Updated March 18, 2023
Introduction to SQL Keys
In SQL, keys are the set of attributes that used to identify the specific row in a table and to find or create the relation between two or more tables i.e keys identify the rows by combining one or more columns. SQL provides super key, primary key, candidate key, alternate key, foreign key, compound key, composite key, and surrogate key. SQL keys use constraints to uniquely identify rows from karger data.
Syntax:
CREATE TABLE `customer` (
`cust_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`cust_name` varchar(100) NOT NULL,
`cust_address` text NOT NULL,
`cust_aadhaar_number` varchar(50) DEFAULT NULL,
`cust_pan_number` varchar(50) NOT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;
ALTER TABLE `customer` ADD PRIMARY KEY (`cust_id`);In the above-given SQL query, we can see how a column ‘cust_id’ is set as a Primary Key.
Type of SQL Keys
Multiple types of Keys are supported by the SQL Server.
The following are the list of SQL Keys:
- Primary Key
- Unique Key
- Candidate Key
- Alternate Key
- Composite Key
- Super Key
- Foreign Key
For Example
| Customer Table | ||||
| cust_id | cust_name | cust_address | cust_aadhaar_number | cust_pan_number |
| 100001 | Sunil Kumar | Noida | 372464389211 | ADSFS3456K |
| 100002 | Ankit Gupta | Gr Noida | 442289458453 | CGHAD7583L |
| 100003 | Suresh Yadav | New Delhi | 878453444144 | NMKRT2278O |
| 100004 | Nilam Singh | Lucknow | 227643441123 | HFJFD3876U |
| 100005 | Amal Rawat | Ghaziabad | 932571156735 | CBMVA9734A |
| 100006 | Harsh Saxena | Kanpur | 1453534363319 | TRYUC2568H |
Below given the “Order” table having the related data corresponding to the “cust_id” from the Customer Table.
| Order Table | ||
| cust_id | order_month_year | order_amount |
| 100001 | 2019 – Jan | $100,000 |
| 100002 | 2019 – Jan | $120,000 |
| 100003 | 2019 – Jan | $100,000 |
| 100004 | 2019 – Jan | $110,000 |
| 100001 | 2019 – Feb | $105,000 |
| 100002 | 2019 – Feb | $125,000 |
Now, we will go through one by one on each of the Key:
1. Primary Key
Primary Key is a field that can be used to identify all the tuples uniquely in the database. Only one of the columns can be declared as a primary key. A Primary Key can not have a NULL value.
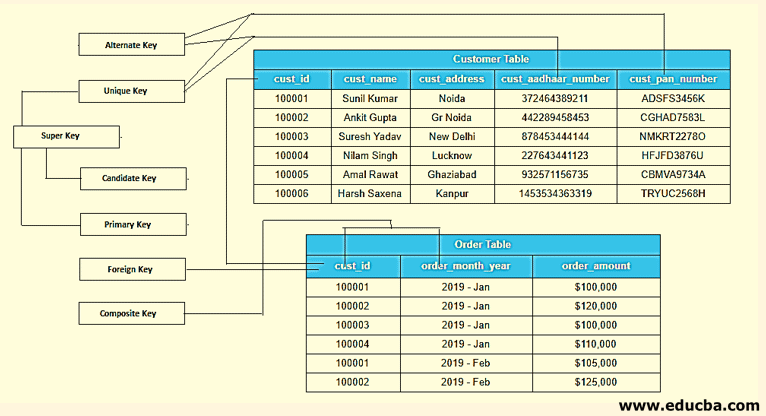
Example: In the above given relational table, “cust_id” is the Primary Key as it can identify all the row uniquely from the table.
2. Unique Key
Unique Key can be a field or set of fields that can be used to uniquely identify the tuple from the database. One or more fields can be declared as a unique Key. The unique Key column can also hold the NULL value. Use of Unique Key improves the performance of data retrieval. It makes searching for records from the database much more faster & efficient.
Example: In the above given relational table, “cust_aadhaar_number”, “cust_pan_number” are the Unique Key as it can allow one value as a NULL in the column
3. Candidate Key
Candidate Key can be a column or group of columns that can qualify for the Unique Key. Every table has at least one Candidate Key. A table may have one or more Candidate Key. Each Candidate Key can work as a Primary Key if required in certain scenarios.
Example: In the above given relational table, “cust_id”, “cust_aadhaar_number”, “cust_pan_number” are the Candidate Key as it can identify all the row uniquely from the table. These columns also qualify the criteria to be a Primary Key.
4. Alternate Key
Alternate Key is that Key which can be used as a Primary Key if required. Alternate Key also qualifies to be a Primary Key but for the time being, It is not the Primary Key.
Example: In the above given relational table, “cust_aadhaar_number”, “cust_pan_number” are the Alternate Key as both of the columns can be a Primary Key but not yet selected for the Primary Key.
5. Composite Key
Composite Key is also known as Compound Key / Concatenated Key. Composite Key refers to a group of two or more columns that can be used to identify a tuple from the table uniquely. A group of the column in combination with each other can identify a row uniquely but a single column of that group doesn’t promise to identify the row uniquely.
Example: In the above given relational table i.e. Order Table, “cust_id”, “order_month_year” group of these columns used in combination to identify the tuple uniquely in the Order Table. The individual column of this table is not able to identify the tuple uniquely from the Order table.
6. Super Key
Super Key is a combination of columns, each column of the table remains dependent on it. Super Key may have some more columns in the group which may or may not be necessary to identify the tuple uniquely from the table. Candidate Key is the subset of the Super Key. Candidate Key is also known as minimal Super Key.
Example: In the above given relational table, Primary Key, Candidate Key & Unique Key is the Super Key. As a single column of Customer Table i.e ‘cust_id’ is sufficient to identify the tuples uniquely from the table. Any set of the column which contains ‘cust_aadhaar_number’, ‘cust_pan_number’ is a Super Key.
7. Foreign Key
A foreign key is a column which is known as Primary Key in the other table i.e. A Primary Key in a table can be referred to as a Foreign Key in another table. Foreign Key may have duplicate & NULL values if it is defined to accept NULL values.
Example: In the above given relational table, ‘cust_id’ is Primary Key in the Customer table but ‘cust_id’ in the Order table known as a ‘Foreign Key’. Foreign Key in a table always becomes the Primary Key on the other table.
The above-given picture displays how each column is shown as a Key according to their qualification to identify the tuples uniquely from the table. Screenshot summarizes all the Key through the use of the relational table.
Conclusion
SQL Keys is one of the attributes of the relational database. which plays important roles to establish a relationship between two or more tables. It also helps queries to execute faster i.e. retrieval of the records from the database becomes much faster by using Keys. Keys also set the different constraint to uniquely identify the tuples from the large data.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL Keys. Here we discuss the introduction to SQL Keys and 7 different types with the appropriate example in detail. You may also look at the following article –