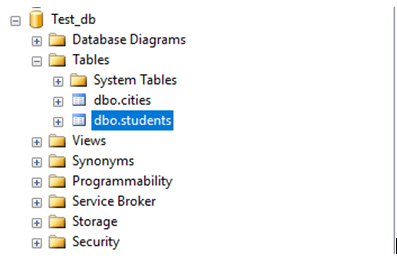
GOAfter successful execution of this script in the SQL server, we will have a new students table created in Test_db database. You can observe all this in the Object Explorer.
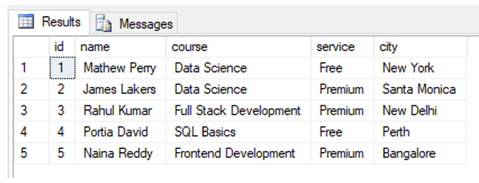
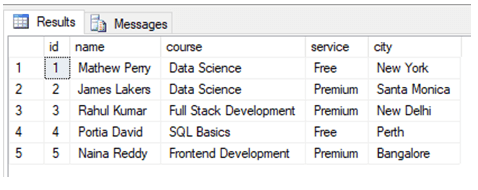
The data in the students’ table looks something as follows:
SELECT TOP 1000 [id]
,[name]
,[course]
,[service]
,[city]
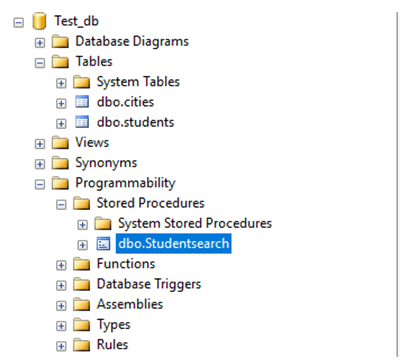
FROM [Test_db].[dbo].[students]Everything went as planned. Finally, let’s check if the stored procedure has been created. Stored Procedures are stored in the Programmability section of the database.
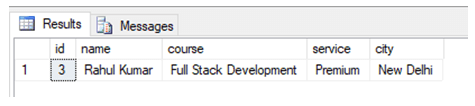
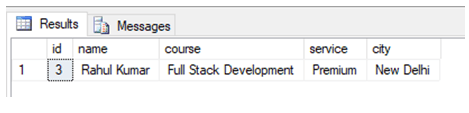
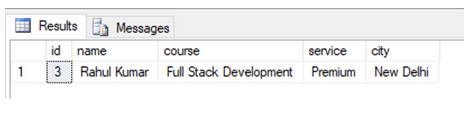
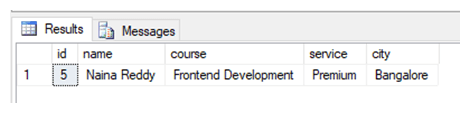
Now we are all set to use the EXECUTE command on stored procedures. Here is the first example. Suppose if we want to find the details of the student with id 3, we can simply write the following command.
EXECUTE Studentsearch @student_id = 3In order to execute a stored procedure, we mention the stored procedure name along with the stored procedure parameter in the execute the command as shown in the above-mentioned query.
It is not always necessary to mention the stored procedure parameter name in the EXECUTE command. We can try the following variation also.
EXECUTE Studentsearch 3;In SQL standard, EXEC is equivalent to the EXECUTE command. Hence, we can use EXEC also.
EXEC Studentsearch @student_id = 33. Execute with Recompile
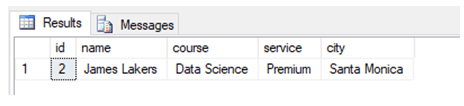
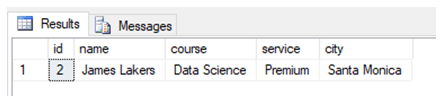
In SQL SERVER, when we run the EXECUTE command on any stored procedure, its execution plan is stored in the cache. Everytime we run a query it is not compiled again. Ergo, in order to force the server to create a new execution plan to compile and discard it after execution, we can use EXECUTE WITH RECOMPILE statement as shown below.
EXECUTE Studentsearch @student_id = 2 WITH RECOMPILE;4. Execute on Stored Procedures with Multiple Parameters
In the previous sections, we explored the execution of a simple stored procedure. What if we want to query with more than one parameter? Yes! That too can be done with stored procedures and EXECUTE command in the following manner.
CREATE PROCEDURE DetailedStudentSearch
@course_name nvarchar(50),
@service nvarchar (50)
AS
SELECT id, name, course, service, city FROM [dbo].[students]
WHERE course = @course_name AND service = @service;
GOHere we have created a new procedure called “DetailedStudentSearch”. Suppose we want to find the details of students based on the courses and type of service taken by them. It can be done using EXECUTE commands as shown below.
EXECUTE DetailedStudentSearch 'Data Science', 'Premium';EXECUTE DetailedStudentSearch 'Frontend Development', 'Premium';5. Execute by Other Users
EXECUTE command in SQL standard, helps us in context switching. That is, we can execute commands as a different login user, at a different server than the one we are currently working on. Here is an example to illustrate the execution of a SQL string by another user.
EXECUTE ('SELECT * FROM students')
AS USER = 'Q27H4-AM\acer';
GO6. Execute with Result Sets
In SQL Server 12 and above, we can even manipulate the result set obtained from the execution of a stored procedure in the following manner with the help of WITH RESULT SETS keyword in the EXECUTE command.
EXEC Studentsearch 3
WITH RESULT SETS
(
(
[Student Id] int NOT NULL,
[Student Name] nvarchar(50) NOT NULL,
[Course Name] nvarchar(50) NOT NULL,
[Service Type] nvarchar(50)NOT NULL,
[Student Location] nvarchar(50) NOT NULL,
)
);Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL EXECUTE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.