Updated March 13, 2023

Introduction to SQL Bulk Insert
Normal insert statements will only insert one row at a time into the database. But if you want to multiple rows into the database table, then we use the SQL bulk insert. Bulk insert allows us to import the CSV file and insert all the data from the file.
The Bulk insert also has the advantage of loading the data “BATCHSIZE” wise. While loading the data if we want to abort the insert process if we get an error we have a parameter called “MAXERRORS”. We can also mention the parameters like “FIELDTERMINATOR” which defines how the fields are separated. “ROWTERMINATOR” defines how the rows are separated. “FIRSTROW” is used to specify from which line the insertion need to be started. Usually, we skip the header so the value will be FIRSTROW = 2.
Syntax:
Most commonly used syntax with the below arguments:
/ * - - - - - - - - Bulk insert query is given below - - - - - */
BULK INSERT { database_name.schema_name.table_or_view_name |
schema_name.table_or_view_name | table_or_view_name }
FROM 'data_file_name'
[ [ WITH
( [ , FORMAT = 'CSV' ]
[ , FIRSTROW = 'first_row' ]
[ , FIELDQUOTE = 'quote_characters']
[ , FORMATFILE = 'format_file_path' ]
[ , FIELDTERMINATOR = 'field_terminator' ]
[ , ROWTERMINATOR = 'row_terminator' ]
)]We have other parameters that can be mentioned as below: –
- ,BATCHSIZE: batch size
- , DATA_SOURCE: ‘data source name’
- ,ERRORFILE: ‘file name’
- , ROWS_PER_BATCH: rowsperbatch
- , ROWTERMINATOR: ‘row terminator’
- ,TABLOCK
- ,CHECK_CONSTRAINTS
- , CODEPAGE: { ‘RAW’ }
- , DATAFILETYPE: { ‘char’ }
- , ERRORFILE_DATA_SOURCE: ‘data sourcename’
- ,FIRSTROW: first row
- ,FIRE_TRIGGERS
- , FORMATFILE_DATA_SOURCE: ‘data sourcename’
- ,KEEPIDENTITY
- ,KEEPNULLS
- , KILOBYTES_PER_BATCH: kilobytes perbatch
- ,LASTROW: last row
- ,MAXERRORS: max errors
- ,ORDER ( { column [ ASC | DESC ] } [ ,…n ] )
How Bulk Insert in SQL?
To know the BULK INSERT in a better way I have downloaded a file with a large amount of data in it and try to load it into the SQL. The file consists of 10 rows consisting of it. Now let us perform bulk load. Below is the table created for which we load the bulk amounts of data.
Code:
create table bus_index_price
(
series_reference_default varchar(20),
period_value decimal(10,3),
data_value int,
current_status varchar(10),
units varchar(10),
subject_value varchar(30),
group_value varchar(30),
series_title_1 varchar(20),
series_title_2 varchar(20),
series_title_3 varchar(20),
series_title_4 varchar(20),
series_title_5 varchar(20)
);Now let us bulk insert the data into the table: –
/ * - - - - - - - - Bulk insert query is given below - - - - - */
create view sample_V
as
select
series_reference_default
,period_value
,data_value
,current_status
, units
,subject_value
,group_value
, series_title_1
, series_title_2
, series_title_3
, series_title_4
, series_title_5
FROM bus_index_price
GO
BULK INSERT bus_index_price
FROM'D:\sample.txt'
WITH
(
FIRSTROW= 2,
FIELDTERMINATOR=',',
ROWTERMINATOR='\n'
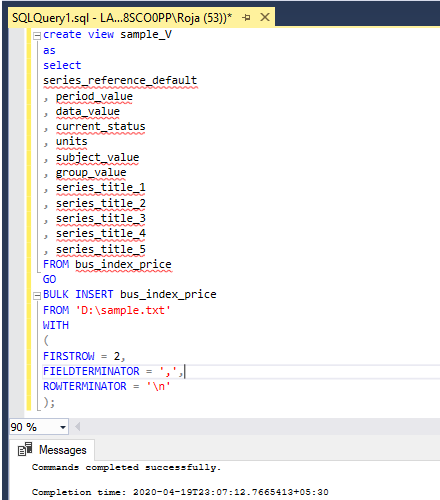
);We are creating the view and mapping the columns of the table to the CSV file so that we don’t get any mapping related errors:-Screenshot of output is for the same: –
Output:
Examples to Implement SQL Bulk Insert
Below are the examples mentioned:
Example #1
Below is the table created for which we load the bulk amounts of data.
Code:
create table bus_price
(
Bus_referenceid varchar(20),
No_of_passenger int,
Bus_source varchar(20),
Bus_destination varchar(30),
Bus_timing varchar(10),
Reached_depo varchar(10),
Bus_description varchar(30)
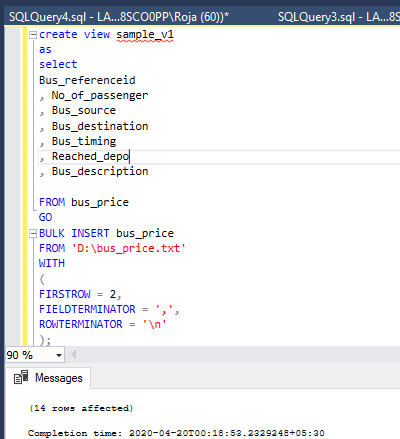
);Now let us bulk insert the data into the table: –
create view sample_v1
as
select
Bus_referenceid
,No_of_passenger
,Bus_source
,Bus_destination
,Bus_timing
,Reached_depo
,Bus_description
FROM bus_price
GO
BULK INSERT bus_price
FROM 'D:\bus_price.txt'
WITH
(
FIRSTROW= 2,
FIELDTERMINATOR=',',
ROWTERMINATOR='\n'
);We are creating the view and mapping the columns of the table to the CSV file so that we don’t get any mapping related errors:- Screenshot of output is for the same: –
Code:
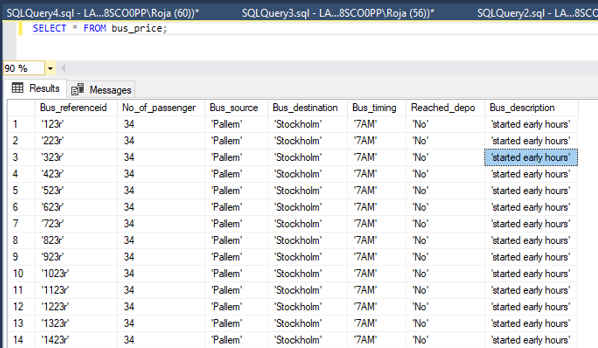
SELECT * FROM bus_price;Output:
Example #2
Now let us see and another example and insert a bulk amount of data: –
Code:
create table Alphabet
(
alphabet_data varchar(10),
data_value int
)Now let us bulk insert the data into the table: –
create view alphabet_v1
as
select
alphabet_data
,data_value
FROM alphabet
GO
BULKINSERT alphabet
FROM 'D:\alphabet.txt'
WITH
(
FIRSTROW= 2,
FIELDTERMINATOR=',',
ROWTERMINATOR='\n'
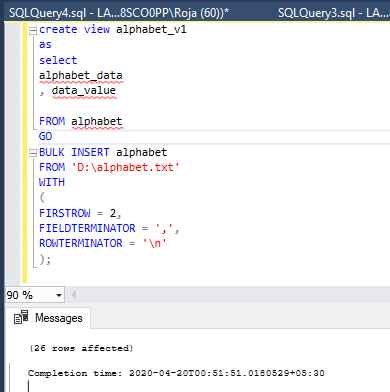
);Below is the screenshot for the above insertion of the data into the table:
Recommended Articles
We hope that this EDUCBA information on “SQL Bulk Insert” was beneficial to you. You can view EDUCBA’s recommended articles for more information.


