Updated March 14, 2023
Introduction to SQL Server Substring
The substrings in SQL Server can be extracted from the given or input string by using the SUBSTRING() function in which the starting position of the substring, as well as its length, are specified and according to the specified position and length, the substrings are extracted and also we will see how the SUBSTRING() can be used with literal strings, on the column of the tables as well as in the nested queries.
Explain all SQL Server Substring
The substring can be defined as a sequence of adjoining characters in a string. If the given string is ‘How are you?’ then the substring in this string can be ‘How’ or ‘ar’ or ‘you’ or ‘ou’ etc. i.e. any sequence of adjoining characters present in the string. These substrings can be extracted from the string ‘How are you?’ by using SUBSTRING() in SQL Server.
The syntax to extract a substring from the given string is as below:
Syntax :
SUBSTRING(input string, start, length);In the above syntax,
- input string: It can be a character or text from which the substring will be extracted.
- start: This is the starting position of the substring which is to be extracted or it states the position or location from where the extracted substring starts. Also, it is to be noted that the starting position in a string is 1.
- length: The ‘length’ specifies the number of characters of the substring which are to be returned and length is a positive integer. When the value of start + length is greater than the length of the input string, the substring begins at the start which will also contain the remaining characters of the input string. But when a length is a negative number, SUBSTRING() will throw an error.
Examples of SQL Server Substring
Let us go through some examples to understand the working of SUBSTRING() in SQL Server and how they can be used within the queries.
Example #1
In the below example, it can be seen that the SUBSTRING() function is used with the literal strings. The below query will extract the substring which will start from the first character of the given input string ‘How are you?’ and the length of the substring will be 3.
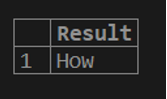
SELECT SUBSTRING('How are you?', 1, 3) AS Result;As a result, the substring which is extracted is ‘How’. The substring starts from the first character ‘H’ and has a length of 3, hence the extracted substring is How.
Output:
Example #2
Also, in the below query, it can be seen that substring is extracted from the first character ‘H’ and has a length of 2.
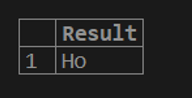
SELECT SUBSTRING('How are you?', 1, 2) AS Result;The result of the above statement is shown below as the extracted substring is ‘Ho’.
Output:
Similarly, we can extract any required substring by using the SUBSTRING() function accordingly i.e. by specifying the starting position or location and the length of the substrings.
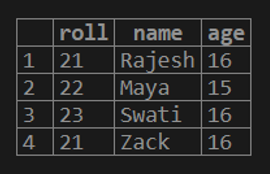
Let us consider the below table ‘STUDENTS’ to understand how the SUBSTRING() function can be used with the columns of a table.
Output:
Example #3
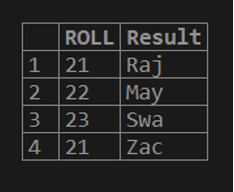
In the below query, the SUBSTRING() is used along with the column ‘NAME’ from the ‘STUDENTS’ table where the substring which will be extracted starts from the first character of the student’s name which has a length of 3.
SELECT ROLL, SUBSTRING(NAME, 1, 3) AS Result FROM STUDENTS;The result of the above query is shown below and it can be seen that the output contains the Roll of the students and the extracted substring from the Name column. The extracted substrings have a length of 3 and start from the first character of the respective Names of the students. So for student ‘Rajesh’, the extracted substring is ‘Raj’ which started from ‘R’ and contains the length of the 3 characters. Similarly, the result is shown for other students.
Output:
Example #4
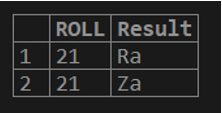
In the below query, SUBSTRING() is used along with the ‘WHERE’ clause in the query. The extracted substring will start from the first character of the string ‘Rajesh’ and has a length of 2.
SELECT ROLL, SUBSTRING(NAME, 1, 2) AS Result FROM STUDENTS WHERE ROLL=21 ;The result of the above query is shown below where we can see that for Roll ‘21’ i.e. the condition specified in the ‘WHERE’ clause, the substring is extracted as ‘Ra’.
Output:
Example #5
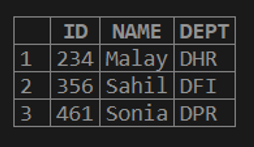
The SUBSTRING() can be used in nested queries too. Let us consider the below table “EMPLOYEE”. In this table, the column ‘DEPT’ has various departments in which the employees work and the department codes start with ‘D’.
Output:
If we want to extract only the department names such as ‘HR’, ‘FI’ and ‘PR’ from the department codes, it can be done by using the nested query as shown below. The charindex() used in the query will search for the substring in a string and will return the position. The charindex() returns 0 if the substring is not found. The len() will return the length of the string. Here we want to remove ‘D’ from the department code in our result, so the usage of charindex() and len() will help in getting the required result.
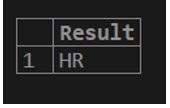
SELECT SUBSTRING(DEPT, charindex('D', DEPT)+ 1, len(DEPT) - charindex('D', DEPT)) AS Result FROM EMPLOYEE WHERE ID=234;In the result below, it can be seen that the ‘D’ is dropped from the department code ‘DHR’ as only ‘HR’ is displayed for the employee with ID 234.
Output:
Conclusion
The SUBSTRING() function in SQL Server plays a vital role in extracting the substrings according to the requirement from the input strings which can be used in nested queries along with WHERE clause. The developers must have a good understanding of this function.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Server Substring” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.