Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL NTILE()
NTILE() in Standard Query Language (SQL) is a window function that is used to divide sorted rows of a partition into a specified number of equal size buckets or groups. Each bucket is assigned a rank starting from 1. Each row in the partition is assigned a bucket number based on the group to which it belongs.
For further understanding, NTILE() functionality can be considered as placing 10 letters in three envelopes. It is a ranking function that will divide a result set of m rows or records into n groups or buckets with m/n records in each bucket. In cases where the result set is not exactly divisible into an equal number of rows, it assigns more records to the starting buckets and less to the following ones.
Syntax and parameters:
The basic syntax for writing NTILE() function in SQL is as follows :
NTILE(buckets) OVER (
[PARTITION BY partition_expression ]
[ORDER BY order_expression [ASC | DESC] ]
)The arguments or parameters used in the above syntax are as follows :
- buckets: The number of groups we want is specified here. It is a positive integer or an expression that returns a positive integer. The number of buckets can not be a NULL value.
- partition_expression: The column on the basis of which the entire dataset has to be divided. By default, the entire result set is considered as a single partition.
- order_expression: The column on the basis of which the rows in the partition set is ordered or sorted in a particular ascending or descending order.
Examples
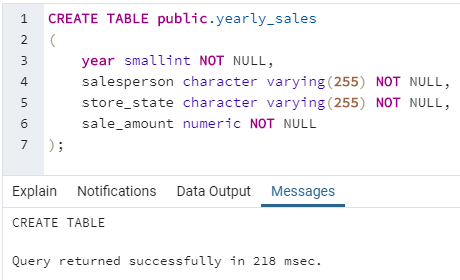
In order to understand SQL NTILE() function in great detail, let us create a table called “yearly_sales” for illustration purposes. This table contains details such as year, amount, and salesperson pertaining to each sale made by the store. We can use the following code snippet for creating the said table.
CREATE TABLE public.yearly_sales
(
year smallint NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
sale_amount numeric NOT NULL
);Now we have successfully created the table. Let us insert some random data in it to work with.
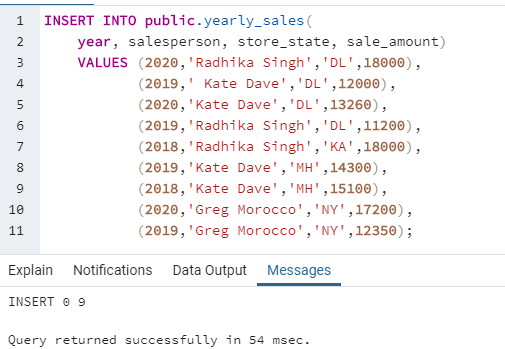
INSERT INTO public.yearly_sales(
year, salesperson, store_state, sale_amount)
VALUES (2020,'Radhika Singh','DL',18000),
(2019,' Kate Dave','DL',12000),
(2020,'Kate Dave','DL',13260),
(2019,'Radhika Singh','DL',11200),
(2018,'Radhika Singh','KA',18000),
(2019,'Kate Dave','MH',14300),
(2018,'Kate Dave','MH',15100),
(2020,'Greg Morocco','NY',17200),
(2019,'Greg Morocco','NY',12350);Finally! After a few insertion operations, the data in the above mentioned “yearly_sales” table looks something like this :
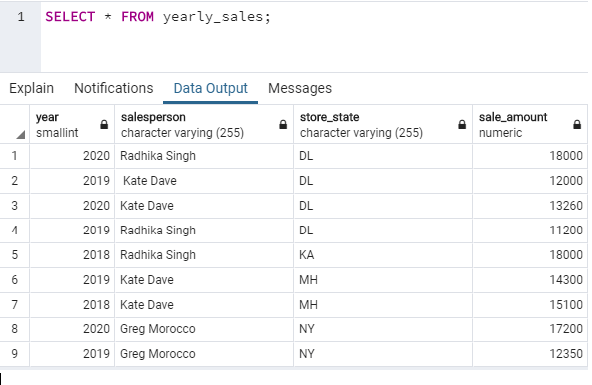
SELECT * FROM yearly_sales;Here are a few examples based on the above-mentioned table to explain NTILE() function in detail.
Example #1
SQL query to illustrate use of NTILE() function to divide records in the yearly_sales table into 3 buckets.
SELECT year,salesperson,sale_amount, NTILE(3) OVER( ORDER BY year ) as year_buckets FROM yearly_sales ORDER BY year,salesperson DESC;,/pre>In the above example, we can observe that the year-wise data or rows mentioned in the yearly_sales table have been divided into three buckets: 1, 2, and 3. First bucket has (2018,2018,2019), second bucket has (2019,2019,2019) and third bucket has (2020,2020,2020). Since there were 9 records, they are divided equally among 3 buckets.
Example #2
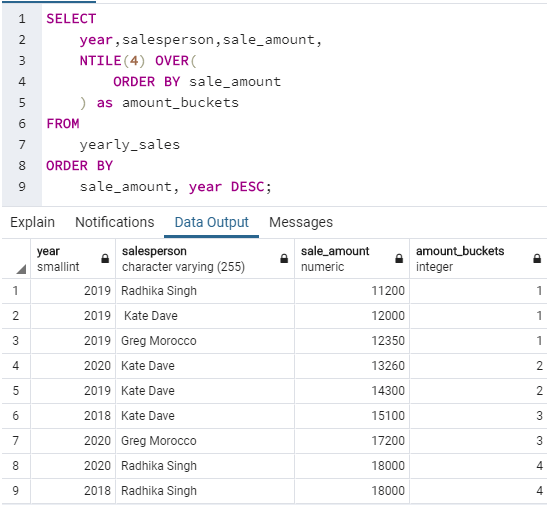
SQL query to illustrate use of NTILE() function to divide records in the yearly_sales table into 4 buckets.
SELECT
year,salesperson,sale_amount,
NTILE(4) OVER(
ORDER BY sale_amount
) as amount_buckets
FROM
yearly_sales
ORDER BY
sale_amount, year DESC;In this example, we observe that NTILE(4) has divided the 9 records into 4 buckets. But we can see that the first bucket has 3 rows whereas the rest of them have 2 rows each. This is because NTILE() assigns more records to the starting buckets and less to the following ones in situations when the recordset cannot be divided equally.
Example #3
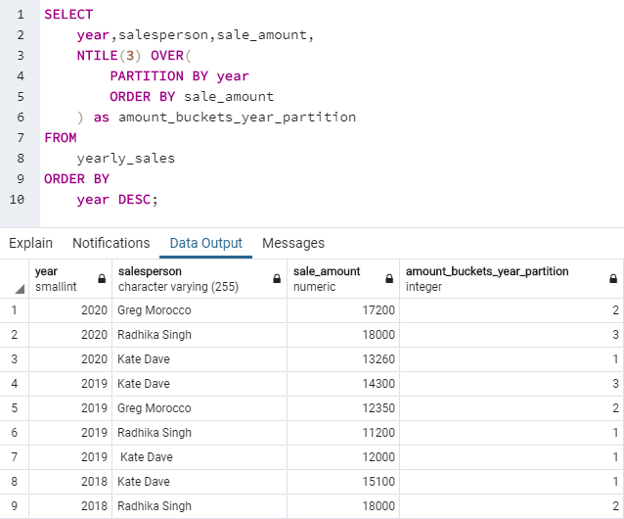
SQL query to illustrate use of NTILE() function to divide records in the yearly_sales table into partitions by year and then divide into 3 buckets.
SELECT
year,salesperson,sale_amount,
NTILE(3) OVER(
PARTITION BY year
ORDER BY sale_amount
) as amount_buckets_year_partition
FROM
yearly_sales
ORDER BY
year DESC;In this example, we can see that three partitions by year have been created. Now in each of these three partitions, the rows are assigned to three buckets, namely 1, 2, and 3.
Example #4
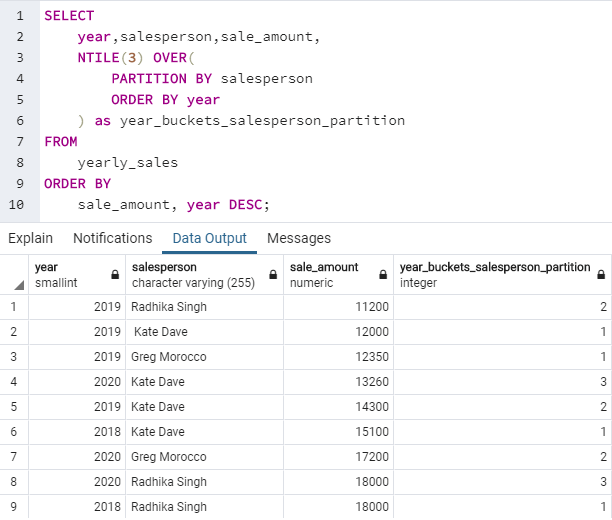
SQL query to illustrate use of NTILE() function to divide records in the yearly_sales table into partitions by salesperson and then divide into 3 buckets.
SELECT
year,salesperson,sale_amount,
NTILE(3) OVER(
PARTITION BY salesperson
ORDER BY year
) as year_buckets_salesperson_partition
FROM
yearly_sales
ORDER BY
sale_amount, year DESC;In this example, we can observe that three partitions by salesperson have been created. Now in each of these three partitions, the rows are assigned to three buckets, namely 1, 2, and 3.
Conclusion
SQL NTILE() is a window function that is primarily used for dividing a window or a partition in the recordset into a specific number of buckets. It is useful for grouping ranked data together for data analysis purposes.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL NTILE()” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


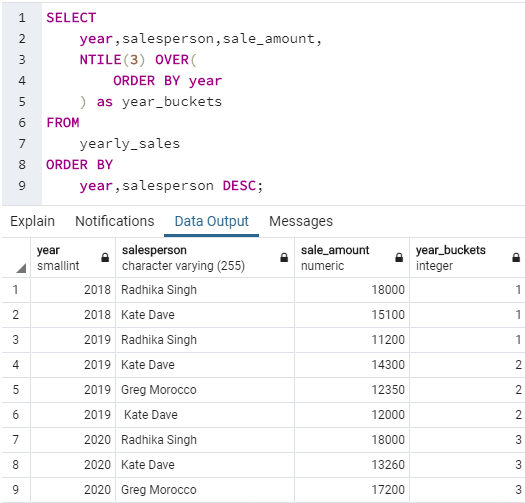 In the above example, we can observe that the year-wise data or rows mentioned in the yearly_sales table have been divided into three buckets: 1, 2, and 3. First bucket has (2018,2018,2019), second bucket has (2019,2019,2019) and third bucket has (2020,2020,2020). Since there were 9 records, they are divided equally among 3 buckets.
In the above example, we can observe that the year-wise data or rows mentioned in the yearly_sales table have been divided into three buckets: 1, 2, and 3. First bucket has (2018,2018,2019), second bucket has (2019,2019,2019) and third bucket has (2020,2020,2020). Since there were 9 records, they are divided equally among 3 buckets.