Updated July 1, 2023
Introduction to SQL UPDATE Trigger
UPDATE Triggers are usually used when we want to track modification details on certain database values. For example, we want to capture the time of login and logout of a user from a website, restaurant, office, etc. In the former case, we can use the BEFORE UPDATE Trigger and AFTER UPDATE Trigger for the latter.
In this post, we will be discussing UPDATE Trigger in detail with the help of some examples. To begin with, let us learn the syntax and parameters used for creating an UPDATE Trigger in SQL.
Syntax and parameter:
The basic syntax used for writing an UPDATE Trigger in SQL is as follows :
CREATE TRIGGER [schema_name. ] trigger_name ON table_name
{AFTER| BEFORE | INSTEAD OF } UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
[SET NOCOUNT {ON/OFF}]
{SQL statements}
ENDThe parameters used in the syntax mentioned above are as follows :
- schema_name: schema_name here corresponds to the schema’s name where the new update trigger will be created. When we do not mention schema_name, the trigger gets created on the current or default schema.
- trigger_name: trigger_name is the name of the new update trigger which we will be creating.
- table_name: table_name is the name of the table in the mentioned schema on which the new update trigger will be created.
- AFTER | BEFORE | INSTEAD OF: This argument is to register the time when the trigger will be invoked if it will be invoked before or after the said UPDATE statements have been executed.
- SQL statements: SQL statements are a set of SQL operations that form the body of an UPDATE trigger.
Having discussed the syntax and parameters used for creating UPDATE triggers in SQL, let us try a few examples to understand it in great detail.
Examples of SQL UPDATE Trigger
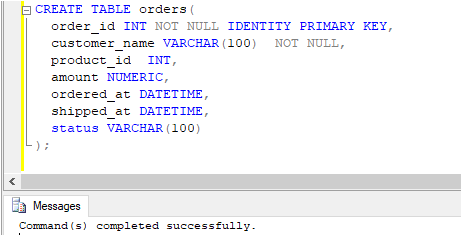
In order to illustrate the working of UPDATE triggers in SQL, what could be better than trying some examples on a dummy table? Ergo, let us create a table called “orders” that contains details such as ordered item, ordered_at, shipped_at, status, etc. We can use the following CREATE command to create the said table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE orders(
order_id INT NOT NULL IDENTITY PRIMARY KEY,
customer_name VARCHAR(100) NOT NULL,
product_id INT,
amount NUMERIC,
ordered_at DATETIME,
shipped_at DATETIME,
status VARCHAR(100)
);Output:
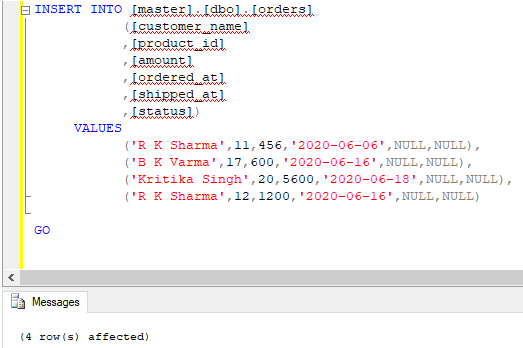
Having created the table, let us insert a few records to work with using the following insert statement.
Code:
INSERT INTO [master].[dbo].[orders]
([customer_name]
,[product_id]
,[amount]
,[ordered_at]
,[shipped_at]
,[status])
VALUES
('R K Sharma',11,456,'2020-06-06',NULL,NULL),
('B K Varma',17,600,'2020-06-16',NULL,NULL),
('Kritika Singh',20,5600,'2020-06-18',NULL,NULL),
('R K Sharma',12,1200,'2020-06-16',NULL,NULL)
GOOutput:
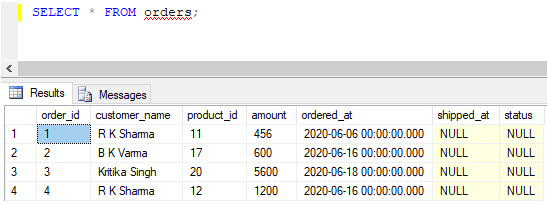
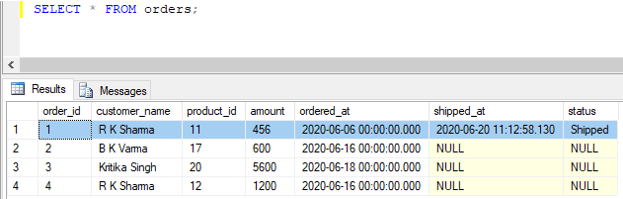
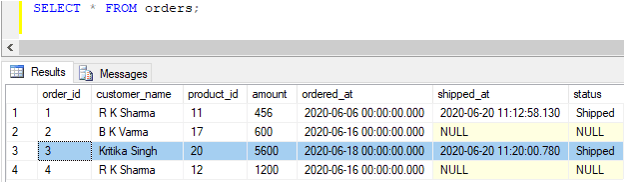
The data in the orders table, after successful insertion, looks something as follows:
Code:
SELECT * FROM orders;Output:
Now we are all set to try a few examples on UPDATE TRIGGER using this table.
Example #1
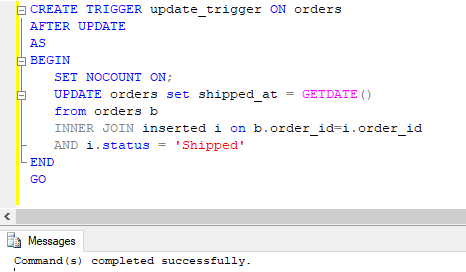
Create a trigger in SQL, which automatically updates the date and time of shipping once the order status has been changed to shipped.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER update_trigger ON orders
AFTER UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE orders set shipped_at = GETDATE()
from orders b
INNER JOIN inserted i on b.order_id=i.order_id
AND i.status = 'Shipped'
END
GOOutput:
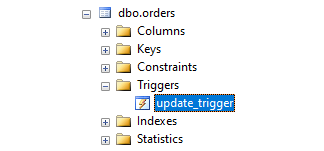
The command has successfully created an UPDATE trigger that gets invoked after successful update statement execution. The trigger name can be seen under the orders table in the object explorer.
Now let us try a few update queries on the orders table.
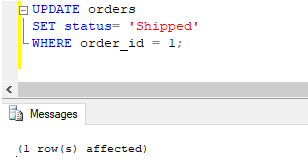
Code:
UPDATE orders
SET status= 'Shipped'
WHERE order_id = 1;Output:
The update query returned successfully. We can check this using a SELECT query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM orders;Output:
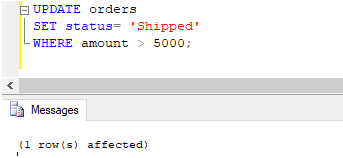
Code:
UPDATE orders
SET status= 'Shipped'
WHERE amount > 5000;Output:
Similar to the previous query, the query returned successfully. We can check this using a SELECT query.
Code:
SELECT * FROM orders;Output:
Example #2
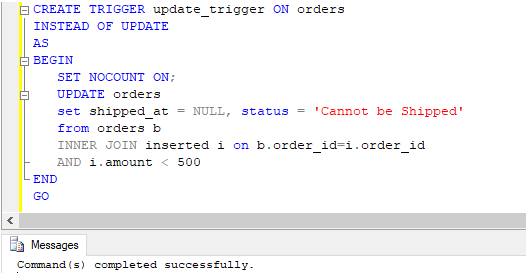
Create a trigger in SQL, which automatically gets invoked and sets shipped_at time to NULL and status to ‘Cannot be Shipped’ when the order value is less than 500.
Code:
CREATE TRIGGER update_trigger ON orders
INSTEAD OF UPDATE
AS
BEGIN
SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE orders
set shipped_at = NULL, status = 'Cannot be Shipped'
from orders b
INNER JOIN inserted i on b.order_id=i.order_id
AND i.amount < 500
END
GOOutput:
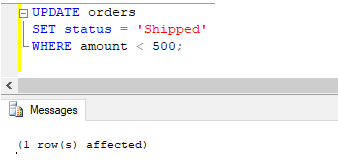
This update trigger is a variation of the previous one. Let’s try an update query to illustrate it further.
Code:
UPDATE orders
SET status = 'Shipped'
WHERE amount < 500;Output:
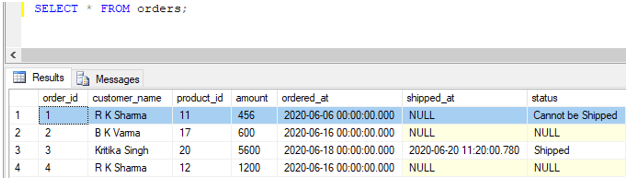
The results of the update query can be checked using a SELECT statement.
Code:
SELECT * FROM orders;Output:
Finally, an update trigger can be deleted or dropped using a DROP TRIGGER command.
Code:
DROP TRIGGER update_trigger;Output:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL UPDATE Trigger” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.