Updated September 5, 2023
Definition of SQL NOT IN
The SQL NOT IN operator is an excellent tool for data filtering in SQL queries. It enables you to exclude rows from a result set based on values not included in a defined list or the result of a subquery.
By negating the condition, it chooses rows when the specified column does not match any of the values in the provided list or subquery result. This function filters data with flexibility. You can use it to exclude specific items or compare against a set of values dynamically generated from another table or subquery.
Table of Content
Syntax
Below is the syntax of the NOT IN statement as follows:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column NOT IN (value1, value2, ...);Parameters:
Below are the parameters, as follows:
- Column: It refers to the column you want to filter on.
- Table: The table name from which you select the data.
- (value1, value2, …): It represents the list of values that the result set excludes. You can specify multiple values for exclusion, separating them with commas.
Alternatively, you can use a subquery instead of a list of values. The subquery dynamically generates the values that are excluded from the result set. A subquery has the following syntax:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column NOT IN (SELECT column FROM subquery);In this case, a valid SQL subquery generates the values for exclusion in the result set.
Usage of SQL NOT IN
SQL queries commonly use the SQL NOT IN operator for data filtering. Its usage can be summarized as follows:
- Excluding specific values: The NOT IN operator allows you to exclude rows from a result set based on a specified list of values. It selects rows where the specified column does not match any of the values in the provided list.
- Dynamic exclusion with subqueries: To filter data based on values from another table or subquery, the NOT IN operator helps create a list of values to exclude dynamically.
- Multiple-column filtering: The NOT IN operator can filter rows based on combinations of values in multiple columns. It enables you to specify various columns to exclude rows with matching combinations of values.
- Alternative to multiple OR conditions: Using the NOT IN operator in the WHERE clause is a simpler and clearer way to exclude specific values than using multiple OR conditions. Rather than listing various conditions, you can define a single condition with the NOT IN operator.
Examples
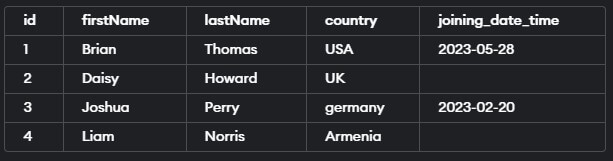
Firstly, Let us create a table named educba_learner using the following create table statements.
CREATE TABLE 'educba_learner' (
'id' INT(11) NOT NULL,
'firstName' VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
'lastName' VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
'country' VARCHAR(10) NOT NULL,
'joining_date_time' DATETIME DEFAULT NULL
);Let us insert some records in the table with the help of the following INSERT query statement.
INSERT INTO 'educba_learner'('id', 'firstName', 'lastName', 'country', 'joining_date_time') VALUES
(1, 'Brian', 'Thomas', 'USA', '2023-05-28'),
(2, 'Daisy', 'Howard', 'UK', NULL),
(3, 'Joshua', 'Perry', ' germany', '2023-02-20'),
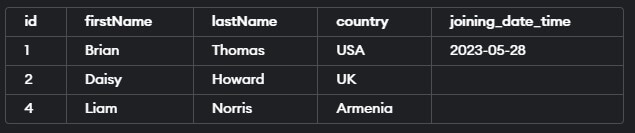
(4, 'Liam', 'Norris', 'Armenia', NULL);As you can see, we have inserted some records in the table. Let us retrieve the records from the table by using the select query statement.
Select * from 'educba_learner';The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
We are ready to use the NOT IN constraint on the above table. We will see the different examples one by one.
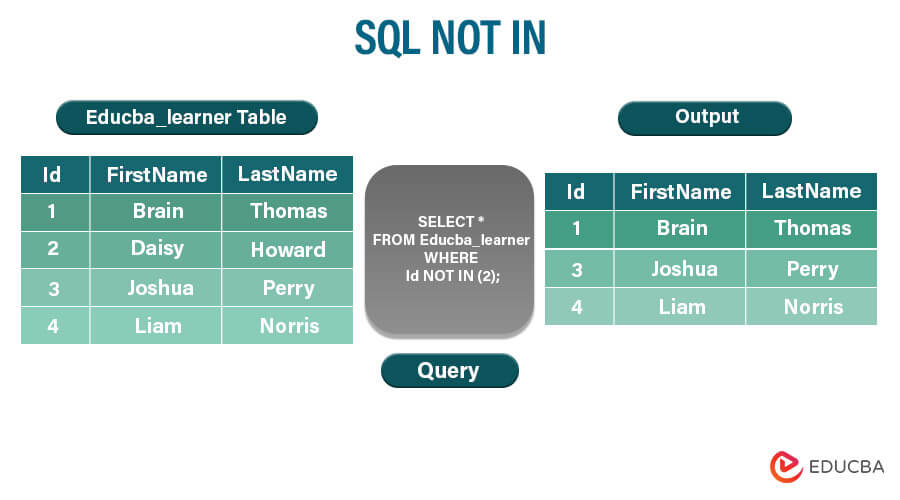
Example #1 – Using NOT IN constraint with the select query
Query:
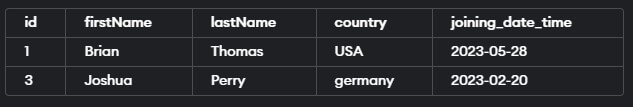
SELECT * FROM educba_learner WHERE id NOT IN (1,4);The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
This query retrieves all rows from the “educba_learner” table where the id is not 1 or 4.
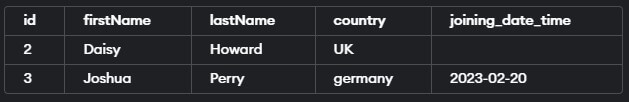
Example #2 – Filtering Rows based on a Single Column
Query:
SELECT * FROM 'educba_learner'
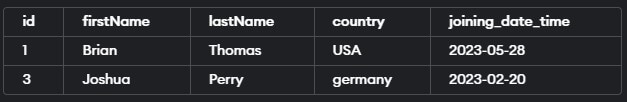
WHERE country NOT IN ('USA', 'Armenia');The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
This query retrieves all rows from the “educba_learner” table where the country is not ‘USA’ or ‘Armenia’.
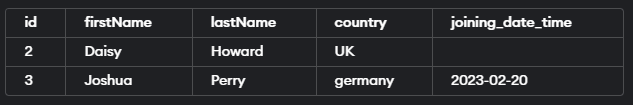
Example 3: Filtering Rows based on Multiple Columns
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba_learner
WHERE (firstName, id) NOT IN (('Daisy', 2), ('Liam', 4));The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
This query returns all rows from the “educba_learner” table where the combination of firstName and id is not (‘Daisy’, 2), (‘Liam’, 4).
Example 4: Filtering Rows with NULL Values
Query:
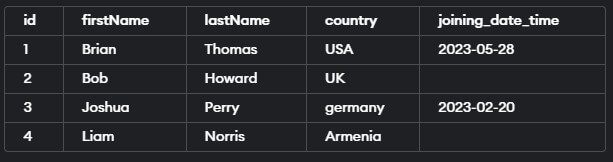
SELECT * FROM educba_learner
WHERE country NOT IN ('Armenia', 'UK') OR country IS NULL;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
This query returns all rows from the “educba_learner” dataset where a country is not ‘Armenia’ or ‘UK’, including rows where the city is NULL.
Example 5: Combining NOT IN with Other Operators
Query:
SELECT * FROM educba_learner
WHERE firstname NOT IN (SELECT firstname FROM educba_learner WHERE firstname LIKE 'J%');The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
This query retrieves all rows from the “educba_learner” table where the firstName is not included in the subquery result, which chooses firstName from the “educba_learner” table where the firstName begins with J.
Example 6: Using NOT IN constraint with the update query
While updating the records, there might be a scenario where you want to update only those records that do not have the values of particular columns set to some specified values. Now, we have to change the firstname to “Bob” in the table educba_learner, where the lastname does not contain the same name as Thomas, Perry, and Norris. We will use the NOT IN operator in the where clause of the update query to satisfy our condition using the following query statement –
Query:
UPDATE educba_learner
SET firstName = "Bob"
WHERE lastName NOT IN ("Thomas" , "Perry" , "Norris");The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
Example 7: Using NOT IN constraint with the delete query
Let us use the subquery instead of specifying the literal values in the NOT IN statement. We have to use a delete query statement to delete those values of the table educba_learner whose expert name field has a value that is not present as the first name in the educba_writers table. For this, we will use the subquery to retrieve all the writers from the educba_writers table, and our query statement will be as follows –
Query:
Delete FROM educba_learner
WHERE country NOT IN (SELECT country FROM educba_learner WHERE country LIKE 'U%');
select * from educba_learner;The execution of the above query statement will give the following output –
Alternatives to SQL NOT IN
When filtering data, you may frequently use the SQL NOT IN operator. However, you should consider other options depending on your specific needs and the type of database system you are using. Here are a few alternatives to the SQL NOT IN operator:
1. SQL NOT EXISTS
Instead of NOT IN, you can use the SQL NOT EXISTS operator with a correlated subquery. This approach checks for the non-existence of rows satisfying a specific condition. Here’s an example:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM other_table WHERE condition);2. SQL LEFT JOIN/IS NULL
You can achieve a similar effect to NOT IN by using a LEFT JOIN and checking for NULL values in the joined table. This approach selects rows that have no matching rows in the joined table. Here’s an example:
SELECT t1.column1, t1.column2, ...
FROM table1 t1
LEFT JOIN table2 t2 ON t1.column = t2.column
WHERE t2.column IS NULL;3. SQL NOT IN with a subquery or temporary table
Instead of directly specifying values in the NOT IN clause, you can use a subquery or create a temporary table to fetch the values dynamically. This approach can be useful when you must fetch the values from another table or generate them based on specific criteria.
4. SQL NOT LIKE
If you are dealing with string values and want to exclude rows based on pattern matching, you can use the SQL NOT LIKE operator. It allows you to filter rows that do not match a specific pattern. For example:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table
WHERE column NOT LIKE 'pattern';5. SQL NOT EXISTS with a JOIN
Another alternative is to use the SQL NOT EXISTS operator in combination with a JOIN. This approach can be helpful when you need to exclude rows based on certain conditions involving multiple tables. Here’s an example:
SELECT column1, column2, ...
FROM table1
WHERE NOT EXISTS (SELECT 1 FROM table2 WHERE condition AND table1.column = table2.column);These alternatives provide flexibility in achieving similar results as the SQL NOT IN operator, allowing you to choose the most suitable approach for your specific SQL query and database system.
Best Practices for Using SQL NOT IN
Here are some best practices for using the SQL NOT IN operator:
- Use NOT IN judiciously: While NOT IN is a powerful operator, it may not always be the most efficient or suitable option for every scenario. Consider alternative approaches like NOT EXISTS, LEFT JOIN/IS NULL, or temporary tables/subqueries, depending on the specific requirements and performance considerations.
- Avoid NULL values: The NOT IN operator does not work well with NULL values in the list or subquery. If NULL values are possible, handle them explicitly using additional conditions like IS NOT NULL or by coalescing NULL values to a suitable default value.
- Be mindful of large lists or subqueries: It may affect performance if you use NOT IN with extensive lists or subqueries. Ensure that the list or subquery result is optimized and indexed appropriately. Consider alternative approaches like temporary tables or JOINs for better performance.
- Understand the impact on performance: Depending on the database system and query complexity, the performance of the NOT IN operator may vary. Evaluate the execution plan, monitor query performance, and consider indexing relevant columns to improve query execution time.
- Use appropriate indexing: Indexing can significantly improve the performance of queries involving the NOT IN operator. Analyze the columns involved in the comparison and create indexes accordingly. Indexes on columns used in the WHERE clause, subqueries, or JOIN conditions can enhance query execution speed.
- Test and optimize: Test the performance of your queries using different approaches, including the NOT IN operator and alternative methods. Measure the execution time and resource usage to identify the most efficient solution. Experiment with indexing strategies and query optimization techniques to improve performance.
By following these best practices, you can use the SQL NOT IN operator effectively. This will ensure optimal query performance and accurate data filtering in your SQL statements.
FAQS
Q1: Can I use NULL values in the list or subquery with NOT IN?
Ans: The NOT IN operator does not work well with NULL values in the list or subquery. Remember to incorporate supplementary conditions such as IS NOT NULL or merge NULL values with an appropriate default value when dealing with NULL values.
Q2: Is it recommended to use NOT IN for large datasets?
Ans: When dealing with large datasets, NOT IN may not be the most efficient option. Consider alternative approaches like JOINs, EXISTS, or temporary tables to improve performance.
Q3: How can I handle performance issues with NOT IN?
Ans: To handle performance issues with NOT IN, consider optimizing the list or subquery size, indexing relevant columns, optimizing the query structure, and monitoring query execution time and resource usage.
Conclusion
The SQL NOT IN operator is a helpful tool for data filtering since it allows the exclusion of rows based on specified values or the result of a subquery. While it is a powerful operator, it is necessary to consider performance implications, handle NULL values carefully, and explore other ways when working with big datasets. To achieve the desired query results, one must understand how to properly use the SQL NOT IN operator for data filtering. Following best practices and applying this knowledge to achieve optimal results is essential.
Recommended Articles
We hope this EDUCBA information on “SQL NOT IN” benefited you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.