Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQLAlchemy count
The SQLAlchemy count is one function that can be used to count the long as run for writing the same query in the database. The data records are to be counted at each stage of the ORM layers with the SQLAlchemy core is the database schema and the model which provides all the datas related and the database part like rows, columns, and tables.
Overview of SQLAlchemy count
SQLAlchemy is one of the popular sql toolkits, and the Object Relational Mapper(ORM) is written in the python language. It will give the full compatibility and flexibility of the SQL databases and their applications. Mainly it’s the open source and cross-platform software under the MIT license; it’s famous for the ORM for which classes have to be mapped to the specific database, and it allows the object model and database.
The size and performance of the database are to be calculated and adopted for the data patterns mappers rather than the other active data records used by the ORMs. Databases and SQL will be viewed in the different propectives using the SQLAlchemy; additionally, expression language has constructed the expressions against the tables with additional rows and columns; it can be called the object that represents the columns in the database table, which is also in turn with represented by the Table object. Metadata is the main part of the role, for it contains the definition of the tables and is associated with the objects such as the index, view, triggers, etc.
How to SQLAlchemy count?
Generally, group by and count functions are mainly performed in the different sets of methods used with the different sets of functions. That will be handled and used in the mathematical operations are the database dependent in the sql like PostgreSQL and Group by is performed, including the count function used by the programmer whenever the aggregate functions are used and calculated with the set of values and returned in the single values that will be summarized from the whole group of table rows and columns. The SQL Count function is aggregated using these types of functions that will be ignored the values like null and other specified values.
We can use the convenience method like query. Count () for counting the rows like below:
We used count () functions like count (*), which denotes and fetches the number of rows and columns from the database table; it will be used as the specified expressions that can be returned with the number of rows that do not include the null type of values it must be calculated and return the total.
The count is one of the common SQLAlchemy functions. He is imported as the necessary functions from the SQLAlchemy package to establish the connection with the PostgreSQL database by using the create_engine() function to perform the CRUD operations like create, read, update and delete datas. On the other hand, metadata information is more useful for storing and fetching datas from the table by using the query.
Why is SQLAlchemy count?
The SQLAlchemy function is the main module that provides the in-built sql functions that can make and helpful for the user operations like counting and summarizing the datas faster and more efficient. Querying the data will be more useful for starting and performing the user operations that can be extracted from the user and current sessions additionally associated with the specified mapped classes linked to the object. Count() function mainly returns the total number of rows of a query, and it is sued to retrieve all the datas from the database, which we needed to fetch the user session from the session factory classes. It is imported with the specified query by using all functions of the query object. It counts all the results of a subquery under the amount of work done and retrieves the table rows with the counting datas.
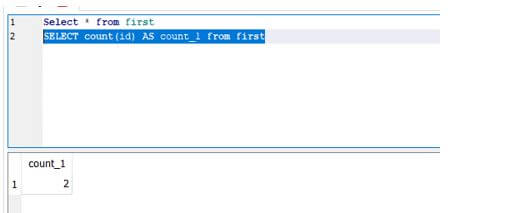
The following screenshot is the basic structure of the SQLAlchemy table rows and columns; based on this; we can retrieve the number of rows in the database table.
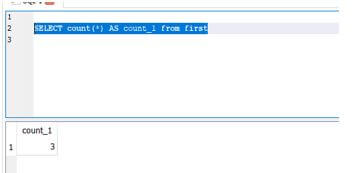
We can use the same set of bad queries with the additional joins and fairly frequently used in the APIs for sufficient frequency, which has to be impacted with the additional performance. Using the count() method is inefficient from the perspectives involved in the subquery, and the columns count through the method called count (*).
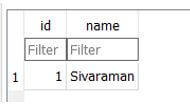
The above screenshot shows for to count and retrieve all the ids from the database table.
Examples of SQLAlchemy count
Given below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Code:
import SQLAlchemy as db
eng = db.create_engine("sqlite:///D:/Mar9.db")
md = db.MetaData(bind=eng)
db.MetaData.reflect(md)
mar13 = md.tables['test3']
res = db.select([db.func.count()]).select_from(mar13).scalar()
print("Count:", res)Output:
In tIn the above example, we used the count () method in a basic way to interact with the databases. We used a database engine to create and connect the database tables like rows and columns. In this case, we use Mar9.db to connect the database tables, and metadata will be handled the user datas like data about data and the results to store on the individual result set variable. The ‘test3’ database table will be called here; it’s already in the sqlite mar9.db. Finally, we can print the number of rows in the output screen using the count () and print statement.
Example #2
Code:
import SQLAlchemy as db
from SQLAlchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
Base = declarative_base()
eng = db.create_engine("sqlite:///D:/Mar9.db")
class First(Base):
__tablename__ = 'test3'
id= db.Column(db.Integer,
primary_key=True,
autoincrement=True)
name = db.Column(db.String(10))
from SQLAlchemy.orm import sessionmaker
Session = sessionmaker(bind = eng)
ses = Session()
result = ses.query(First).count()
print("Count:", result)Output:
For this example, we used the same as above; the count() function is used. Additionally, we create the class and map the database table in a separate variable. Additionally, we used the the SessionMaker package to be imported and stored in the separate session as the variable we can bind the engine in the session maker. So the result will be stored in a separate variable, and the same will be printed on the screen with the help of the count () method.
Conclusion
The SQLAlchemy has many functions, operators, and keywords for utilizing the datas in the database for the application UI. Among that count () is one of the aggregate functions, and it will calculate the table rows from the specified databases and the tables already created.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQLAlchemy count” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.