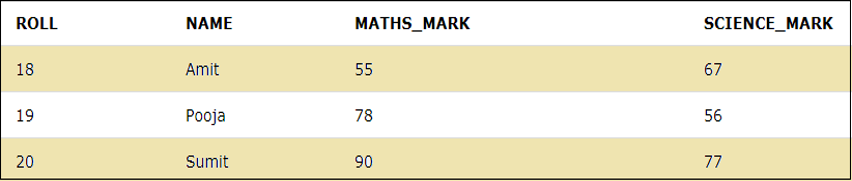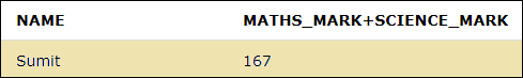Updated March 28, 2023
Introduction to SQL Arithmetic Operators
The arithmetic operators in SQL are used to perform mathematical operations such as addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and modulus, etc. on the data stored in the database tables and these arithmetic operators can be used along with a WHERE clause in an SQL statement if there are multiple conditions which need to be satisfied in the query, but in case there is any Null value present in the table, upon performing arithmetic operations on the Null value, we will get the result as Null.
Main Top 5 Arithmetic Operators in SQL
The various arithmetic operators in SQL are addition (+), subtraction (-), multiplication (*), division (/) and modulus (%) which are used to perform the mathematical operations on the data which is stored in the database tables. Let us go through the below examples to understand the working of various arithmetic operators in SQL.
1. Addition Operator (+)
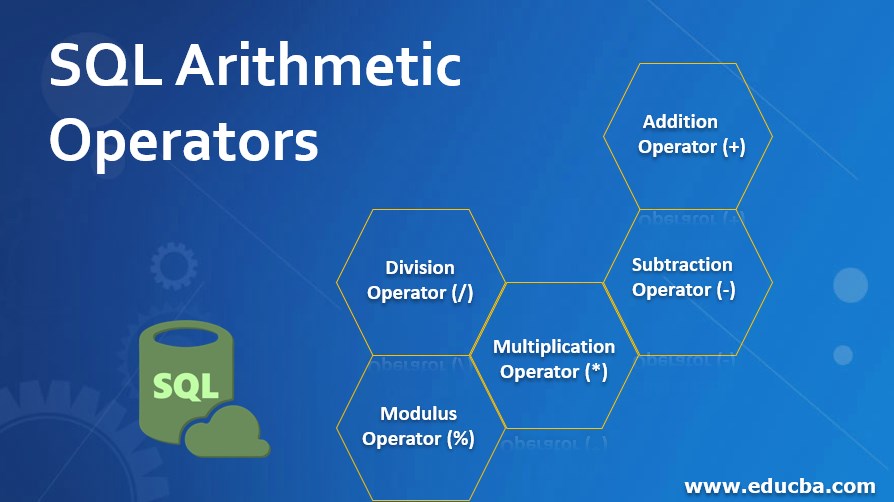
The operator ‘+’ is used to perform addition operation on two operands. In the below example, we can see that the addition operator is used to add 100 and 220.
SELECT 100 + 220 as Addition;Output:
Let us take the example of a table “EMPLOYEES” as below to understand how the operators work.
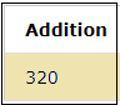
The table contains various employees and their details. Let us perform the addition operation on the column SALARY. In the below query, 10000 is added to the SALARY column.
SELECT SALARY+10000 as new_salary FROM EMPLOYEES;Output:
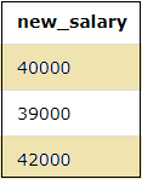
Let us perform the addition of two columns using the addition operator as shown in the below query.
SELECT SALARY+ID as added_salary FROM EMPLOYEES;The result of the above query can be seen below where the salary and ID columns are added.
2. Subtraction Operator (-)
The subtraction operator ‘-’ is used to subtract the right-hand operand from the left-hand operand. Let us take the below example to perform subtraction of 99 from 260.
SELECT 260-99 as Subtract;Output:
Let us now take the example of the previously stated table “EMPLOYEES”. In the below query, we can see that 5500 is subtracted from the SALARY column.
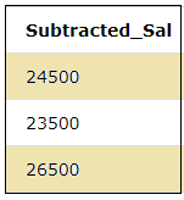
SELECT SALARY-5500 as Subtracted_Sal FROM EMPLOYEES;Output:
In the below query, the subtraction operation of two columns i.e. SALARY and ID is shown.
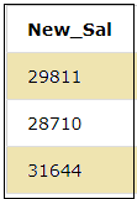
SELECT SALARY-ID as New_Sal FROM EMPLOYEES;We can see that in the above query, the ID column is subtracted from the SALARY columns and the result of the subtraction operation is as shown below.
3. Multiplication Operator (*)
This operator performs the multiplication of two operands. In the below example, we can see the multiplication of 99 and 89.
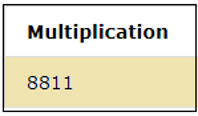
SELECT 99*89 as Multiplication;Output:
Considering the previously stated EMPLOYEES table, let us perform the multiplication of the column SALARY with 15 as shown below.
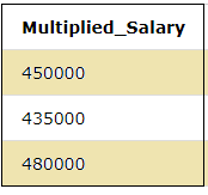
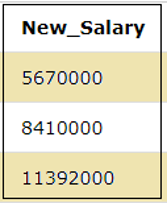
SELECT SALARY*15 as Multiplied_Salary FROM EMPLOYEES;The result of the above query can be seen below and we can see that 15 is multiplied with the SALARY column.
In the below query, we can see that the multiplication of two columns i.e. SALARY and ID from the table EMPLOYEES is done.
SELECT SALARY*ID as New_Salary FROM EMPLOYEES;Output:
4. Division Operator (/)
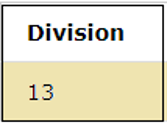
This operator performs the division of the left-hand side operand by the right-hand side operand. In the below example, the division operation is performed where 79 is divided by 6.
SELECT 79/6 as Division;The below result shows that the above operation gives the quotient of the division i.e. 13 as output.
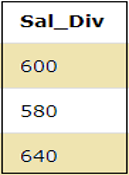
Let us again consider the previously stated table “EMPLOYEES”. The below query shows the division operation performed where the column SALARY is divided by 50.
SELECT SALARY/50 as Sal_Div FROM EMPLOYEES;Output:
5. Modulus Operator (%)
This arithmetic operator is used to get the remainder of the division of the left-hand side operand by the right-hand side operand.
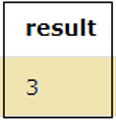
SELECT 23%4 as result;The above query shows that 23 when divided by 4, gives the remainder of the division which is 3 as output as displayed in the result.
The modulus operation is performed on the SALARY column of the EMPLOYEES table below.
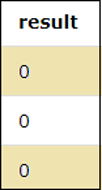
SELECT SALARY%100 as result FROM EMPLOYEES;The above query performs the modulus operation and when the salary of the employees is divided by 100, the result shows the remainder values of the division which is 0.
If a table contains any Null value, then on performing any arithmetic operations on the Null values, we get the result as Null.
Let us consider the below EMPLOYEES table with Null value as shown below.
Let us now perform addition and multiplication operation on the SALARY column which also contains a Null value.
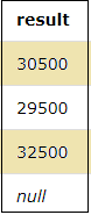
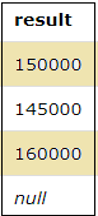
SELECT SALARY+500 as result FROM EMPLOYEES;SELECT SALARY*5 as result FROM EMPLOYEES;From the above output, we can see that in case a Null value is present, on performing multiplication or addition operation on it, we get the result as Null.
The arithmetic operators can be used along with the WHERE clause.
Let us take the example of the below table “STUDENTS”.
If we want to calculate the sum of the marks secured by the students greater than 150, then we can use the arithmetic operator along with the WHERE clause as shown in the below query.
SELECT NAME, MATHS_MARK+SCIENCE_MARK FROM STUDENTS WHERE MATHS_MARK+SCIENCE_MARK > 150;The above query will give the output as below where the student who has secured the sum of the marks greater than 150 is displayed.
Conclusion
The SQL arithmetic operators are vital for performing important mathematical operations on the data stored in the tables in a database. It is essential for the developers to have a good understanding of these operators.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Arithmetic Operators” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.