Updated May 20, 2023
We
Introduction of SQL DML Commands
Data Manipulation Language (DML) commands in SQL manage data records stored within the database tables. It does not deal with changes to database objects and their structure. The commonly known DML commands are INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE. We can consider even SELECT statements as a part of DML commands. Albeit, it strictly forms part of the Data Query Language (DQL) command. In the subsequent sections, we will learn about the DML commands in detail. But let us first look at this summary table for a brief overview.
|
Command |
Description |
| SELECT | Used to query or fetch selected fields or columns from a database table |
| INSERT | Used to insert new data records or rows in the database table |
| UPDATE | Used to set the value of a field or column for a particular record to a new value |
| DELETE | Used to remove one or more rows from the database table |
Commands of DML
Now let us try to understand each of the DML mentioned above commands in detail one by one.
1. SELECT
SELECT command or statement in SQL is used to fetch data records from the database table and present it in the form of a result set. It is usually considered a DQL command, but it can also be considered a DML.
The basic syntax for writing a SELECT query in SQL is as follows :
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, …
FROM table_name
WHERE condition_ expression;The parameters used in the above syntax are as follows :
- column_name1, column_name2, … : Specify the column_names which have to be fetched or selected for the final result set.
- table_name: Specify the name of the database table from which these results have to be fetched.
- condition_expression: Specify the condition expression for filtering records for the final result set.
Here are a few examples to illustrate the use of the SELECT command.
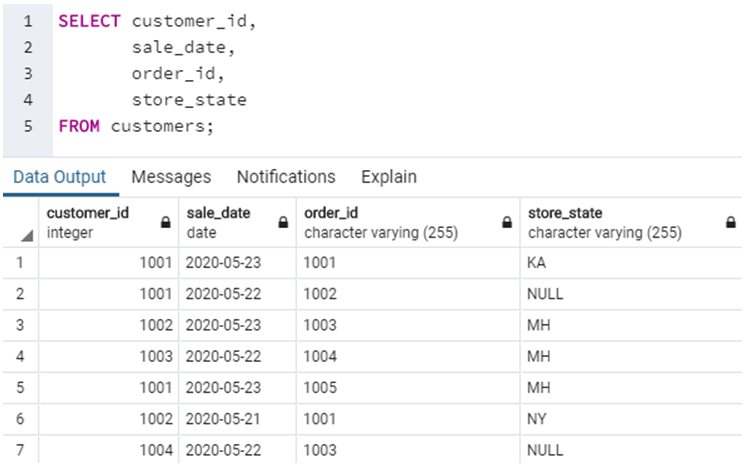
SELECT customer_id,
sale_date,
order_id,
store_state
FROM customers;The query returns the following output.
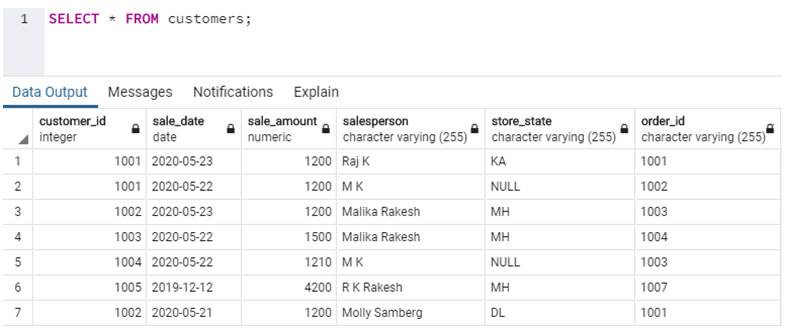
In this example, we have fetched fields such as customer_id, sale_date, order_id, and store_state from customer’s table. Next, suppose if we want to fetch all the records from the customers’ table. This can be achieved by a simple query, as shown below.
SELECT * FROM customers;The query returns the following output.
2. INSERT
INSERT commands in SQL are used to insert data records or rows in a database table. In an INSERT statement, we specify both the column_names for which the entry has to be made along with the data value that has to be inserted.
The basic syntax for writing INSERT statements in SQL is as follows :
INSERT INTO table_name (column_name_1, column_name_2, column_name_3, ...)
VALUES (value1, value2, value3, ...)By VALUES, we mean the value of the corresponding columns.
Here are a few examples to further illustrate the INSERT statement.
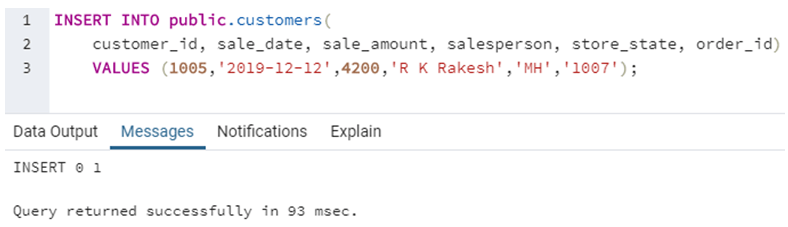
INSERT INTO public.customers(
customer_id, sale_date, sale_amount, salesperson, store_state, order_id)
VALUES (1005,'2019-12-12',4200,'R K Rakesh','MH','1007');We have tried inserting a new row in the Customers table using the INSERT command. The query accepts two sets of arguments: field names or column names and their corresponding values.
Suppose we have to insert values into all the fields of the database table; then, we need not specify the column names, unlike the previous query. Follow the following query for further illustration.
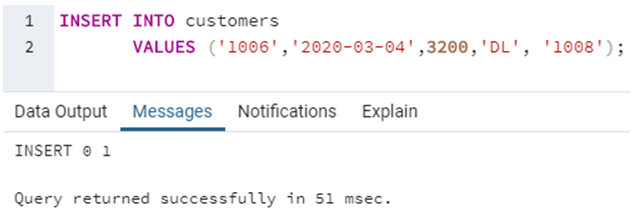
INSERT INTO customers
VALUES ('1006','2020-03-04',3200,'DL', '1008');In this example, we have successfully inserted all the values without having to specify the fieldnames.
3. UPDATE
UPDATE command or statement is used to modify the value of an existing column in a database table.
The syntax for writing an UPDATE statement is as follows :
UPDATE table_name
SET column_name_1 = value1, column_name_2 = value2, ...
WHERE condition;Having learned the syntax, let us now try an example based on the UPDATE statement in SQL.
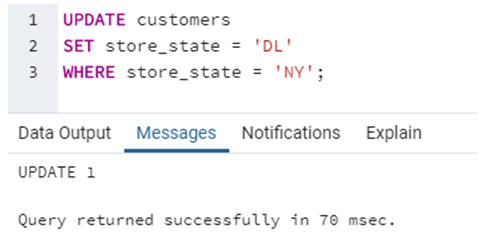
UPDATE customers
SET store_state = 'DL'
WHERE store_state = 'NY';In this example, we have modified the value of store_state for a record where store_state was ‘NY’ and set it to a new value, ‘DL’.
4. DELETE
DELETE statement in SQL is used to remove one or more rows from the database table. It does not delete the data records permanently. We can always perform a rollback operation to undo a DELETE command. With DELETE statements, we can use the WHERE clause for filtering specific rows.
The syntax for writing a DELETE statement is as follows :
DELETE FROM table_name WHERE condition;Having learned the syntax, we are all set to try an example based on the DELETE command in SQL.
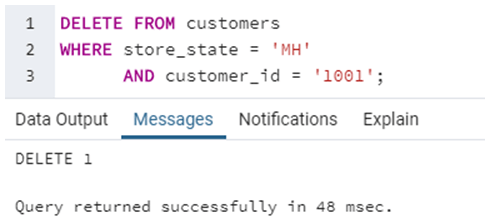
DELETE FROM customers
WHERE store_state = 'MH'
AND customer_id = '1001';In this example, we have removed a row from the customer’s table where store_state was ‘MH’ and customer_id was ‘1001’.
Conclusion
We can use DML commands to modify or manipulate data records present in the database tables. Some of the basic DML operations are data insert (INSERT), data updation (UPDATE), data removal (DELETE), and data querying (SELECT).
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DML Commands” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.