Updated March 13, 2023
Introduction to SQL Timestamp
Timestamp is a data type and function in Standard Structured Query Language (SQL) that lets us store and work with both date and time data values, usually without specified time zones. The timestamp has a storage size of 8 bytes that can accept date and time values ranging from 4713 BC and 294276 AD and provides a resolution of 1 microsecond or 14 digits. Some SQL databases allow for customization of a timestamp data type where we can specify a timezone for the timestamp so that every time the database is used in a different timezone, it shows and accepts the corresponding date and time. For example, in PostgreSQL, we have a “timestamptz” data type that takes care of time zone changes as well. Timestamptz data type also has a storage size similar to a timestamp of 8 bytes that can accept date and time values ranging from 4713 BC and 294276 AD and provides a resolution of 1 microsecond or 14 digits.
In this article, we will be learning the functions and differences of “timestamp” and “timestamptz” data types with the help of a few examples.
Syntax and Parameters:
The basic syntax of “timestamp” data type in SQL is as follows :
Timestamp 'date_expression time_expression';A valid timestamp data expression consists of a date and a time, followed by an optional BC or AD.
Timestamptz 'date_expression time_expression +/- time_zone_expression ';
2004-10-19 10:23:54;In this case, a valid timestamp data expression consists of a date and a time, followed by a time_zone expression concatenated with a ‘+/-’ sign based on the position of the time zone with respect to ‘GMT’ and finally followed by an optional BC or AD.
Examples to Implement of SQL Timestamp
Below are a few examples to understand SQL Timestamp data type:
Example #1
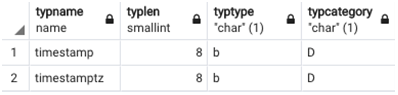
Getting to know important details of timestamp and timestamptz data type in SQL.
Code:
SELECT typname, typlen, typtype, typcategory
FROM pg_type
WHERE typname ~ '^timestamp';Output:
Example #2
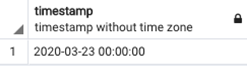
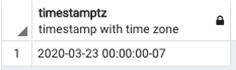
SQL query to illustrate the difference between timestamp and timestamptz data types.
Code:
SELECT TIMESTAMP '2020-03-23 00:00';Output:
SELECT TIMESTAMPTZ '2020-03-23 00:00';Output:
Example #3
Some examples to show functions related to timestamp data type in SQL. First, let’s start by converting or casting a given date into a timestamp format, as shown below.
Code:
SELECT '2020-03-23' :: timestamptz;Output:
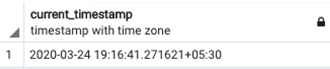
Suppose if we want to know the current timestamp, we can use the current_timestamp function as shown below. It will return the current timestamp, i.e. current date and time implicitly converted into the default timezone.
SELECT current_timestamp;Output:
Further, we can also check the timezone we are currently working in by using the SHOW timezone statement below. This becomes very helpful when you have operations all over the world.
SHOW timezone;Output:
Next, we can even change the current timezone to a different timezone using the SET timezone statement. Here, you may choose from a wide variety of timezones like ‘Asia/Kolkata’, ‘Europe/Zurich’, ‘US/Pacific’ etc. In this example, we have changed the timezone from ‘Asia/Kolkata’ to ‘US/Pacific’.
SET timezone = 'US/Pacific';A few functions like EXTRACT in SQL let us extract a specific piece of information from the timestamp. For example, we can extract DAY, MONTH, YEAR, HOUR, MINUTE, SECONDS, etc., from the timestamp.
In the following examples, we have tried to extract DAY and MONTH from the timestamp.
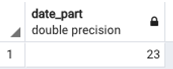
SELECT EXTRACT(DAY FROM '2020-03-23 00:00':: timestamp);Output:
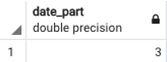
SELECT EXTRACT(MONTH FROM '2020-03-23 00:00':: timestamp);Output:
Example #4
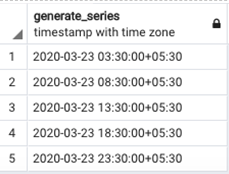
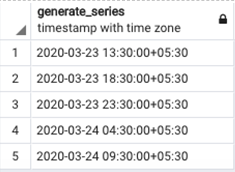
SQL query to generate a series of timestamps in a specified timezone. In this example, we have generated a series of timestamps with a regular interval of 5 hours in two time zones, namely, ‘Indian Standard Time’ and ‘Pacific Standard Time. We can observe the difference between the two series by closely looking at the outputs.
Code:
SELECT generate_series(
timezone('IST', '2020-03-23 00:00'::timestamp),
timezone('IST', '2020-03-23 23:00'::timestamp),
'5 hour'::interval
);Output:
SELECT generate_series(
timezone('PST', '2020-03-23 00:00'::timestamp),
timezone('PST', '2020-03-23 23:00'::timestamp),
'5 hour'::interval
);Output:
Example #5
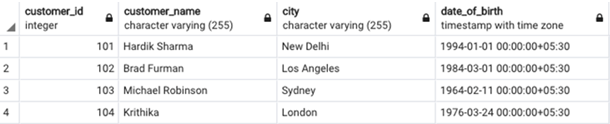
A practical example to illustrate the use of timestamp or timestamptz data type in SQL. Let’s take an example of a business case, where a multinational bank wants to wish its customers “Happy Birthday” based on the customer’s local time. The bank’s database has a list of customers with their date of births. So the customers’ table can be created something like this :
Code:
CREATE TABLE Customers (
customer_id int,
customer_name varchar(255),
city varchar(255),
date_of_birth timestamptz
);Output:
After inserting the relevant information, the data in the table will look something like this:
Suppose we want to wish our customers in London who have their birthdays today i.e. ‘24th March 2020’ as per Indian Standard Time; we might be required to write a SQL query as shown below:
SELECT customer_name, date_of_birth
FROM customers
WHERE EXTRACT(DAY FROM date_of_birth) = '24'
AND EXTRACT(MONTH FROM date_of_birth) = '03';Output:
But in the above example, we can see that since the customer is from London and it’s not 24th March there, the first query might not be the best option. So we can improve the query by mentioning the time zone as ‘GMT’, as mentioned in the query below.
SELECT customer_name, date_of_birth
FROM customers
WHERE EXTRACT(DAY FROM date_of_birth at time zone 'GMT') = '24'
AND EXTRACT(MONTH FROM date_of_birth at time zone 'GMT') = '03';Output:
Conclusion
SQL timestamp is a data type and function used to store and work with data values in date and time formats, sometimes along with time zones and AD/BCs. They are very helpful when we have operations all over the world.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Timestamp” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.