Updated February 27, 2023
Introduction to Array in SQL
An array in structured query language (SQL) can be considered as a data structure or data type that lets us define columns of a data table as multidimensional arrays. They are basically an ordered set of elements having all the elements of the same built-in data type arranged in contiguous memory locations. Arrays can be of integer type, enum type or character type, etc.
How to Create an Array in SQL?
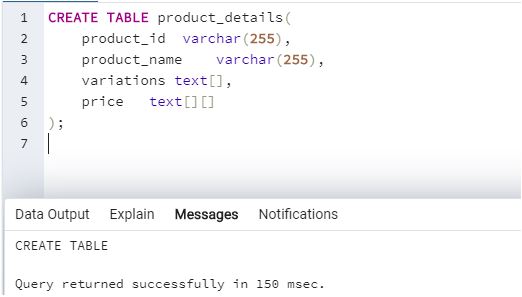
In order to understand array creation in SQL, let us first create a ‘product_details’ table which contains product id, product name, variations, and prices for demonstration purposes. We can use the following SQL statements to perform the task.
Here, we have successfully created a product_details table with two columns/attributes variations and prices having an array data type. “Variations” have a one-dimensional array data type and “prices” have a multi-dimensional array data type. A one-dimensional array is denoted by the data type of elements in the array followed by “[]” and a multi-dimensional array is denoted by “[][]”.
How to insert Array elements in SQL?
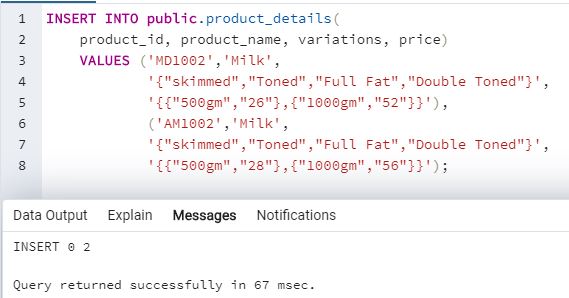
We can insert array elements in an array by mentioning them within curly braces {} with each element separated by commas. Here is an example to illustrate the method for element addition in an array in SQL. Let us insert details into the above mentioned “product_details” table.
The parts in “Green” color are the sections that illustrate array insertion.
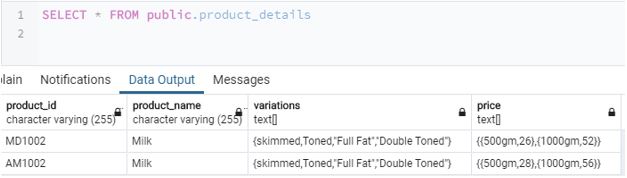
Now we have successfully inserted elements in the table as well as in the mentioned arrays. The data in the product_details table are performing the above-mentioned array insertion looks something like this.
Array Operations in SQL
In this section, we will be discussing some basic array operations like accessing an array element, using array elements in search queries and modifying array elements, etc. So, let us begin.
Accessing an Array element
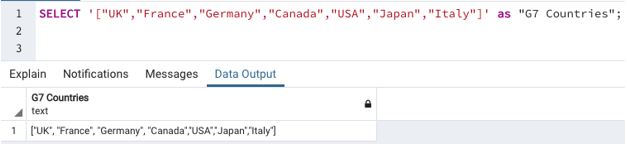
Accessing an array is as simple as this. Here, we have shown an array called ‘G7 countries’.
In order to further illustrate accessing array elements, we will take the help of the “product_details” table.
Examples to Implement Array in SQL
Below are the examples mentioned:
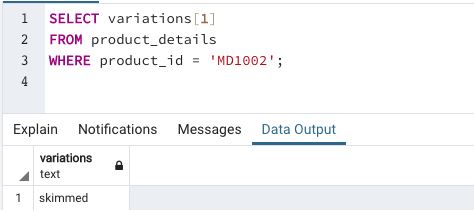
Example #1
Find the first variation of milk with product_id = ‘MD1002’
In this example we are trying to illustrate accessing elements in a one-dimensional array.
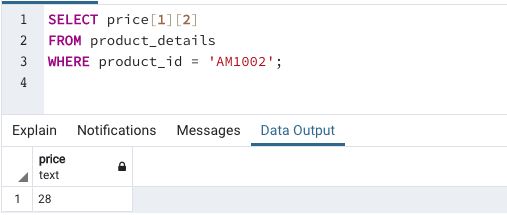
Example #2
Find the price of 500gm of milk for “AM1002” product
In this example, we are trying to illustrate accessing elements in a multidimensional array.
The order of accessing elements in a multidimensional array is similar to accessing elements of a matrix, but the only difference is here elements start with index = 1 instead of index = 0 as in the case of matrices.
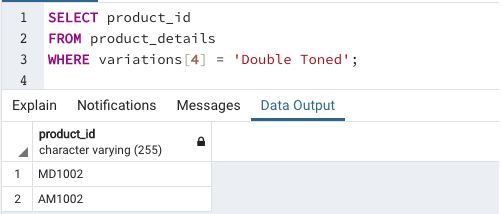
Example #3
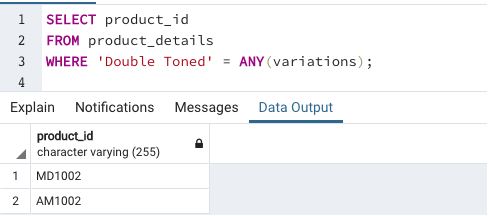
Find the product_id for which we can find “double toned” milk variation
This example illustrates the usage of one-dimensional array elements in searching database tables.
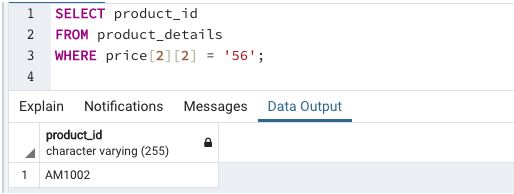
Example #4
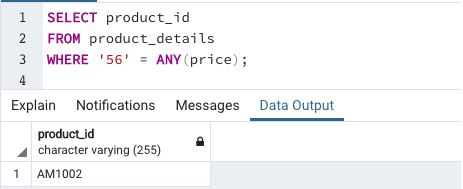
Find the product_id for which the 1 kg of milk costs ‘56’ rupees
This example illustrates the usage of multidimensional array elements in searching database tables
The above examples are very helpful if we know the size or the location of attributes in an array. But they become very tedious once the size of the array becomes large. So, what to do to avoid such situations?
We can use parameters like ANY and ALL. The above-mentioned SQL queries can be alternatively written as follows
We can observe that the results of both the queries are the same. Alternatively, if you do not want to use ANY or ALL, you can use the generate_script() function in pgSQL.
Modifying or Updating Array elements :
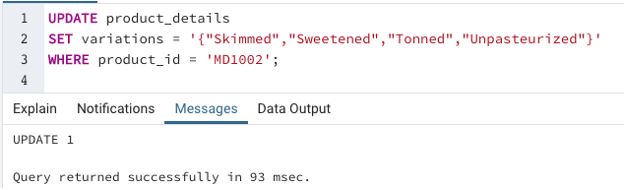
Example #5
SQL query to illustrate updating of an entire array
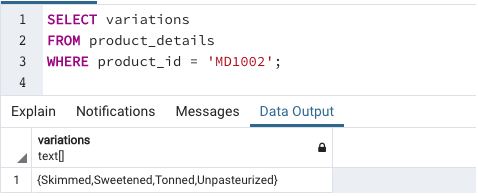
We have successfully updated the variations array in the product_details table. Next, we can check if the changes have been made using a SELECT query.
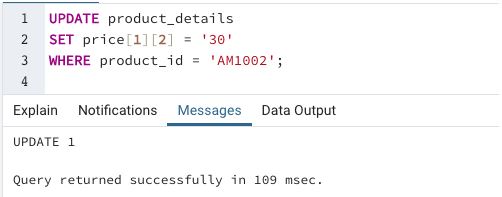
Example #6
SQL query to illustrate updating an element of the array
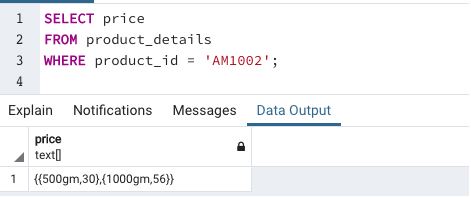
We have successfully updated the price array in the product_details table. Next, we can check if the changes have been made using a SELECT query.
Conclusion
An array is a data structure that stores elements of the same built-in data-type in a contiguous memory location. Arrays can be one dimensional or multidimensional. They are very useful because they allow for easy access to data elements.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to Array in SQL. Here we discuss an introduction to Array in SQL, how to create and insert array with examples. You can also go through our other related articles to learn more –