Updated July 1, 2023
Introduction to SQL Compare String
String Comparison is a collective term used for functions and methods to compare strings, text, or character data type values. The commonly used string comparison functions can either be pattern-matching functions like regex and LIKE or WHERE clause comparison operators. Some databases, like the MYSQL database, also have built-in functions such as STRCMP() for string comparison.
However, we might encounter cases where we might have to perform data type conversions before performing string comparisons.
Do not get overwhelmed by the comparison functions and methods mentioned here; we will be discussing them in great detail in the subsequent sections.
Syntax and parameters:
The basic syntax for string comparison in SQL is as follows :
SELECT column_name1, column_name2, …
FROM table_name1
WHERE column_name1:: [varchar, text] comparison_operator [>,<,=,!=,...]
comparison_expression :: [varchar, text]The parameters used in the syntax as mentioned earlier are as follows :
- column_name1, column_name2, …: It is the name of the columns that we want to fetch for the final result set.
- table_name1: The database table from which said columns will be fetched.
- column_name1: string in any character data type that has to be compared with another string.
- comparision_expression: Another string value or string convertible value with which column_name1 will be compared.
We can always make data-type conversions. In PostgreSQL, it can be done as shown in the syntax.
The syntax for STRCMP() function in MYSQL is as follows :
SELECT STRCMP(argument1, argument2);Here, argument1 and argument2 are string-type data values that we want to compare.
The syntax for using LIKE wildcard for comparing strings in SQL :
SELECT column_name1, column_name2,...
FROM table_name1
WHERE column_name1 LIKE %abc%Here %abc% means abc occurring anywhere in the string. % abc means abc at the start of the string. Similarly, abc% means abc at the end of the string.
Examples of SQL Compare String
In order to illustrate string comparisons in SQL, let us create a dummy table called “sales_details.” This table contains sales information pertaining to sales made by each salesperson in the company.
We can use the following code snippet to perform the given task.
Code:
CREATE TABLE sales_details
(
salesperson_id integer NOT NULL,
salesperson character varying(255) NOT NULL,
store_state character varying(255) NOT NULL,
sales_target numeric NOT NULL,
sales_current numeric NOT NULL
);The query returned successfully, and sales_details have been created. Now, let us insert some records in it to work with.
We can use the following insert query for this purpose.
INSERT INTO sales_details
(salesperson_id
,salesperson
,store_state
,sales_target
,sales_current)
VALUES
(106,'Sahil Singh','KA',12000,7778),
(107,'Rohit Sharma','DL',22000,15600),
(108,'Max Muller','MH',20000,16780),
(109,'Ashley K','WB',13000,11780),
(110,'Mathew Harris','TN',6000,5678),
(101,'Danish K','KA',10000,10000),
(102,'Rashmi Sharma','DL',23000,18000),
(103,'Mohak Patel','MH',21000,21000),
(104,'Devika Ramaswamy','TN',10000,8000),
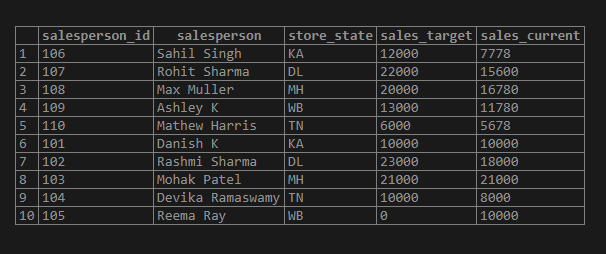
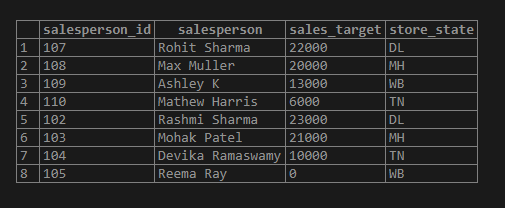
(105,'Reema Ray','WB',0,10000);The data in the sales_details table after insertion looks something like this.
SELECT * FROM sales_details;Now we are all set to try a few examples on string comparison.
Example #1
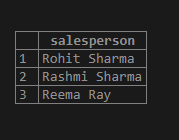
Find all the salespersons whose name begins with the letter R.
Code:
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_details
WHERE salesperson LIKE 'R%';Output:
In this example, the query returns all the names which start with ‘R’. LIKE is a pattern-matching keyword.
Example #2
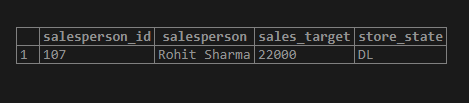
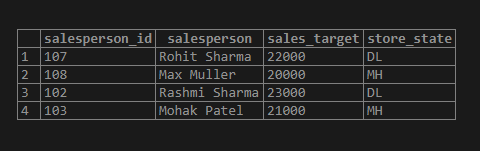
Find the salesperson_id, sales_target, and store location of the salesperson named Rohit Sharma.
Code:
SELECT salesperson_id, salesperson, sales_target, store_state
FROM sales_details
WHERE salesperson = 'Rohit Sharma';Output:
Example #3
Find the salesperson_id, sales_target, and store location of salespersons whose sales_target is less than 20000 using the NOT IN comparison operator.
Code:
SELECT salesperson_id, salesperson, sales_target, store_state
FROM sales_details
WHERE salesperson NOT IN
(SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_details
WHERE sales_target < 20000);Output:
This query illustrates the use of NOT IN comparison operators when comparing strings. It also focuses on the uses of subqueries.
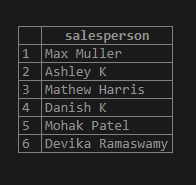
Example #4
Find the salesperson_id, sales_target, and store location of salespersons whose store location is not KA or NY.
Code:
SELECT salesperson_id, salesperson, sales_target, store_state
FROM sales_details
WHERE store_state <> 'KA' AND store_state <> 'NY';Output:
Example #5
Find the salespersons whose names are lexologically smaller than ‘Rashmi’.
Code:
SELECT salesperson
FROM sales_details
WHERE salesperson < 'Rashmi';Output:
When used with strings, the greater than and less than comparison operator returns the lexicologically greater or lesser strings after comparison. We can observe in this example that the query returns all names lexically smaller than ‘Rashmi’.
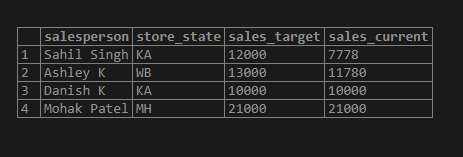
Example #6
Find the details of the salesperson whose names do not contain the letter ‘R.’
Code:
SELECT salesperson, store_state, sales_target, sales_current
FROM sales_details
WHERE salesperson NOT LIKE '%R%';Output:
Conclusion
String comparison in SQL involves a comparison of string, text, varchar, or any other character data type values with others using built-in functions like STRCMP(), wildcard pattern matching keywords such as LIKE, and as part of condition clause with comparison operators. We have tried to explain the same in this post.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Compare String” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.