Updated March 16, 2023
Introduction to SQL Foreign Key
The following article provides an outline for SQL Foreign Key. Each row of a column that has a foreign key allocated to it should contain a value from the column it links. The referenced (i.e., “foreign”) field must only hold distinct values; frequently, it acts as the table’s primary key.
Key Takeaways
- A referring key is also known as a foreign key. A column, or group of columns, that has values that match a Primary Key in another table is known as a foreign key.
- We need numerous tables to connect the work when working on multiple projects. Keys are typically needed to join the tables. In SQL, a key is a field or set of columns that can be used to uniquely identify a table’s entries.
What is SQL Foreign Key?
A foreign key restriction ensures that a value may only be added to the column first if the identical value previously appears in another table by connecting a column with one table to a column in another table. The referenced key and any associated columns must use the same type of data. Static precision types like integers and decimals must be of the same size and sign. String lengths must not all be equal. Having a Foreign Key constraint in a database helps to check the correctness of the information. And also adding Constraints may slow the speed of a database.
Why Use SQL Foreign Key?
Foreign keys help to establish the connection between tables, which is what puts the “relational” in the “relational database.” They enable database developers to preserve referential integrity throughout their system. By reducing mistakes and speeding up any process that pulls data from tables connected by indexed foreign keys, foreign keys also benefit end users.
1. Data Normalisation
We can decrease redundancy and equalize the data across several tables with the use of the FOREIGN KEY. This implies that a database may have several tables that are connected.
2. Prevent Insertion of the Wrong Data
Using a FOREIGN KEY ensures that the correct data is not placed into a field that connects two database tables. This aids in removing database-level problems.
How to Create SQL Foreign Key?
A Foreign Key is created in a CREATE Table using a Keyword ‘FOREIGN KEY’ along with ‘REFERENCES’ which refer to a parent table.
Code:
CREATE TABLE table name(col1 datatype….coln , FOREIGN KEY (Col1) REFERENCES Parent table (ColA));After the above-mentioned query has been executed, col1 from the child database will therefore function as a foreign key in this new table. We connected these two tables using the above-mentioned query based on a shared column called ColA.
Using Create Table
A sql table is created using the CREATE command. In a new table, a Foreign Key is also made use of, though. Let’s look at an example of using the create command to define a foreign key.
Code:
Create table actors (actor_id int references film(id),
actor name varchar2(20));SQL Foreign Key Table
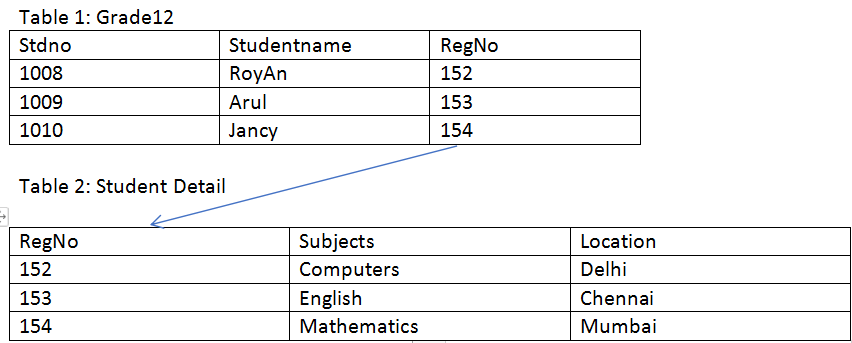
Let us consider two tables and see how the relationship exists using a Foreign Key.
In the above table structure RegNo a column field act as a Foreign key, which at the same time is considered the primary key in the Student detail Table.
SQL Foreign Key Constraint
We employ SQL foreign key constraints to stop operations that would break the connections between the tables. The addition of incorrect data to a table is not even permitted under these constraints.
Code:
[CONSTRAINT ] FOREIGN KEY
[index_name] (col_name, ...)
REFERENCES tbl_name (col_name,...)
[ DELETE reference_option]It needs one of the privileges on the Primary Table (like select, insert, update, delete).
How do Foreign Keys Works in SQL?
Here is a representation of how foreign key restriction functions and how it works in create, insert and drop.
Examples:
Foreign key functionality will be more clearly demonstrated with this sample database, and the same general concepts will hold for larger, more complex databases.
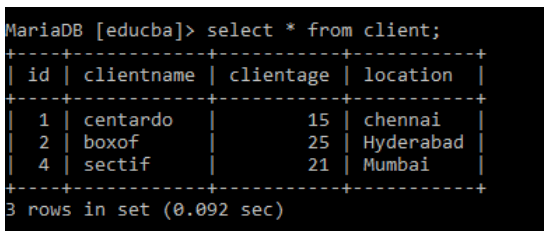
Here first we create a Parent table ‘client’ and it has a specific primary key as ‘id’.
Code:
create table client(id int PRIMARY KEY, clientname varchar(20),clientage int, location varchar(20));After inserting a particular value in the table, it looks like this:
Code:
insert into client values (01,'centardo',15,'chennai');
insert into client values (02,'boxof',25,'Hyderabad');
insert into client values (04,'sectif',21,'Mumbai');
MariaDB [educba]> select * from client;The table looks like this:
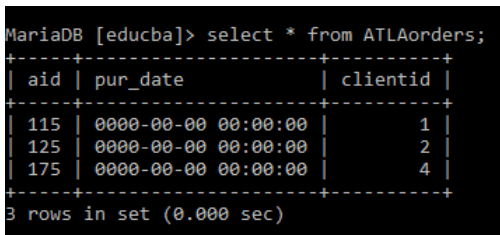
Next following this, we are creating a child table ‘ATLorders’ with the foreign key(clientid) referencing the primary key of the parent table.
The foreign key on Create table.
Code:
create table ATLAorders(aid int PRIMARY KEY, pur_date datetime, clientid int References client(id));After inserting corresponding values the table with a foreign key looks like this.
We could see from the above table that the ‘clientid’ and ‘id’attributes from parent and child tables are the same. The values are the same. If we try to enter a different value then it shows a warning. See the below screenshot. I tried to enter value ‘10’ in clientid. It shows the warning.
Next, using Alter table I am adding my Foreign key constraint.
Code:
alter table ATLAorders ADD CONSTRAINT fk FOREIGN KEY (clientid) REFERENCES client(id);Output:
Difference Between Primary Keys and Foreign Keys
Given below are the differences mentioned:
| Sr. No | Primary Key |
Foreign Key |
| 1 | An item in the table is uniquely identified by its primary key. | A column in a table that serves as the primary key in another table is known as a foreign key. |
| 2 | To guarantee that the data in a given column is unique, a primary key is employed. | A relational database table’s foreign key is a column or set of columns that create a connection between the data in two tables. |
| 3 | The parent table will not let users remove its value. | We can remove its value from the child table. |
| 4 | The temporary tables allow for the implicit definition of its constraint. | There is no way to define its constraint on either local or global temporary tables. |
FAQ
Given below are the FAQs mentioned:
Q1. How primary key and foreign key are related?
Answer: The primary table is the one that holds the primary key, while the child table is the one that includes the foreign key. A foreign key thereby connects two databases of information.
Q2. List a few rules for creating a foreign key.
Answer: The very same kinds of data must be included in both the primary key columns in the primary table and the foreign key fields in the child table. The same database should contain both the referencing and the referred records.
Q3. What is the advantage of using a foreign key?
Answer: Performance is the primary benefit of employing foreign key limitations. Teams can easily determine the database’s design. We may also look at the data retrieval strategy used by the query.
Conclusion
The foreign key in SQL along with how to utilize them with the aid of examples was covered in this article. Additionally, we used the foreign key constraint to construct a relationship between two tables.
Recommended Articles
This is a guide to SQL Foreign Key. Here we discuss the introduction, why use SQL foreign key? key constraint and FAQs. You may also have a look at the following articles to learn more –