Updated March 10, 2023
Introduction to SQL Import CSV
In MySQL, we store the data in the database in table format. Manier times, there is a necessity to get the data stored in the tables of MySQL database from some other format such as CSV, JSON, or SQL format. This is often the requirement when we do data transfer and sharing between multiple companies and individuals.
If we have to import the data from other platforms such as google docs, open office, or Microsoft Excel for further analysis of resultset into the tables of MySQL then we can do so and conclude the necessary statistics by performing various operations on the imported data to get certain conclusions.
In this article, we will learn how we can make use of the LOAD DATA INFILE statement to import the data to MySQL database and its table contents from any CSV format using the command-line MySQL shell and we can import the data to MySQL tables from CSV format when we are using the MySQL Workbench editor with the help of an example.
Importing Using command-line MySQL queries
Before importing from CSV format, we need to make sure that the table with the same number and type of the columns exist in the database for which we are trying to import the data with matching columns exists and the user has to insert permission for that table and file permissions.
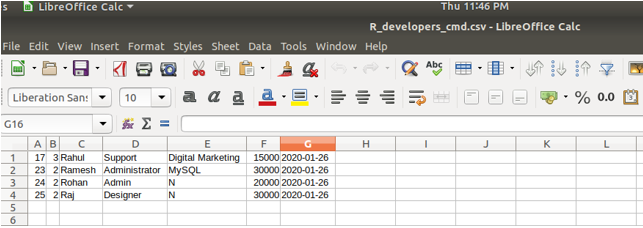
Suppose that I have a certain CSV file that is created in Microsoft Excel or LibreOffice Calc named R_developers_cmd.csv and it contains the following contents in it as shown below
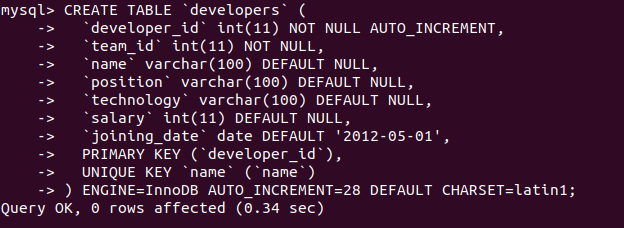
Let us create the developer’s named table in our database educba that will hold all the above data –
CREATE TABLE `developers` (
`developer_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`team_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`name` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`position` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`technology` varchar(100) DEFAULT NULL,
`salary` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`joining_date` date DEFAULT '2012-05-01',
PRIMARY KEY (`developer_id`),
UNIQUE KEY `name` (`name`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=28 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1;Output:
To import resultset from CSV file we will make the use of LOAD DATA INFILE clause as shown below –
LOAD DATA INFILE 'https://cdn.educba.com/var/lib/mysql-files/R_developers_cmd.csv'
INTO TABLE developers
FIELDS ENCLOSED BY '"'
TERMINATED BY ';'
ESCAPED BY '"'
LINES TERMINATED BY '\n';Output:
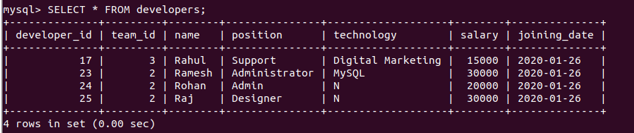
We can see that four rows were affected and all the four rows got inserted successfully without any warning or error. To confirm whether the imported data of the CSV got inserted in the table properly, let us retrieve the contents of the developers’ table and compare them with the CSV file we had earlier using the following query statement –
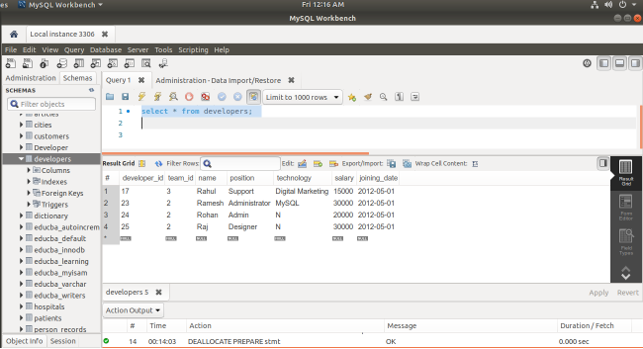
SELECT * FROM developers;Output:
Importing data from CSV to Table Contents in Workbench
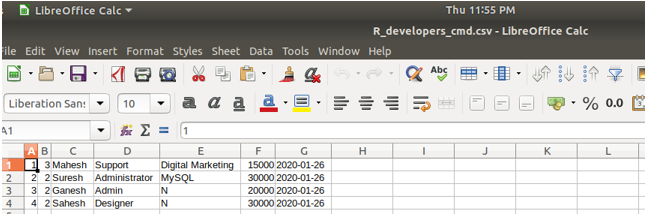
There is also the provision to import the contents of the CSV file into the table contents in Workbench by simply clicking on the import button and then specifying the path and name of the file. Note that in MySQL using the command-line, we can import the contents of the CSV file into the table contents by using the LOAD DATA INFILE statement. Let us look at how we can import the contents of the CSV file into the table in workbench with the help of an example. Consider the following CSV file that has the same name as earlier but different contents than previous with developer names Mahesh, Suresh, Ganesh, and Saheeh –
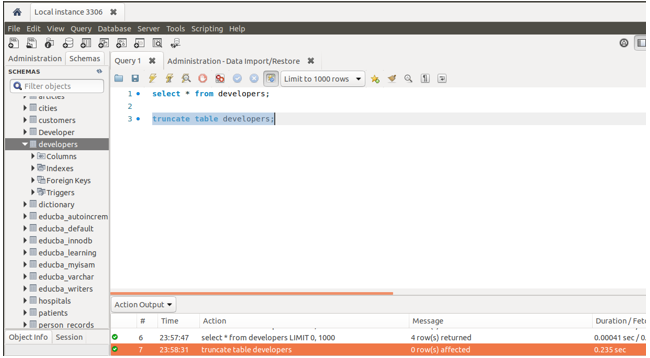
- Let us try importing this content in the workbench. Firstly, we will truncate the table in order to make the concepts clear and understanding better. However, note that we can add the data by importing the CSV in the table that already contains the records in the same manner and it does not have any effects on the existing records. Just in case, if they duplicate while importing then an error will be given. Let us first truncate the developers’ table using the following statement –
TRUNCATE TABLE developers;Output:
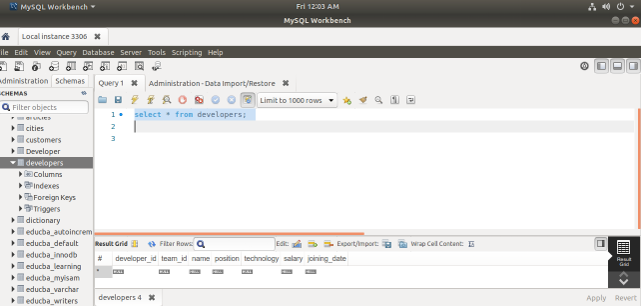
- Simply select the contents of the developers’ table by using the SELECT * FROM developers; query statement in the workbench to check its contents before importing the CSV file contents that give the following output after execution in workbench platform
- Let us now start with the import process. As you can see there is an Export/Import buttons provided in the resultset panel above it. You will have to select the Import button out of them. After moving the mouse over the button near Export/ Import it will automatically display on tooltip which button is it. After clicking on the Import button you will be prompted with the following screen
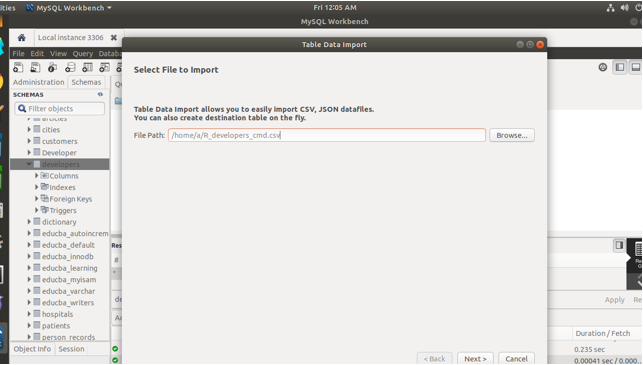
- Here you need to browse the path and the file whose contents you wish to import. The file can be in either CSV or JSON format. We will choose our CSV file or developers which we have created and then click on the Next button. As soon as you will click on Next, you will be prompted with the following screen –
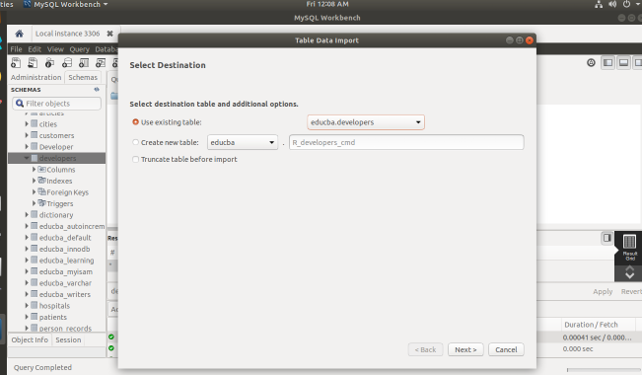
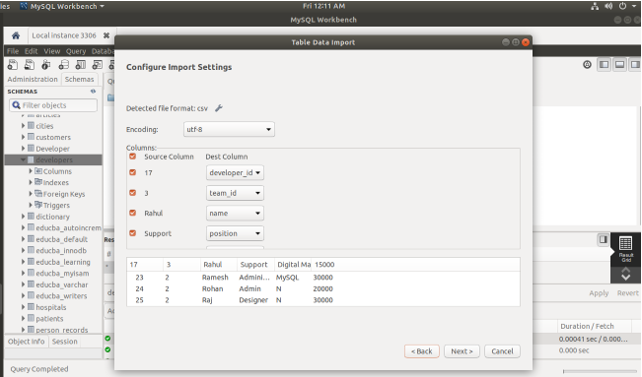
- Where you will see two options that whether you wish to import the data to an existing table if so then you will have to mention the name of the table in the dropdown list of existing tables provided and also choose whether you want to truncate the table before importing option if you want to. Be careful here. The other option is that you can create a new table with the file name as the table name and import the contents of that CSV file into a newly created table. Here, you need to specify whether you wish to drop the table before creating it. After choosing your options click on the next that will result in the following output –
- Here, you can see how the mapping of the CSV file contents will be done to the table contents. If it is appropriate and correct according to you click on Next else make the changes into the table or CSV as per your requirement and then try importing. After clicking next following will be the screen and it will display the process that will be carried out for importing –
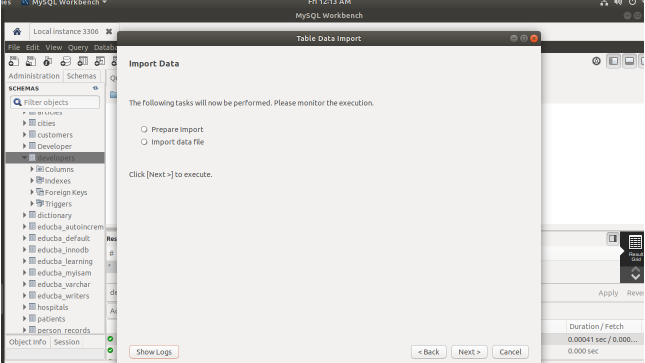
- Simply, click on next which will result in status updation window as follows –
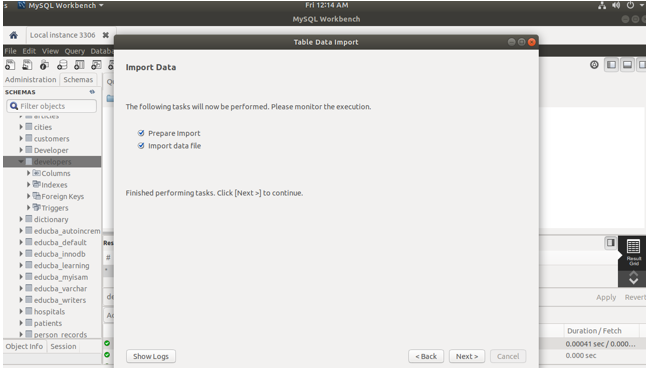
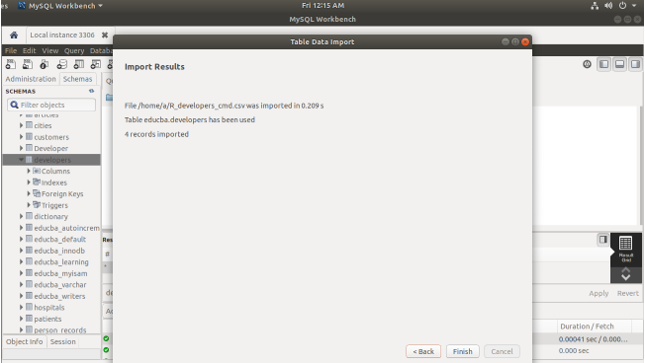
- Now, clicking next gives the following screen that will display the results of the import process. Finally, click on finish to complete the whole process –
- Now, select the contents of the table by executing SELECT * FROM developers; query statement that results in the following output after the execution of the query –
Conclusion – SQL Import CSV
We can import the files using the command-line using MySQL query statements and even using various options provided in the MySQL Workbench client tool. We can specify the carriage return values, file and line separators, and even the value with which the column value should be enclosed by in both of the above methods.
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Import CSV” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.