Updated March 15, 2023
Introduction to SQL DELETE
SQL delete is used to delete the records from the table. We can use the where clause with the delete statement to delete the selected records from the table. Suppose we have not used any condition in our query all the records from the table are deleted. The SQL delete is a DML query that allows the modification of database tables; it will delete the existing rows from the database tables.
Overview of SQL DELETE
- We need to be careful while executing this command because it will delete the records from the table.
- As we know, we are using inset statements in SQL for inserting statements. Same for deleting records from the table, we are using the delete statement.
- We can delete the table rows as per the condition that we have used in the query by using the delete statement.
- When deleting records from table, we can use more than one condition in a single query, the records will be deleted as per the condition.
SQL DELETE Statement
- This statement is used to delete the existing records from the table. We need to define the table name from which we have deleted the records.
- In the below first syntax, we have not used the where condition, so all the records from a table will be deleted. In the fourth syntax, we have used only on where condition, so all the rows will be deleted that match this condition. In the second syntax, we use two conditions with a where clause, so data is deleted at the time matching both the conditions.
Syntax
Delete from name_of_table;Delete from name_of_table where name_of_column1 = value AND name_of_column = values;Delete from name_of_table where name_of_column <comparison operator> values;Delete from name_of_table where condition;Below is the parameter description of syntax.
- Delete – This statement is used to delete the rows from a table. We can use the delete statement with and without where condition to delete rows from the table.
- From – This is the SQL keyword used to define the table name from which we deleted the records.
- Name of table – This is nothing but the table name from which we have deleted the records. When deleting records or executing a query, we need to define the table name.
- Where condition – This is the most important parameter at the time of execution. The where condition in the delete statement of SQL will be used to delete the specified row which we have defined in the where condition. Where condition is very useful to delete specific condition row using the sql delete statement.
- Name of column – This table column is used to delete data from a table. Suppose we have used the delete statement with a specified column it will be deleting the records from the table.
- AND – This keyword is used in the delete statement to delete the rows from the specified column that we have defined in the query.
- When using a single column in the where condition, the delete query will be deleting the specified row that matches the condition.
SQL DELETE Query
- SQL delete query is not case sensitive we can use DELETE or delete to execute the sql delete query.
- The below example shows that the query is not case sensitive. In the first example, we have used sql delete query in the lowercase letter; after using sql delete query, it will execute without issuing any error. In the second example, we have used sql delete query in the uppercase letter; after using a delete query in the uppercase letter, it will also execute without issuing any error. So we can say that the SQL delete query is not case sensitive.
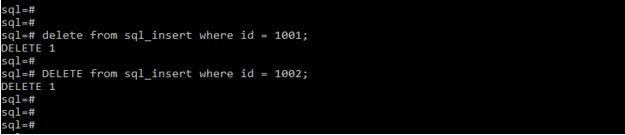
delete from sql_insert where id = 1001;
DELETE from sql_insert where id = 1001;- When executing any delete query on the production database server, we need to be very careful because it may take downtime of the system.
- Suppose our application needs to contain only new records, and we need to delete old records at the same time; we can use this statement to delete old records from the table.
- We can also use the comparison operator to delete the records from a table; after using the comparison operator, the matched rows will be deleted.
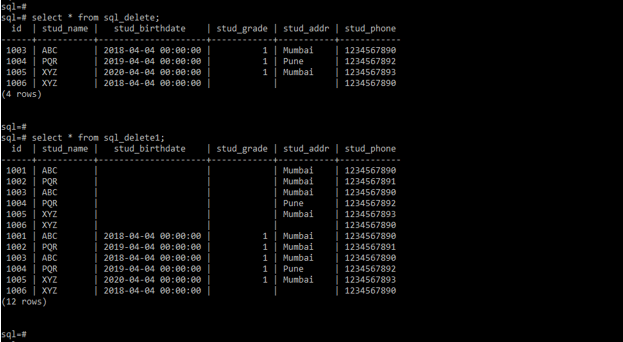
Select * from sql_delete;
Select * from sql_delete1;- In the below example, we deleted the specified records using the where condition. We have used the where condition on the id column. We can see that two records will be deleted because where condition will match the two rows.
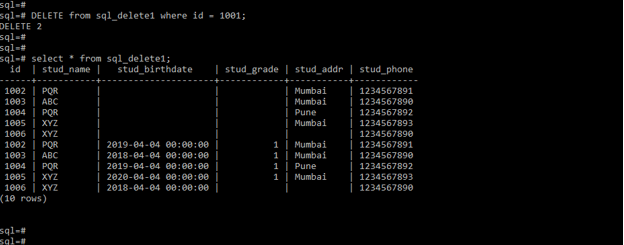
DELETE from sql_delete1 where id = 1001;
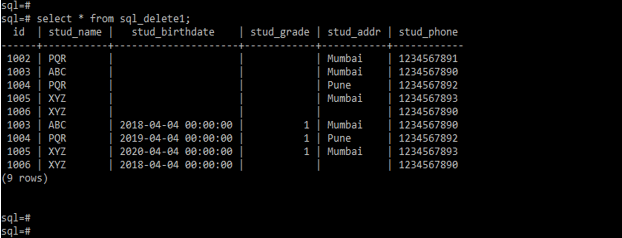
Select * from sql_delete1;2. In the below example we are using a two-column with where condition to delete records from a table. We are using the id and stud_grade column with the where condition.
DELETE from sql_delete1 where id = 1002 and stud_grade = 1;
Select * from sql_delete1;3. In the below example we are using the comparison operator to delete the records from a table. We are using the>, < and = operator to delete the records.
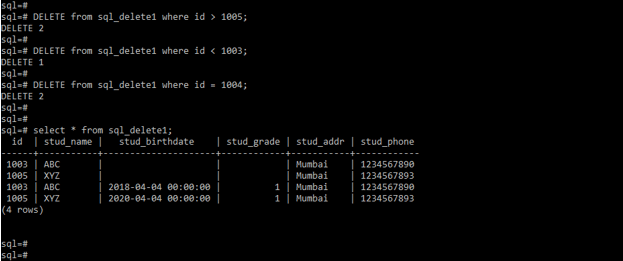
DELETE from sql_delete1 where id > 1005;
DELETE from sql_delete1 where id < 1003;DELETE from sql_delete1 where id = 1004;
Select * from sql_delete1;4. In the below example we are deleting the records as per the varchar data type column as follows.
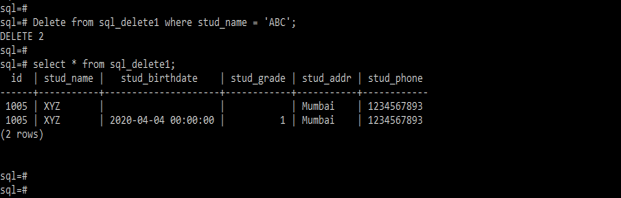
Delete from sql_delete1 where stud_name = 'ABC';
Select * from sql_delete1;5. In the below example we are deleting whole the records from the sql_delete1 table as follows.
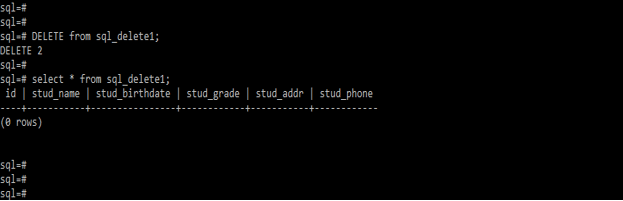
Delete from sql_delete1;
Select * from sql_delete1;Conclusion
To delete the whole records from the table, we do not need to use any other condition while executing the delete query; we need to use only the table name with the delete query. SQL delete query is a handy and important command in SQL database to delete the unwanted records from the table.
Recommended Article
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL DELETE” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.